Yuanjie Yan
Attribute-Specific Manipulation Based on Layer-Wise Channels
Feb 18, 2023Abstract:Image manipulation on the latent space of the pre-trained StyleGAN can control the semantic attributes of the generated images. Recently, some studies have focused on detecting channels with specific properties to directly manipulate the latent code, which is limited by the entanglement of the latent space. To detect the attribute-specific channels, we propose a novel detection method in the context of pre-trained classifiers. We analyse the gradients layer by layer on the style space. The intensities of the gradients indicate the channel's responses to specific attributes. The latent style codes of channels control separate attributes in the layers. We choose channels with top-$k$ gradients to control specific attributes in the maximum response layer. We implement single-channel and multi-channel manipulations with a certain attribute. Our methods can accurately detect relevant channels for a large number of face attributes. Extensive qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed methods outperform state-of-the-art methods in generalization and scalability.
Review Neural Networks about Image Transformation Based on IGC Learning Framework with Annotated Information
Jun 21, 2022



Abstract:Image transformation, a class of vision and graphics problems whose goal is to learn the mapping between an input image and an output image, develops rapidly in the context of deep neural networks. In Computer Vision (CV), many problems can be regarded as the image transformation task, e.g., semantic segmentation and style transfer. These works have different topics and motivations, making the image transformation task flourishing. Some surveys only review the research on style transfer or image-to-image translation, all of which are just a branch of image transformation. However, none of the surveys summarize those works together in a unified framework to our best knowledge. This paper proposes a novel learning framework including Independent learning, Guided learning, and Cooperative learning, called the IGC learning framework. The image transformation we discuss mainly involves the general image-to-image translation and style transfer about deep neural networks. From the perspective of this framework, we review those subtasks and give a unified interpretation of various scenarios. We categorize related subtasks about the image transformation according to similar development trends. Furthermore, experiments have been performed to verify the effectiveness of IGC learning. Finally, new research directions and open problems are discussed for future research.
Multi-View Partial Point Cloud Challenge 2021 on Completion and Registration: Methods and Results
Dec 22, 2021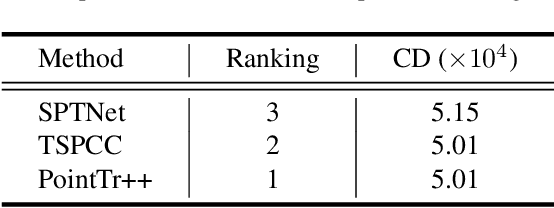
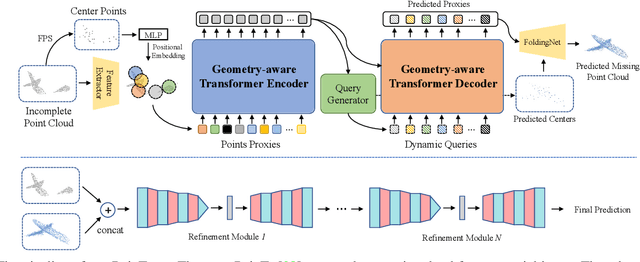
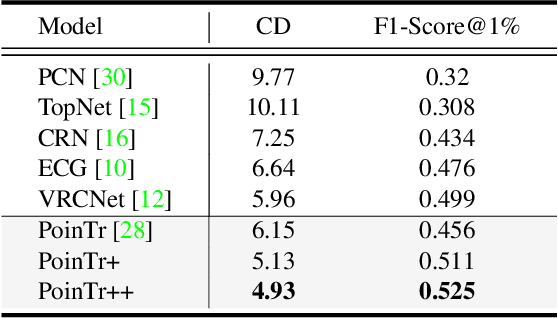
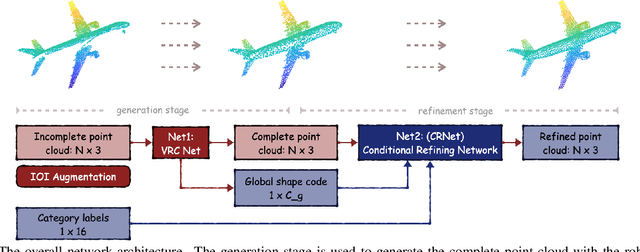
Abstract:As real-scanned point clouds are mostly partial due to occlusions and viewpoints, reconstructing complete 3D shapes based on incomplete observations becomes a fundamental problem for computer vision. With a single incomplete point cloud, it becomes the partial point cloud completion problem. Given multiple different observations, 3D reconstruction can be addressed by performing partial-to-partial point cloud registration. Recently, a large-scale Multi-View Partial (MVP) point cloud dataset has been released, which consists of over 100,000 high-quality virtual-scanned partial point clouds. Based on the MVP dataset, this paper reports methods and results in the Multi-View Partial Point Cloud Challenge 2021 on Completion and Registration. In total, 128 participants registered for the competition, and 31 teams made valid submissions. The top-ranked solutions will be analyzed, and then we will discuss future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge