Yanqing Wang
ECCoT: A Framework for Enhancing Effective Cognition via Chain of Thought in Large Language Model
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:In the era of large-scale artificial intelligence, Large Language Models (LLMs) have made significant strides in natural language processing. However, they often lack transparency and generate unreliable outputs, raising concerns about their interpretability. To address this, the Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting method structures reasoning into step-by-step deductions. Yet, not all reasoning chains are valid, and errors can lead to unreliable conclusions. We propose ECCoT, an End-to-End Cognitive Chain of Thought Validation Framework, to evaluate and refine reasoning chains in LLMs. ECCoT integrates the Markov Random Field-Embedded Topic Model (MRF-ETM) for topic-aware CoT generation and Causal Sentence-BERT (CSBert) for causal reasoning alignment. By filtering ineffective chains using structured ordering statistics, ECCoT improves interpretability, reduces biases, and enhances the trustworthiness of LLM-based decision-making. Key contributions include the introduction of ECCoT, MRF-ETM for topic-driven CoT generation, and CSBert for causal reasoning enhancement. Code is released at: https://github.com/erwinmsmith/ECCoT.git.
Coordinated Transformer with Position \& Sample-aware Central Loss for Anatomical Landmark Detection
May 18, 2023Abstract:Heatmap-based anatomical landmark detection is still facing two unresolved challenges: 1) inability to accurately evaluate the distribution of heatmap; 2) inability to effectively exploit global spatial structure information. To address the computational inability challenge, we propose a novel position-aware and sample-aware central loss. Specifically, our central loss can absorb position information, enabling accurate evaluation of the heatmap distribution. More advanced is that our central loss is sample-aware, which can adaptively distinguish easy and hard samples and make the model more focused on hard samples while solving the challenge of extreme imbalance between landmarks and non-landmarks. To address the challenge of ignoring structure information, a Coordinated Transformer, called CoorTransformer, is proposed, which establishes long-range dependencies under the guidance of landmark coordination information, making the attention more focused on the sparse landmarks while taking advantage of global spatial structure. Furthermore, CoorTransformer can speed up convergence, effectively avoiding the defect that Transformers have difficulty converging in sparse representation learning. Using the advanced CoorTransformer and central loss, we propose a generalized detection model that can handle various scenarios, inherently exploiting the underlying relationship between landmarks and incorporating rich structural knowledge around the target landmarks. We analyzed and evaluated CoorTransformer and central loss on three challenging landmark detection tasks. The experimental results show that our CoorTransformer outperforms state-of-the-art methods, and the central loss significantly improves the performance of the model with p-values< 0.05.
Localizing Discriminative Visual Landmarks for Place Recognition
Apr 14, 2019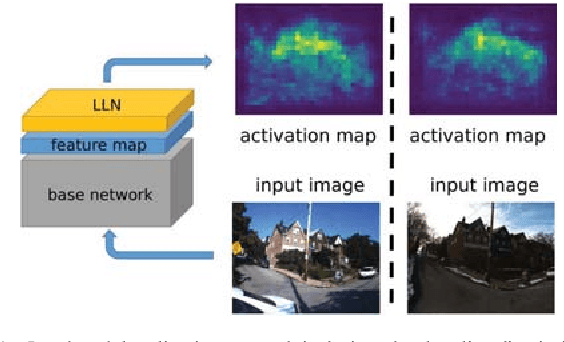
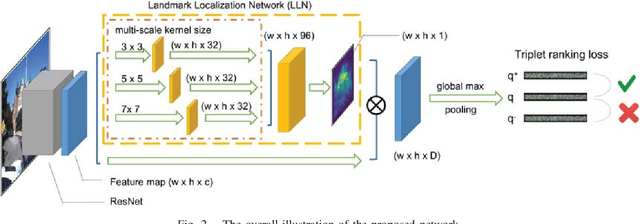
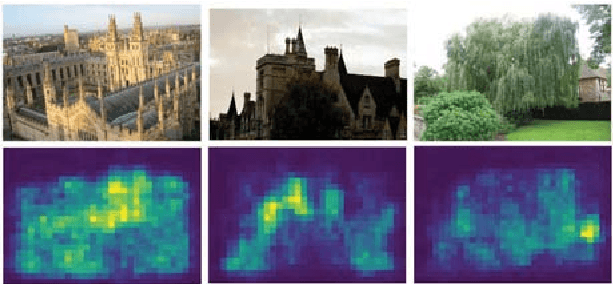
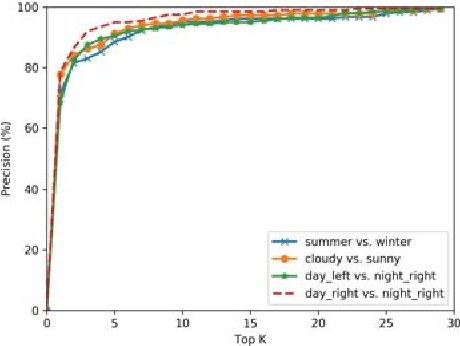
Abstract:We address the problem of visual place recognition with perceptual changes. The fundamental problem of visual place recognition is generating robust image representations which are not only insensitive to environmental changes but also distinguishable to different places. Taking advantage of the feature extraction ability of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), we further investigate how to localize discriminative visual landmarks that positively contribute to the similarity measurement, such as buildings and vegetations. In particular, a Landmark Localization Network (LLN) is designed to indicate which regions of an image are used for discrimination. Detailed experiments are conducted on open source datasets with varied appearance and viewpoint changes. The proposed approach achieves superior performance against state-of-the-art methods.
Human and Machine Speaker Recognition Based on Short Trivial Events
Feb 06, 2018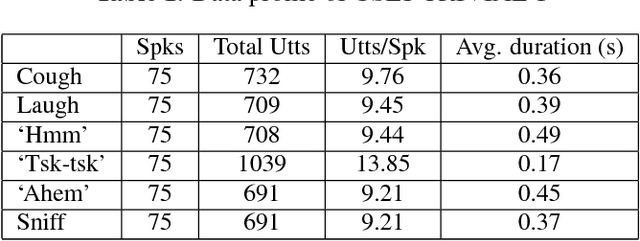
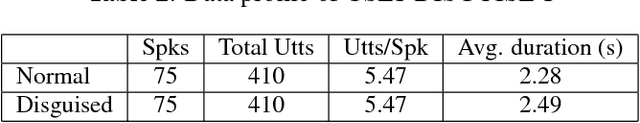
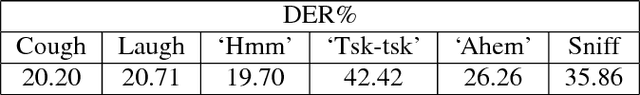
Abstract:Trivial events are ubiquitous in human to human conversations, e.g., cough, laugh and sniff. Compared to regular speech, these trivial events are usually short and unclear, thus generally regarded as not speaker discriminative and so are largely ignored by present speaker recognition research. However, these trivial events are highly valuable in some particular circumstances such as forensic examination, as they are less subjected to intentional change, so can be used to discover the genuine speaker from disguised speech. In this paper, we collect a trivial event speech database that involves 75 speakers and 6 types of events, and report preliminary speaker recognition results on this database, by both human listeners and machines. Particularly, the deep feature learning technique recently proposed by our group is utilized to analyze and recognize the trivial events, which leads to acceptable equal error rates (EERs) despite the extremely short durations (0.2-0.5 seconds) of these events. Comparing different types of events, 'hmm' seems more speaker discriminative.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge