Yawen Xue
Agent Fine-tuning through Distillation for Domain-specific LLMs in Microdomains
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Agentic large language models (LLMs) have become prominent for autonomously interacting with external environments and performing multi-step reasoning tasks. Most approaches leverage these capabilities via in-context learning with few-shot prompts, but this often results in lengthy inputs and higher computational costs. Agent fine-tuning offers an alternative by enabling LLMs to internalize procedural reasoning and domain-specific knowledge through training on relevant data and demonstration trajectories. While prior studies have focused on general domains, their effectiveness in specialized technical microdomains remains unclear. This paper explores agent fine-tuning for domain adaptation within Hitachi's JP1 middleware, a microdomain for specialized IT operations. We fine-tuned LLMs using JP1-specific datasets derived from domain manuals and distilled reasoning trajectories generated by LLMs themselves, enhancing decision making accuracy and search efficiency. During inference, we used an agentic prompt with retrieval-augmented generation and introduced a context-answer extractor to improve information relevance. On JP1 certification exam questions, our method achieved a 14% performance improvement over the base model, demonstrating the potential of agent fine-tuning for domain-specific reasoning in complex microdomains.
Towards Neural Diarization for Unlimited Numbers of Speakers Using Global and Local Attractors
Jul 04, 2021
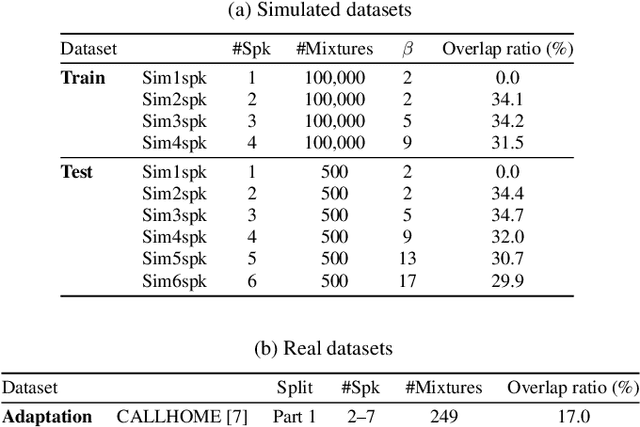

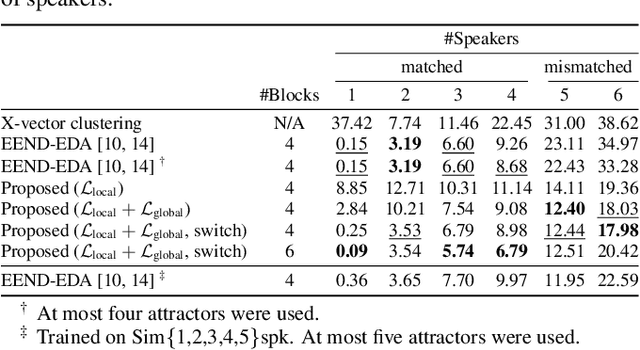
Abstract:Attractor-based end-to-end diarization is achieving comparable accuracy to the carefully tuned conventional clustering-based methods on challenging datasets. However, the main drawback is that it cannot deal with the case where the number of speakers is larger than the one observed during training. This is because its speaker counting relies on supervised learning. In this work, we introduce an unsupervised clustering process embedded in the attractor-based end-to-end diarization. We first split a sequence of frame-wise embeddings into short subsequences and then perform attractor-based diarization for each subsequence. Given subsequence-wise diarization results, inter-subsequence speaker correspondence is obtained by unsupervised clustering of the vectors computed from the attractors from all the subsequences. This makes it possible to produce diarization results of a large number of speakers for the whole recording even if the number of output speakers for each subsequence is limited. Experimental results showed that our method could produce accurate diarization results of an unseen number of speakers. Our method achieved 11.84 %, 28.33 %, and 19.49 % on the CALLHOME, DIHARD II, and DIHARD III datasets, respectively, each of which is better than the conventional end-to-end diarization methods.
Encoder-Decoder Based Attractor Calculation for End-to-End Neural Diarization
Jun 20, 2021



Abstract:This paper investigates an end-to-end neural diarization (EEND) method for an unknown number of speakers. In contrast to the conventional pipeline approach to speaker diarization, EEND methods are better in terms of speaker overlap handling. However, EEND still has a disadvantage in that it cannot deal with a flexible number of speakers. To remedy this problem, we introduce encoder-decoder-based attractor calculation module (EDA) to EEND. Once frame-wise embeddings are obtained, EDA sequentially generates speaker-wise attractors on the basis of a sequence-to-sequence method using an LSTM encoder-decoder. The attractor generation continues until a stopping condition is satisfied; thus, the number of attractors can be flexible. Diarization results are then estimated as dot products of the attractors and embeddings. The embeddings from speaker overlaps result in larger dot product values with multiple attractors; thus, this method can deal with speaker overlaps. Because the maximum number of output speakers is still limited by the training set, we also propose an iterative inference method to remove this restriction. Further, we propose a method that aligns the estimated diarization results with the results of an external speech activity detector, which enables fair comparison against pipeline approaches. Extensive evaluations on simulated and real datasets show that EEND-EDA outperforms the conventional pipeline approach.
The Hitachi-JHU DIHARD III System: Competitive End-to-End Neural Diarization and X-Vector Clustering Systems Combined by DOVER-Lap
Feb 02, 2021



Abstract:This paper provides a detailed description of the Hitachi-JHU system that was submitted to the Third DIHARD Speech Diarization Challenge. The system outputs the ensemble results of the five subsystems: two x-vector-based subsystems, two end-to-end neural diarization-based subsystems, and one hybrid subsystem. We refine each system and all five subsystems become competitive and complementary. After the DOVER-Lap based system combination, it achieved diarization error rates of 11.58 % and 14.09 % in Track 1 full and core, and 16.94 % and 20.01 % in Track 2 full and core, respectively. With their results, we won second place in all the tasks of the challenge.
Online End-to-End Neural Diarization Handling Overlapping Speech and Flexible Numbers of Speakers
Jan 21, 2021
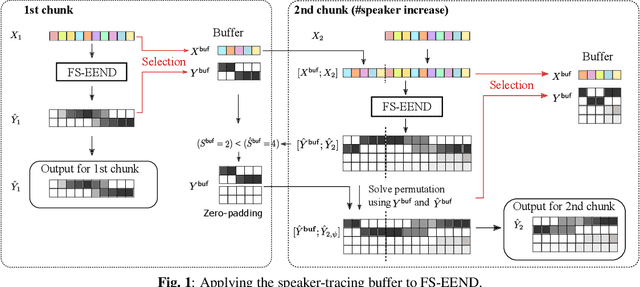


Abstract:This paper proposes an online end-to-end diarization that can handle overlapping speech and flexible numbers of speakers. The end-to-end neural speaker diarization (EEND) model has already achieved significant improvement when compared with conventional clustering-based methods. However, the original EEND has two limitations: i) EEND does not perform well in online scenarios; ii) the number of speakers must be fixed in advance. This paper solves both problems by applying a modified extension of the speaker-tracing buffer method that deals with variable numbers of speakers. Experiments on CALLHOME and DIHARD II datasets show that the proposed online method achieves comparable performance to the offline EEND method. Compared with the state-of-the-art online method based on a fully supervised approach (UIS-RNN), the proposed method shows better performance on the DIHARD II dataset.
Neural Speaker Diarization with Speaker-Wise Chain Rule
Jun 02, 2020



Abstract:Speaker diarization is an essential step for processing multi-speaker audio. Although an end-to-end neural diarization (EEND) method achieved state-of-the-art performance, it is limited to a fixed number of speakers. In this paper, we solve this fixed number of speaker issue by a novel speaker-wise conditional inference method based on the probabilistic chain rule. In the proposed method, each speaker's speech activity is regarded as a single random variable, and is estimated sequentially conditioned on previously estimated other speakers' speech activities. Similar to other sequence-to-sequence models, the proposed method produces a variable number of speakers with a stop sequence condition. We evaluated the proposed method on multi-speaker audio recordings of a variable number of speakers. Experimental results show that the proposed method can correctly produce diarization results with a variable number of speakers and outperforms the state-of-the-art end-to-end speaker diarization methods in terms of diarization error rate.
End-to-End Speaker Diarization for an Unknown Number of Speakers with Encoder-Decoder Based Attractors
May 20, 2020



Abstract:End-to-end speaker diarization for an unknown number of speakers is addressed in this paper. Recently proposed end-to-end speaker diarization outperformed conventional clustering-based speaker diarization, but it has one drawback: it is less flexible in terms of the number of speakers. This paper proposes a method for encoder-decoder based attractor calculation (EDA), which first generates a flexible number of attractors from a speech embedding sequence. Then, the generated multiple attractors are multiplied by the speech embedding sequence to produce the same number of speaker activities. The speech embedding sequence is extracted using the conventional self-attentive end-to-end neural speaker diarization (SA-EEND) network. In a two-speaker condition, our method achieved a 2.69 % diarization error rate (DER) on simulated mixtures and a 8.07 % DER on the two-speaker subset of CALLHOME, while vanilla SA-EEND attained 4.56 % and 9.54 %, respectively. In unknown numbers of speakers conditions, our method attained a 15.29 % DER on CALLHOME, while the x-vector-based clustering method achieved a 19.43 % DER.
End-to-End Neural Diarization: Reformulating Speaker Diarization as Simple Multi-label Classification
Feb 24, 2020



Abstract:The most common approach to speaker diarization is clustering of speaker embeddings. However, the clustering-based approach has a number of problems; i.e., (i) it is not optimized to minimize diarization errors directly, (ii) it cannot handle speaker overlaps correctly, and (iii) it has trouble adapting their speaker embedding models to real audio recordings with speaker overlaps. To solve these problems, we propose the End-to-End Neural Diarization (EEND), in which a neural network directly outputs speaker diarization results given a multi-speaker recording. To realize such an end-to-end model, we formulate the speaker diarization problem as a multi-label classification problem and introduce a permutation-free objective function to directly minimize diarization errors. Besides its end-to-end simplicity, the EEND method can explicitly handle speaker overlaps during training and inference. Just by feeding multi-speaker recordings with corresponding speaker segment labels, our model can be easily adapted to real conversations. We evaluated our method on simulated speech mixtures and real conversation datasets. The results showed that the EEND method outperformed the state-of-the-art x-vector clustering-based method, while it correctly handled speaker overlaps. We explored the neural network architecture for the EEND method, and found that the self-attention-based neural network was the key to achieving excellent performance. In contrast to conditioning the network only on its previous and next hidden states, as is done using bidirectional long short-term memory (BLSTM), self-attention is directly conditioned on all the frames. By visualizing the attention weights, we show that self-attention captures global speaker characteristics in addition to local speech activity dynamics, making it especially suitable for dealing with the speaker diarization problem.
Simultaneous Speech Recognition and Speaker Diarization for Monaural Dialogue Recordings with Target-Speaker Acoustic Models
Sep 17, 2019



Abstract:This paper investigates the use of target-speaker automatic speech recognition (TS-ASR) for simultaneous speech recognition and speaker diarization of single-channel dialogue recordings. TS-ASR is a technique to automatically extract and recognize only the speech of a target speaker given a short sample utterance of that speaker. One obvious drawback of TS-ASR is that it cannot be used when the speakers in the recordings are unknown because it requires a sample of the target speakers in advance of decoding. To remove this limitation, we propose an iterative method, in which (i) the estimation of speaker embeddings and (ii) TS-ASR based on the estimated speaker embeddings are alternately executed. We evaluated the proposed method by using very challenging dialogue recordings in which the speaker overlap ratio was over 20%. We confirmed that the proposed method significantly reduced both the word error rate (WER) and diarization error rate (DER). Our proposed method combined with i-vector speaker embeddings ultimately achieved a WER that differed by only 2.1 % from that of TS-ASR given oracle speaker embeddings. Furthermore, our method can solve speaker diarization simultaneously as a by-product and achieved better DER than that of the conventional clustering-based speaker diarization method based on i-vector.
End-to-End Neural Speaker Diarization with Self-attention
Sep 13, 2019



Abstract:Speaker diarization has been mainly developed based on the clustering of speaker embeddings. However, the clustering-based approach has two major problems; i.e., (i) it is not optimized to minimize diarization errors directly, and (ii) it cannot handle speaker overlaps correctly. To solve these problems, the End-to-End Neural Diarization (EEND), in which a bidirectional long short-term memory (BLSTM) network directly outputs speaker diarization results given a multi-talker recording, was recently proposed. In this study, we enhance EEND by introducing self-attention blocks instead of BLSTM blocks. In contrast to BLSTM, which is conditioned only on its previous and next hidden states, self-attention is directly conditioned on all the other frames, making it much suitable for dealing with the speaker diarization problem. We evaluated our proposed method on simulated mixtures, real telephone calls, and real dialogue recordings. The experimental results revealed that the self-attention was the key to achieving good performance and that our proposed method performed significantly better than the conventional BLSTM-based method. Our method was even better than that of the state-of-the-art x-vector clustering-based method. Finally, by visualizing the latent representation, we show that the self-attention can capture global speaker characteristics in addition to local speech activity dynamics. Our source code is available online at https://github.com/hitachi-speech/EEND.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge