Xuchong Zhang
Expand Your SCOPE: Semantic Cognition over Potential-Based Exploration for Embodied Visual Navigation
Nov 12, 2025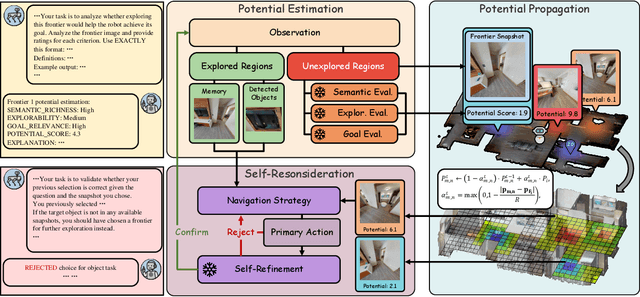
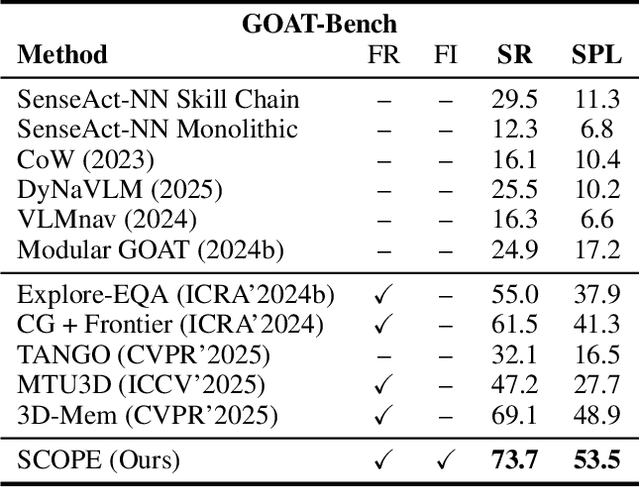
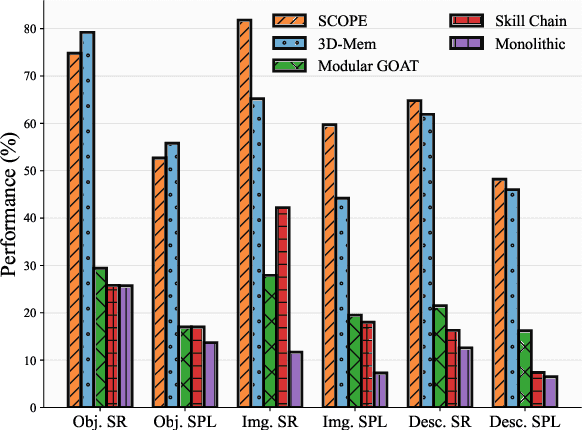
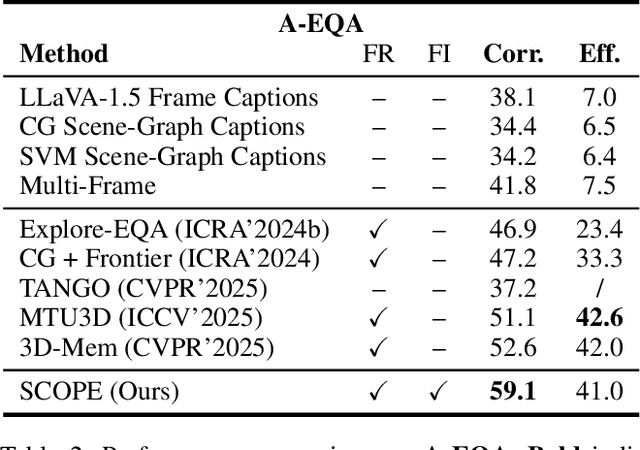
Abstract:Embodied visual navigation remains a challenging task, as agents must explore unknown environments with limited knowledge. Existing zero-shot studies have shown that incorporating memory mechanisms to support goal-directed behavior can improve long-horizon planning performance. However, they overlook visual frontier boundaries, which fundamentally dictate future trajectories and observations, and fall short of inferring the relationship between partial visual observations and navigation goals. In this paper, we propose Semantic Cognition Over Potential-based Exploration (SCOPE), a zero-shot framework that explicitly leverages frontier information to drive potential-based exploration, enabling more informed and goal-relevant decisions. SCOPE estimates exploration potential with a Vision-Language Model and organizes it into a spatio-temporal potential graph, capturing boundary dynamics to support long-horizon planning. In addition, SCOPE incorporates a self-reconsideration mechanism that revisits and refines prior decisions, enhancing reliability and reducing overconfident errors. Experimental results on two diverse embodied navigation tasks show that SCOPE outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by 4.6\% in accuracy. Further analysis demonstrates that its core components lead to improved calibration, stronger generalization, and higher decision quality.
TensorAR: Refinement is All You Need in Autoregressive Image Generation
May 22, 2025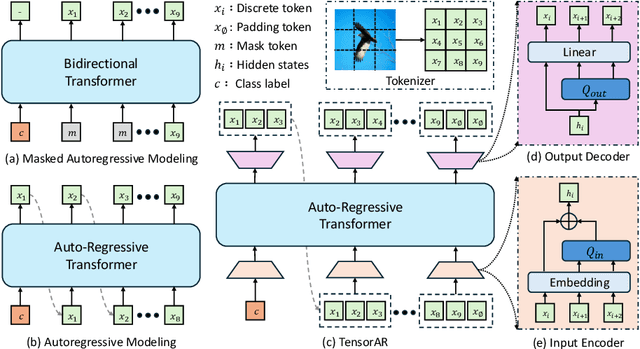

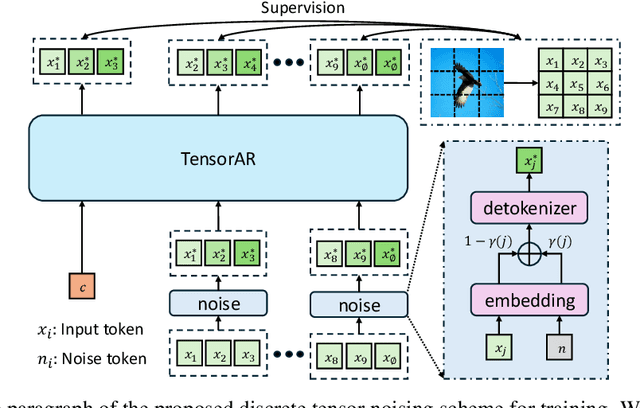
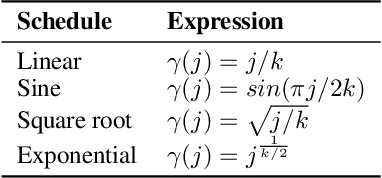
Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) image generators offer a language-model-friendly approach to image generation by predicting discrete image tokens in a causal sequence. However, unlike diffusion models, AR models lack a mechanism to refine previous predictions, limiting their generation quality. In this paper, we introduce TensorAR, a new AR paradigm that reformulates image generation from next-token prediction to next-tensor prediction. By generating overlapping windows of image patches (tensors) in a sliding fashion, TensorAR enables iterative refinement of previously generated content. To prevent information leakage during training, we propose a discrete tensor noising scheme, which perturbs input tokens via codebook-indexed noise. TensorAR is implemented as a plug-and-play module compatible with existing AR models. Extensive experiments on LlamaGEN, Open-MAGVIT2, and RAR demonstrate that TensorAR significantly improves the generation performance of autoregressive models.
Latent Feature and Attention Dual Erasure Attack against Multi-View Diffusion Models for 3D Assets Protection
Aug 21, 2024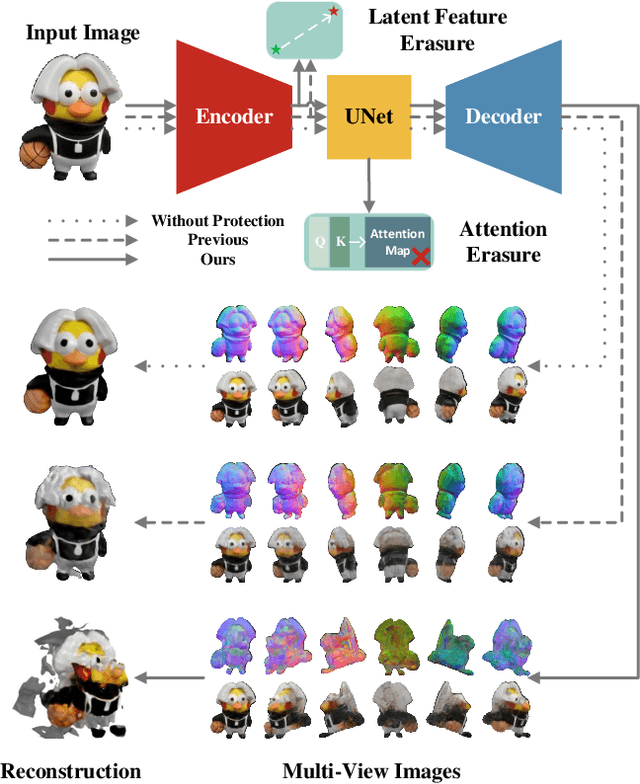
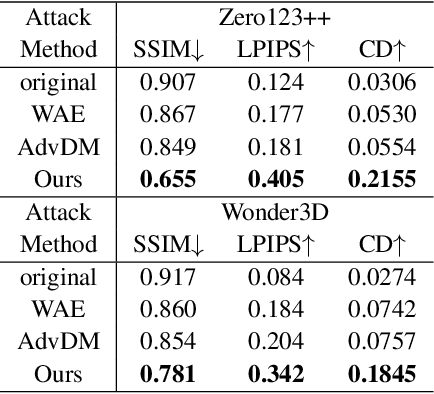
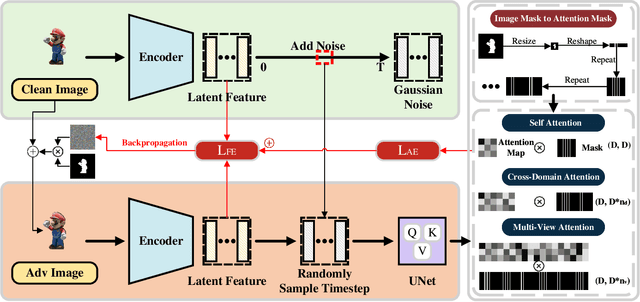
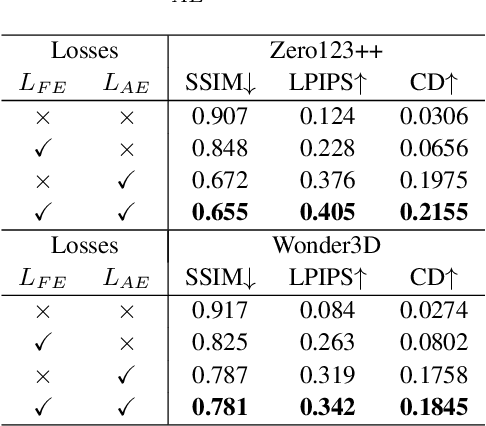
Abstract:Multi-View Diffusion Models (MVDMs) enable remarkable improvements in the field of 3D geometric reconstruction, but the issue regarding intellectual property has received increasing attention due to unauthorized imitation. Recently, some works have utilized adversarial attacks to protect copyright. However, all these works focus on single-image generation tasks which only need to consider the inner feature of images. Previous methods are inefficient in attacking MVDMs because they lack the consideration of disrupting the geometric and visual consistency among the generated multi-view images. This paper is the first to address the intellectual property infringement issue arising from MVDMs. Accordingly, we propose a novel latent feature and attention dual erasure attack to disrupt the distribution of latent feature and the consistency across the generated images from multi-view and multi-domain simultaneously. The experiments conducted on SOTA MVDMs indicate that our approach achieves superior performances in terms of attack effectiveness, transferability, and robustness against defense methods. Therefore, this paper provides an efficient solution to protect 3D assets from MVDMs-based 3D geometry reconstruction.
Object-fabrication Targeted Attack for Object Detection
Dec 14, 2022Abstract:Recent researches show that the deep learning based object detection is vulnerable to adversarial examples. Generally, the adversarial attack for object detection contains targeted attack and untargeted attack. According to our detailed investigations, the research on the former is relatively fewer than the latter and all the existing methods for the targeted attack follow the same mode, i.e., the object-mislabeling mode that misleads detectors to mislabel the detected object as a specific wrong label. However, this mode has limited attack success rate, universal and generalization performances. In this paper, we propose a new object-fabrication targeted attack mode which can mislead detectors to `fabricate' extra false objects with specific target labels. Furthermore, we design a dual attention based targeted feature space attack method to implement the proposed targeted attack mode. The attack performances of the proposed mode and method are evaluated on MS COCO and BDD100K datasets using FasterRCNN and YOLOv5. Evaluation results demonstrate that, the proposed object-fabrication targeted attack mode and the corresponding targeted feature space attack method show significant improvements in terms of image-specific attack, universal performance and generalization capability, compared with the previous targeted attack for object detection. Code will be made available.
Artificial Intelligence Security Competition (AISC)
Dec 07, 2022



Abstract:The security of artificial intelligence (AI) is an important research area towards safe, reliable, and trustworthy AI systems. To accelerate the research on AI security, the Artificial Intelligence Security Competition (AISC) was organized by the Zhongguancun Laboratory, China Industrial Control Systems Cyber Emergency Response Team, Institute for Artificial Intelligence, Tsinghua University, and RealAI as part of the Zhongguancun International Frontier Technology Innovation Competition (https://www.zgc-aisc.com/en). The competition consists of three tracks, including Deepfake Security Competition, Autonomous Driving Security Competition, and Face Recognition Security Competition. This report will introduce the competition rules of these three tracks and the solutions of top-ranking teams in each track.
ADCPNet: Adaptive Disparity Candidates Prediction Network for Efficient Real-Time Stereo Matching
Nov 18, 2020

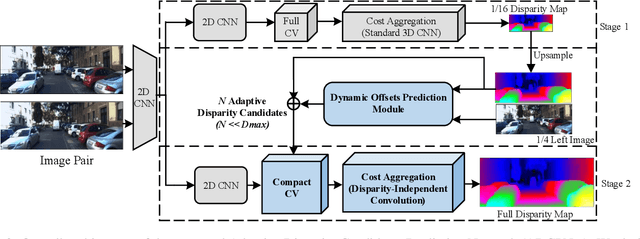

Abstract:Efficient real-time disparity estimation is critical for the application of stereo vision systems in various areas. Recently, stereo network based on coarse-to-fine method has largely relieved the memory constraints and speed limitations of large-scale network models. Nevertheless, all of the previous coarse-to-fine designs employ constant offsets and three or more stages to progressively refine the coarse disparity map, still resulting in unsatisfactory computation accuracy and inference time when deployed on mobile devices. This paper claims that the coarse matching errors can be corrected efficiently with fewer stages as long as more accurate disparity candidates can be provided. Therefore, we propose a dynamic offset prediction module to meet different correction requirements of diverse objects and design an efficient two-stage framework. Besides, we propose a disparity-independent convolution to further improve the performance since it is more consistent with the local statistical characteristics of the compact cost volume. The evaluation results on multiple datasets and platforms clearly demonstrate that, the proposed network outperforms the state-of-the-art lightweight models especially for mobile devices in terms of accuracy and speed. Code will be made available.
Deep Neural Networks with Auxiliary-Model Regulated Gating for Resilient Multi-Modal Sensor Fusion
Jan 29, 2019



Abstract:Deep neural networks allow for fusion of high-level features from multiple modalities and have become a promising end-to-end solution for multi-modal sensor fusion. While the recently proposed gating architectures improve the conventional fusion mechanisms employed in CNNs, these models are not always resilient particularly under the presence of sensor failures. This paper shows that the existing gating architectures fail to robustly learn the fusion weights that critically gate different modalities, leading to the issue of fusion weight inconsistency. We propose a new gating architecture by incorporating an auxiliary model to regularize the main model such that the fusion weight for each sensory modality can be robustly learned. As a result, this new auxiliary-model regulated architecture and its variants outperform the existing non-gating and gating fusion architectures under both clean and corrupted sensory inputs resulted from sensor failures. The obtained performance gains are rather significant in the latter case.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge