Yuda Fan
ROME: Robustifying Memory-Efficient NAS via Topology Disentanglement and Gradients Accumulation
Nov 23, 2020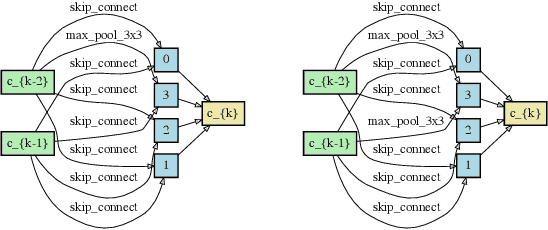

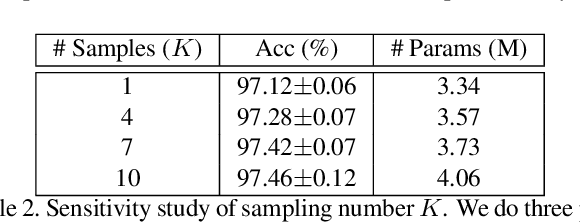

Abstract:Single-path based differentiable neural architecture search has great strengths for its low computational cost and memory-friendly nature. However, we surprisingly discover that it suffers from severe searching instability which has been primarily ignored, posing a potential weakness for a wider application. In this paper, we delve into its performance collapse issue and propose a new algorithm called RObustifying Memory-Efficient NAS (ROME). Specifically, 1) for consistent topology in the search and evaluation stage, we involve separate parameters to disentangle the topology from the operations of the architecture. In such a way, we can independently sample connections and operations without interference; 2) to discount sampling unfairness and variance, we enforce fair sampling for weight update and apply a gradient accumulation mechanism for architecture parameters. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method has strong performance and robustness, where it mostly achieves state-of-the-art results on a large number of standard benchmarks.
Transferable Active Grasping and Real Embodied Dataset
Apr 28, 2020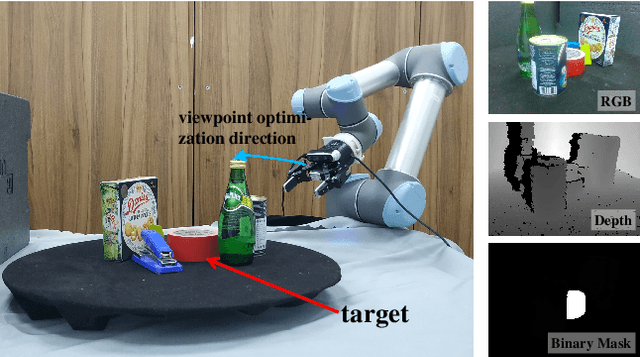


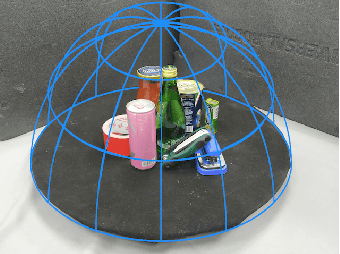
Abstract:Grasping in cluttered scenes is challenging for robot vision systems, as detection accuracy can be hindered by partial occlusion of objects. We adopt a reinforcement learning (RL) framework and 3D vision architectures to search for feasible viewpoints for grasping by the use of hand-mounted RGB-D cameras. To overcome the disadvantages of photo-realistic environment simulation, we propose a large-scale dataset called Real Embodied Dataset (RED), which includes full-viewpoint real samples on the upper hemisphere with amodal annotation and enables a simulator that has real visual feedback. Based on this dataset, a practical 3-stage transferable active grasping pipeline is developed, that is adaptive to unseen clutter scenes. In our pipeline, we propose a novel mask-guided reward to overcome the sparse reward issue in grasping and ensure category-irrelevant behavior. The grasping pipeline and its possible variants are evaluated with extensive experiments both in simulation and on a real-world UR-5 robotic arm.
Image Based Review Text Generation with Emotional Guidance
Jan 14, 2019


Abstract:In the current field of computer vision, automatically generating texts from given images has been a fully worked technique. Up till now, most works of this area focus on image content describing, namely image-captioning. However, rare researches focus on generating product review texts, which is ubiquitous in the online shopping malls and is crucial for online shopping selection and evaluation. Different from content describing, review texts include more subjective information of customers, which may bring difference to the results. Therefore, we aimed at a new field concerning generating review text from customers based on images together with the ratings of online shopping products, which appear as non-image attributes. We made several adjustments to the existing image-captioning model to fit our task, in which we should also take non-image features into consideration. We also did experiments based on our model and get effective primary results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge