Yuan Hao
StyleDrop: Text-to-Image Generation in Any Style
Jun 01, 2023
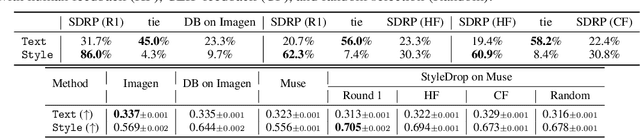

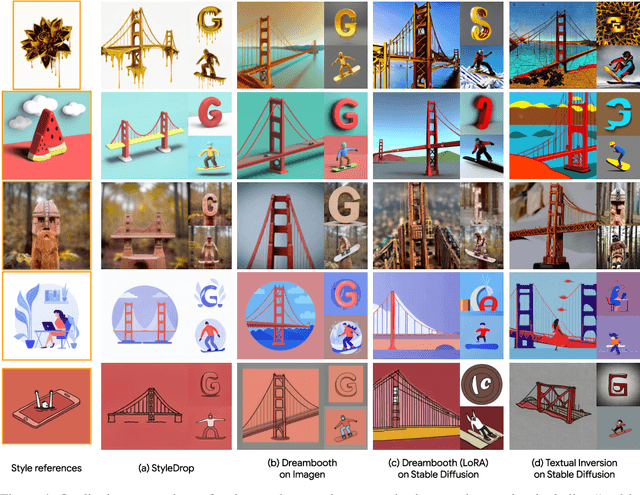
Abstract:Pre-trained large text-to-image models synthesize impressive images with an appropriate use of text prompts. However, ambiguities inherent in natural language and out-of-distribution effects make it hard to synthesize image styles, that leverage a specific design pattern, texture or material. In this paper, we introduce StyleDrop, a method that enables the synthesis of images that faithfully follow a specific style using a text-to-image model. The proposed method is extremely versatile and captures nuances and details of a user-provided style, such as color schemes, shading, design patterns, and local and global effects. It efficiently learns a new style by fine-tuning very few trainable parameters (less than $1\%$ of total model parameters) and improving the quality via iterative training with either human or automated feedback. Better yet, StyleDrop is able to deliver impressive results even when the user supplies only a single image that specifies the desired style. An extensive study shows that, for the task of style tuning text-to-image models, StyleDrop implemented on Muse convincingly outperforms other methods, including DreamBooth and textual inversion on Imagen or Stable Diffusion. More results are available at our project website: https://styledrop.github.io
Learning Disentangled Prompts for Compositional Image Synthesis
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:We study domain-adaptive image synthesis, the problem of teaching pretrained image generative models a new style or concept from as few as one image to synthesize novel images, to better understand the compositional image synthesis. We present a framework that leverages a pretrained class-conditional generation model and visual prompt tuning. Specifically, we propose a novel source class distilled visual prompt that learns disentangled prompts of semantic (e.g., class) and domain (e.g., style) from a few images. Learned domain prompt is then used to synthesize images of any classes in the style of target domain. We conduct studies on various target domains with the number of images ranging from one to a few to many, and show qualitative results which show the compositional generalization of our method. Moreover, we show that our method can help improve zero-shot domain adaptation classification accuracy.
MAGVIT: Masked Generative Video Transformer
Dec 10, 2022



Abstract:We introduce the MAsked Generative VIdeo Transformer, MAGVIT, to tackle various video synthesis tasks with a single model. We introduce a 3D tokenizer to quantize a video into spatial-temporal visual tokens and propose an embedding method for masked video token modeling to facilitate multi-task learning. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the quality, efficiency, and flexibility of MAGVIT. Our experiments show that (i) MAGVIT performs favorably against state-of-the-art approaches and establishes the best-published FVD on three video generation benchmarks, including the challenging Kinetics-600. (ii) MAGVIT outperforms existing methods in inference time by two orders of magnitude against diffusion models and by 60x against autoregressive models. (iii) A single MAGVIT model supports ten diverse generation tasks and generalizes across videos from different visual domains. The source code and trained models will be released to the public at https://magvit.cs.cmu.edu.
Visual Prompt Tuning for Generative Transfer Learning
Oct 03, 2022



Abstract:Transferring knowledge from an image synthesis model trained on a large dataset is a promising direction for learning generative image models from various domains efficiently. While previous works have studied GAN models, we present a recipe for learning vision transformers by generative knowledge transfer. We base our framework on state-of-the-art generative vision transformers that represent an image as a sequence of visual tokens to the autoregressive or non-autoregressive transformers. To adapt to a new domain, we employ prompt tuning, which prepends learnable tokens called prompt to the image token sequence, and introduce a new prompt design for our task. We study on a variety of visual domains, including visual task adaptation benchmark~\cite{zhai2019large}, with varying amount of training images, and show effectiveness of knowledge transfer and a significantly better image generation quality over existing works.
BLT: Bidirectional Layout Transformer for Controllable Layout Generation
Dec 09, 2021



Abstract:Creating visual layouts is an important step in graphic design. Automatic generation of such layouts is important as we seek scale-able and diverse visual designs. Prior works on automatic layout generation focus on unconditional generation, in which the models generate layouts while neglecting user needs for specific problems. To advance conditional layout generation, we introduce BLT, a bidirectional layout transformer. BLT differs from autoregressive decoding as it first generates a draft layout that satisfies the user inputs and then refines the layout iteratively. We verify the proposed model on multiple benchmarks with various fidelity metrics. Our results demonstrate two key advances to the state-of-the-art layout transformer models. First, our model empowers layout transformers to fulfill controllable layout generation. Second, our model slashes the linear inference time in autoregressive decoding into a constant complexity, thereby achieving 4x-10x speedups in generating a layout at inference time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge