Yixin Guo
Beyond Inpainting: Unleash 3D Understanding for Precise Camera-Controlled Video Generation
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Camera control has been extensively studied in conditioned video generation; however, performing precisely altering the camera trajectories while faithfully preserving the video content remains a challenging task. The mainstream approach to achieving precise camera control is warping a 3D representation according to the target trajectory. However, such methods fail to fully leverage the 3D priors of video diffusion models (VDMs) and often fall into the Inpainting Trap, resulting in subject inconsistency and degraded generation quality. To address this problem, we propose DepthDirector, a video re-rendering framework with precise camera controllability. By leveraging the depth video from explicit 3D representation as camera-control guidance, our method can faithfully reproduce the dynamic scene of an input video under novel camera trajectories. Specifically, we design a View-Content Dual-Stream Condition mechanism that injects both the source video and the warped depth sequence rendered under the target viewpoint into the pretrained video generation model. This geometric guidance signal enables VDMs to comprehend camera movements and leverage their 3D understanding capabilities, thereby facilitating precise camera control and consistent content generation. Next, we introduce a lightweight LoRA-based video diffusion adapter to train our framework, fully preserving the knowledge priors of VDMs. Additionally, we construct a large-scale multi-camera synchronized dataset named MultiCam-WarpData using Unreal Engine 5, containing 8K videos across 1K dynamic scenes. Extensive experiments show that DepthDirector outperforms existing methods in both camera controllability and visual quality. Our code and dataset will be publicly available.
Global-Local Distillation Network-Based Audio-Visual Speaker Tracking with Incomplete Modalities
Aug 26, 2024Abstract:In speaker tracking research, integrating and complementing multi-modal data is a crucial strategy for improving the accuracy and robustness of tracking systems. However, tracking with incomplete modalities remains a challenging issue due to noisy observations caused by occlusion, acoustic noise, and sensor failures. Especially when there is missing data in multiple modalities, the performance of existing multi-modal fusion methods tends to decrease. To this end, we propose a Global-Local Distillation-based Tracker (GLDTracker) for robust audio-visual speaker tracking. GLDTracker is driven by a teacher-student distillation model, enabling the flexible fusion of incomplete information from each modality. The teacher network processes global signals captured by camera and microphone arrays, and the student network handles local information subject to visual occlusion and missing audio channels. By transferring knowledge from teacher to student, the student network can better adapt to complex dynamic scenes with incomplete observations. In the student network, a global feature reconstruction module based on the generative adversarial network is constructed to reconstruct global features from feature embedding with missing local information. Furthermore, a multi-modal multi-level fusion attention is introduced to integrate the incomplete feature and the reconstructed feature, leveraging the complementarity and consistency of audio-visual and global-local features. Experimental results on the AV16.3 dataset demonstrate that the proposed GLDTracker outperforms existing state-of-the-art audio-visual trackers and achieves leading performance on both standard and incomplete modalities datasets, highlighting its superiority and robustness in complex conditions. The code and models will be available.
Unseen No More: Unlocking the Potential of CLIP for Generative Zero-shot HOI Detection
Aug 12, 2024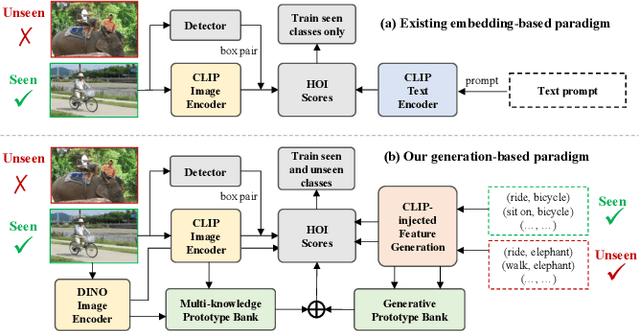
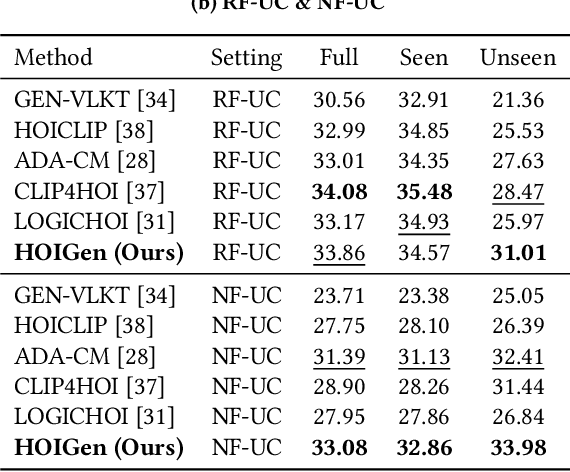
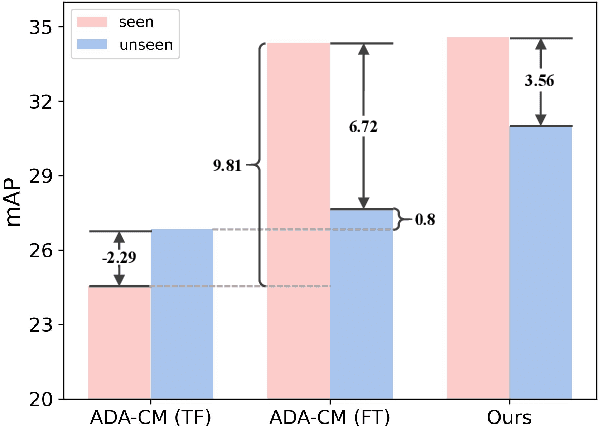
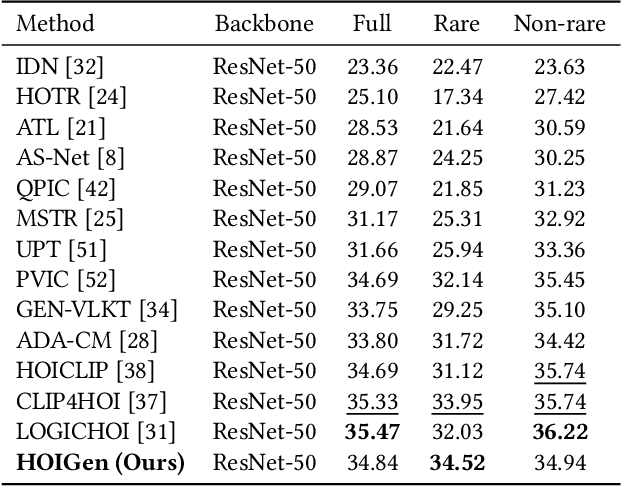
Abstract:Zero-shot human-object interaction (HOI) detector is capable of generalizing to HOI categories even not encountered during training. Inspired by the impressive zero-shot capabilities offered by CLIP, latest methods strive to leverage CLIP embeddings for improving zero-shot HOI detection. However, these embedding-based methods train the classifier on seen classes only, inevitably resulting in seen-unseen confusion for the model during inference. Besides, we find that using prompt-tuning and adapters further increases the gap between seen and unseen accuracy. To tackle this challenge, we present the first generation-based model using CLIP for zero-shot HOI detection, coined HOIGen. It allows to unlock the potential of CLIP for feature generation instead of feature extraction only. To achieve it, we develop a CLIP-injected feature generator in accordance with the generation of human, object and union features. Then, we extract realistic features of seen samples and mix them with synthetic features together, allowing the model to train seen and unseen classes jointly. To enrich the HOI scores, we construct a generative prototype bank in a pairwise HOI recognition branch, and a multi-knowledge prototype bank in an image-wise HOI recognition branch, respectively. Extensive experiments on HICO-DET benchmark demonstrate our HOIGen achieves superior performance for both seen and unseen classes under various zero-shot settings, compared with other top-performing methods. Code is available at: https://github.com/soberguo/HOIGen
GRAPHSPY: Fused Program Semantic-Level Embedding via Graph Neural Networks for Dead Store Detection
Nov 18, 2020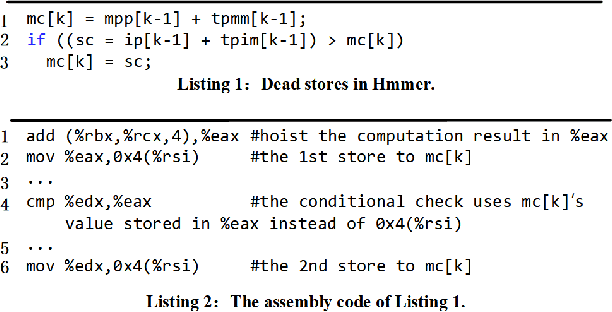
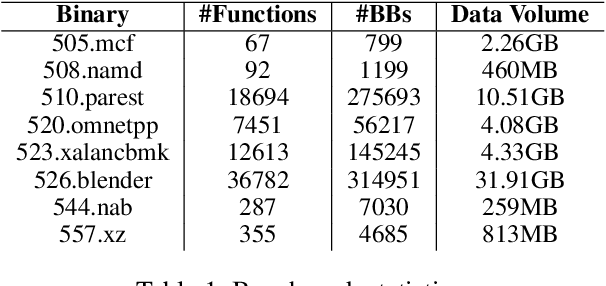
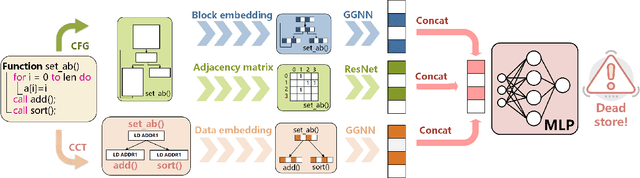
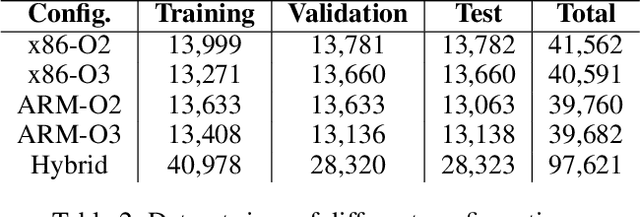
Abstract:Production software oftentimes suffers from the issue of performance inefficiencies caused by inappropriate use of data structures, programming abstractions, and conservative compiler optimizations. It is desirable to avoid unnecessary memory operations. However, existing works often use a whole-program fine-grained monitoring method with incredibly high overhead. To this end, we propose a learning-aided approach to identify unnecessary memory operations intelligently with low overhead. By applying several prevalent graph neural network models to extract program semantics with respect to program structure, execution order and dynamic states, we present a novel, hybrid program embedding approach so that to derive unnecessary memory operations through the embedding. We train our model with tens of thousands of samples acquired from a set of real-world benchmarks. Results show that our model achieves 90% of accuracy and incurs only around a half of time overhead of the state-of-art tool.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge