Yaru Zhao
ShotFinder: Imagination-Driven Open-Domain Video Shot Retrieval via Web Search
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have made rapid progress in information retrieval, yet existing research has mainly focused on text or static multimodal settings. Open-domain video shot retrieval, which involves richer temporal structure and more complex semantics, still lacks systematic benchmarks and analysis. To fill this gap, we introduce ShotFinder, a benchmark that formalizes editing requirements as keyframe-oriented shot descriptions and introduces five types of controllable single-factor constraints: Temporal order, Color, Visual style, Audio, and Resolution. We curate 1,210 high-quality samples from YouTube across 20 thematic categories, using large models for generation with human verification. Based on the benchmark, we propose ShotFinder, a text-driven three-stage retrieval and localization pipeline: (1) query expansion via video imagination, (2) candidate video retrieval with a search engine, and (3) description-guided temporal localization. Experiments on multiple closed-source and open-source models reveal a significant gap to human performance, with clear imbalance across constraints: temporal localization is relatively tractable, while color and visual style remain major challenges. These results reveal that open-domain video shot retrieval is still a critical capability that multimodal large models have yet to overcome.
ZipMoE: Efficient On-Device MoE Serving via Lossless Compression and Cache-Affinity Scheduling
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:While Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures substantially bolster the expressive power of large-language models, their prohibitive memory footprint severely impedes the practical deployment on resource-constrained edge devices, especially when model behavior must be preserved without relying on lossy quantization. In this paper, we present ZipMoE, an efficient and semantically lossless on-device MoE serving system. ZipMoE exploits the synergy between the hardware properties of edge devices and the statistical redundancy inherent to MoE parameters via a caching-scheduling co-design with provable performance guarantee. Fundamentally, our design shifts the paradigm of on-device MoE inference from an I/O-bound bottleneck to a compute-centric workflow that enables efficient parallelization. We implement a prototype of ZipMoE and conduct extensive experiments on representative edge computing platforms using popular open-source MoE models and real-world workloads. Our evaluation reveals that ZipMoE achieves up to $72.77\%$ inference latency reduction and up to $6.76\times$ higher throughput than the state-of-the-art systems.
RepBNN: towards a precise Binary Neural Network with Enhanced Feature Map via Repeating
Jul 19, 2022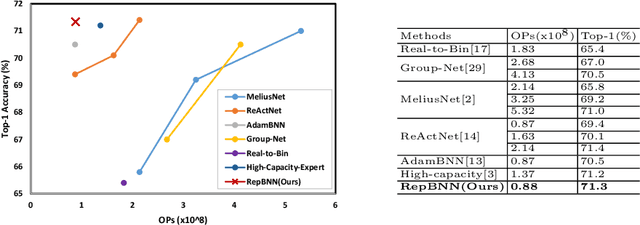



Abstract:Binary neural network (BNN) is an extreme quantization version of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with all features and weights mapped to just 1-bit. Although BNN saves a lot of memory and computation demand to make CNN applicable on edge or mobile devices, BNN suffers the drop of network performance due to the reduced representation capability after binarization. In this paper, we propose a new replaceable and easy-to-use convolution module RepConv, which enhances feature maps through replicating input or output along channel dimension by $\beta$ times without extra cost on the number of parameters and convolutional computation. We also define a set of RepTran rules to use RepConv throughout BNN modules like binary convolution, fully connected layer and batch normalization. Experiments demonstrate that after the RepTran transformation, a set of highly cited BNNs have achieved universally better performance than the original BNN versions. For example, the Top-1 accuracy of Rep-ReCU-ResNet-20, i.e., a RepBconv enhanced ReCU-ResNet-20, reaches 88.97% on CIFAR-10, which is 1.47% higher than that of the original network. And Rep-AdamBNN-ReActNet-A achieves 71.342% Top-1 accuracy on ImageNet, a fresh state-of-the-art result of BNNs. Code and models are available at:https://github.com/imfinethanks/Rep_AdamBNN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge