Yanxu Li
CT-NeRF: Incremental Optimizing Neural Radiance Field and Poses with Complex Trajectory
Apr 23, 2024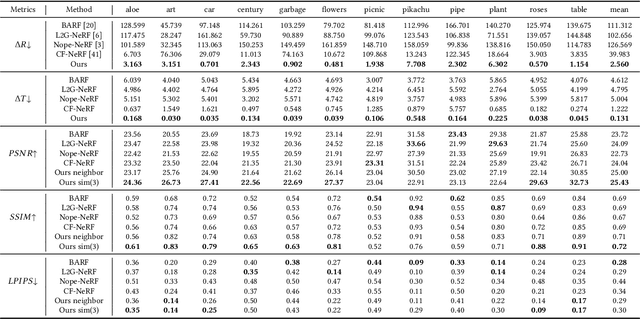

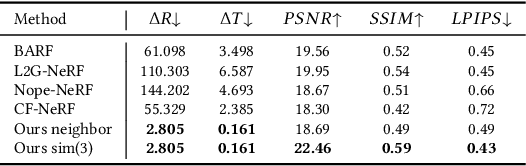

Abstract:Neural radiance field (NeRF) has achieved impressive results in high-quality 3D scene reconstruction. However, NeRF heavily relies on precise camera poses. While recent works like BARF have introduced camera pose optimization within NeRF, their applicability is limited to simple trajectory scenes. Existing methods struggle while tackling complex trajectories involving large rotations. To address this limitation, we propose CT-NeRF, an incremental reconstruction optimization pipeline using only RGB images without pose and depth input. In this pipeline, we first propose a local-global bundle adjustment under a pose graph connecting neighboring frames to enforce the consistency between poses to escape the local minima caused by only pose consistency with the scene structure. Further, we instantiate the consistency between poses as a reprojected geometric image distance constraint resulting from pixel-level correspondences between input image pairs. Through the incremental reconstruction, CT-NeRF enables the recovery of both camera poses and scene structure and is capable of handling scenes with complex trajectories. We evaluate the performance of CT-NeRF on two real-world datasets, NeRFBuster and Free-Dataset, which feature complex trajectories. Results show CT-NeRF outperforms existing methods in novel view synthesis and pose estimation accuracy.
Autonomous Implicit Indoor Scene Reconstruction with Frontier Exploration
Apr 16, 2024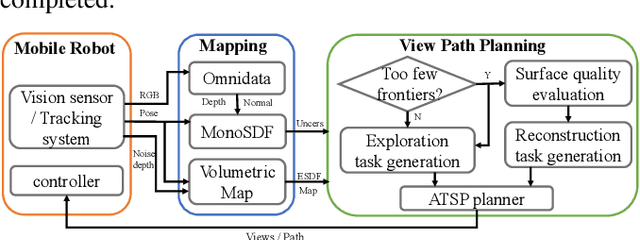
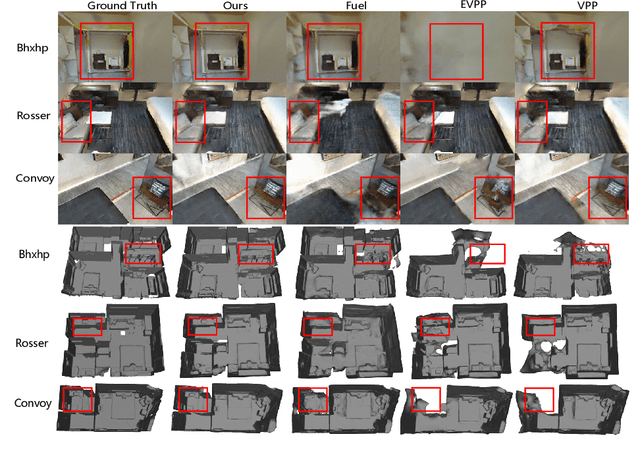
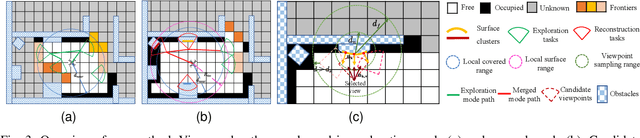

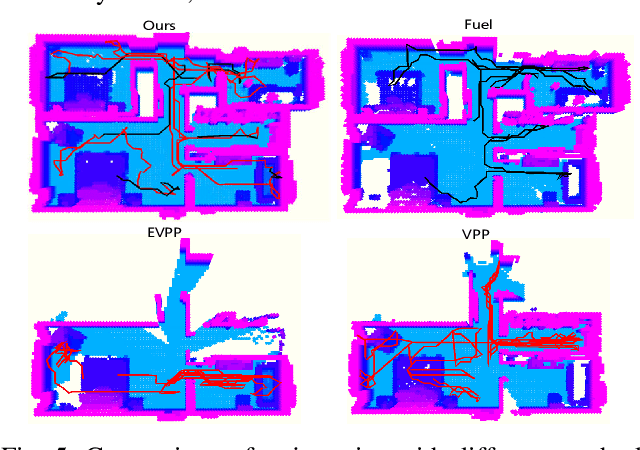
Abstract:Implicit neural representations have demonstrated significant promise for 3D scene reconstruction. Recent works have extended their applications to autonomous implicit reconstruction through the Next Best View (NBV) based method. However, the NBV method cannot guarantee complete scene coverage and often necessitates extensive viewpoint sampling, particularly in complex scenes. In the paper, we propose to 1) incorporate frontier-based exploration tasks for global coverage with implicit surface uncertainty-based reconstruction tasks to achieve high-quality reconstruction. and 2) introduce a method to achieve implicit surface uncertainty using color uncertainty, which reduces the time needed for view selection. Further with these two tasks, we propose an adaptive strategy for switching modes in view path planning, to reduce time and maintain superior reconstruction quality. Our method exhibits the highest reconstruction quality among all planning methods and superior planning efficiency in methods involving reconstruction tasks. We deploy our method on a UAV and the results show that our method can plan multi-task views and reconstruct a scene with high quality.
* 7 pages
Efficient View Path Planning for Autonomous Implicit Reconstruction
Sep 27, 2022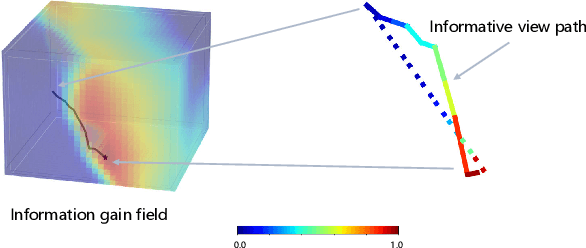
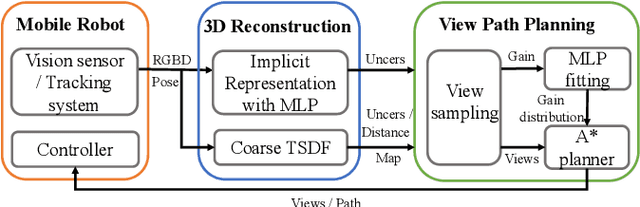

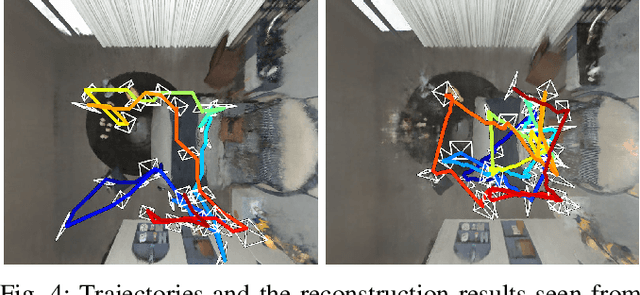
Abstract:Implicit neural representations have shown promising potential for the 3D scene reconstruction. Recent work applies it to autonomous 3D reconstruction by learning information gain for view path planning. Effective as it is, the computation of the information gain is expensive, and compared with that using volumetric representations, collision checking using the implicit representation for a 3D point is much slower. In the paper, we propose to 1) leverage a neural network as an implicit function approximator for the information gain field and 2) combine the implicit fine-grained representation with coarse volumetric representations to improve efficiency. Further with the improved efficiency, we propose a novel informative path planning based on a graph-based planner. Our method demonstrates significant improvements in the reconstruction quality and planning efficiency compared with autonomous reconstructions with implicit and explicit representations. We deploy the method on a real UAV and the results show that our method can plan informative views and reconstruct a scene with high quality.
mmBody Benchmark: 3D Body Reconstruction Dataset and Analysis for Millimeter Wave Radar
Sep 12, 2022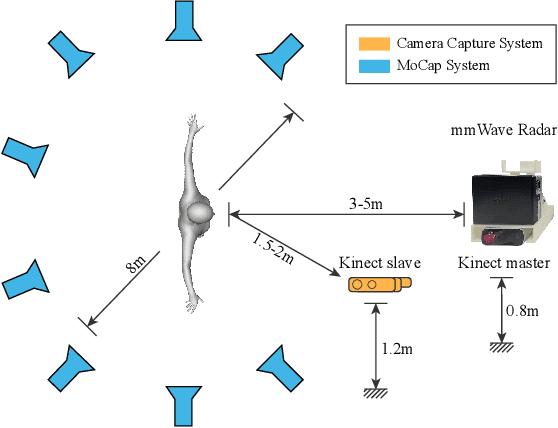
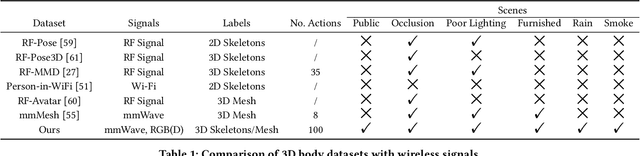
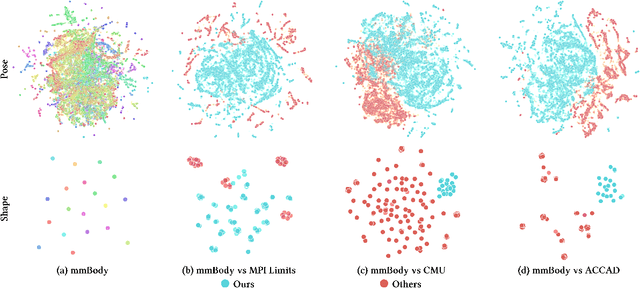
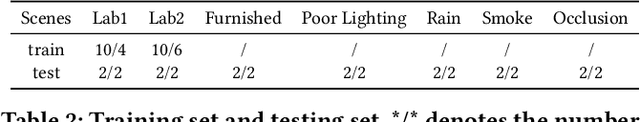
Abstract:Millimeter Wave (mmWave) Radar is gaining popularity as it can work in adverse environments like smoke, rain, snow, poor lighting, etc. Prior work has explored the possibility of reconstructing 3D skeletons or meshes from the noisy and sparse mmWave Radar signals. However, it is unclear how accurately we can reconstruct the 3D body from the mmWave signals across scenes and how it performs compared with cameras, which are important aspects needed to be considered when either using mmWave radars alone or combining them with cameras. To answer these questions, an automatic 3D body annotation system is first designed and built up with multiple sensors to collect a large-scale dataset. The dataset consists of synchronized and calibrated mmWave radar point clouds and RGB(D) images in different scenes and skeleton/mesh annotations for humans in the scenes. With this dataset, we train state-of-the-art methods with inputs from different sensors and test them in various scenarios. The results demonstrate that 1) despite the noise and sparsity of the generated point clouds, the mmWave radar can achieve better reconstruction accuracy than the RGB camera but worse than the depth camera; 2) the reconstruction from the mmWave radar is affected by adverse weather conditions moderately while the RGB(D) camera is severely affected. Further, analysis of the dataset and the results shadow insights on improving the reconstruction from the mmWave radar and the combination of signals from different sensors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge