Xuan-Nga Cao
LSCP, CoML
Probing mental health information in speech foundation models
Sep 27, 2024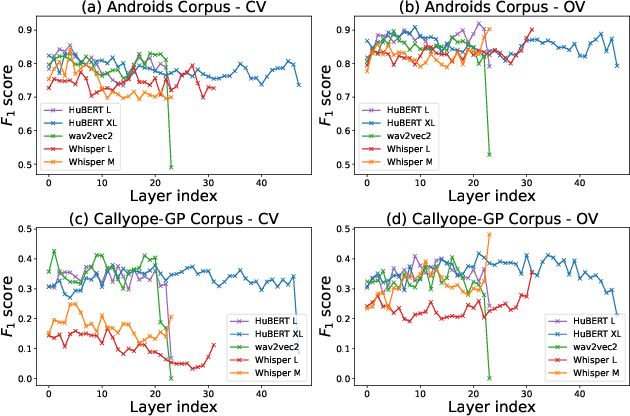
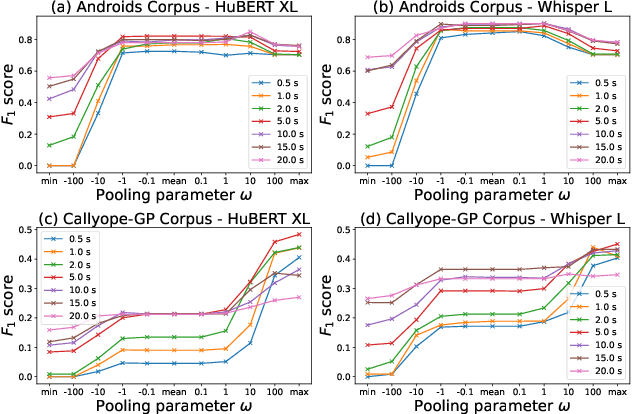
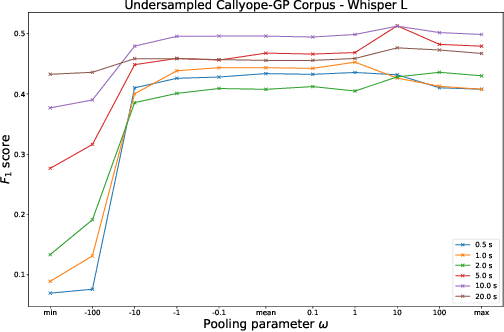
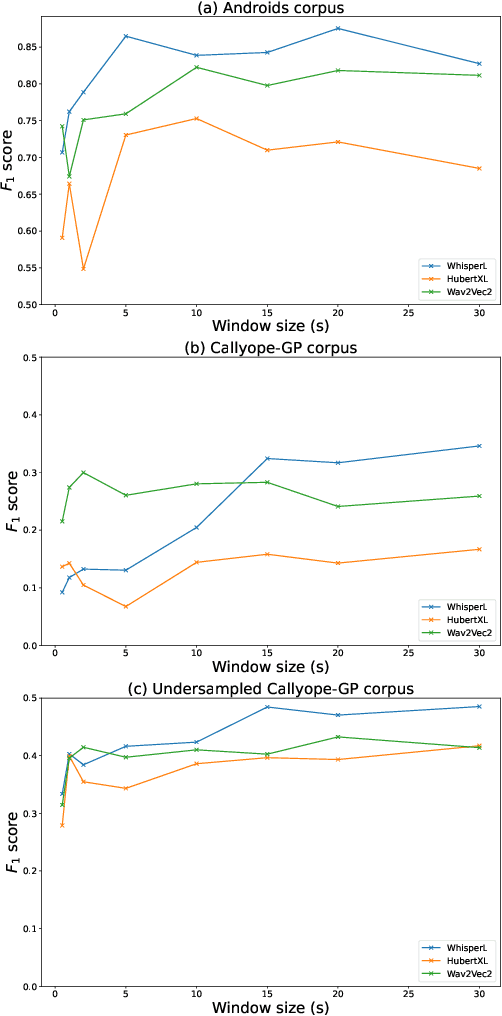
Abstract:Non-invasive methods for diagnosing mental health conditions, such as speech analysis, offer promising potential in modern medicine. Recent advancements in machine learning, particularly speech foundation models, have shown significant promise in detecting mental health states by capturing diverse features. This study investigates which pretext tasks in these models best transfer to mental health detection and examines how different model layers encode features relevant to mental health conditions. We also probed the optimal length of audio segments and the best pooling strategies to improve detection accuracy. Using the Callyope-GP and Androids datasets, we evaluated the models' effectiveness across different languages and speech tasks, aiming to enhance the generalizability of speech-based mental health diagnostics. Our approach achieved SOTA scores in depression detection on the Androids dataset.
The Zero Resource Speech Challenge 2020: Discovering discrete subword and word units
Oct 12, 2020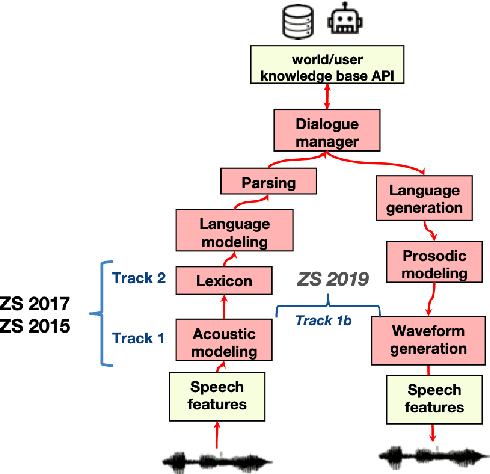
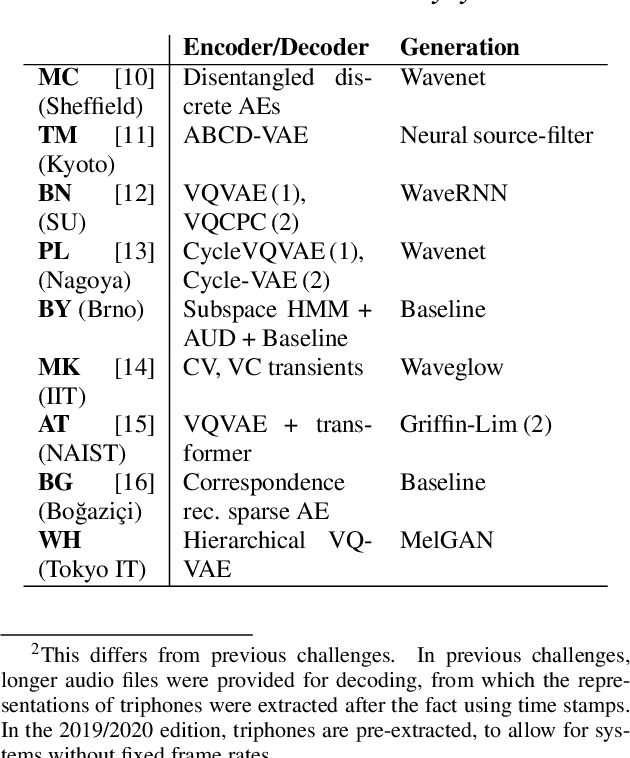
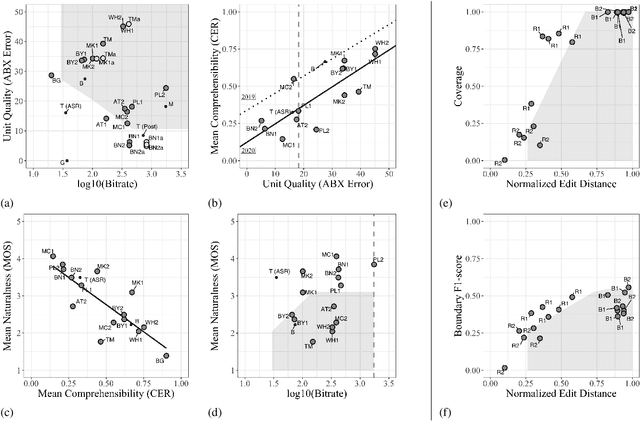
Abstract:We present the Zero Resource Speech Challenge 2020, which aims at learning speech representations from raw audio signals without any labels. It combines the data sets and metrics from two previous benchmarks (2017 and 2019) and features two tasks which tap into two levels of speech representation. The first task is to discover low bit-rate subword representations that optimize the quality of speech synthesis; the second one is to discover word-like units from unsegmented raw speech. We present the results of the twenty submitted models and discuss the implications of the main findings for unsupervised speech learning.
Seshat: A tool for managing and verifying annotation campaigns of audio data
Mar 03, 2020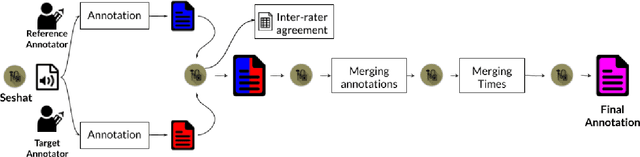
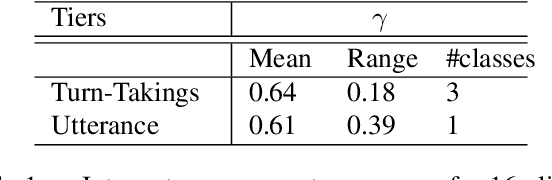


Abstract:We introduce Seshat, a new, simple and open-source software to efficiently manage annotations of speech corpora. The Seshat software allows users to easily customise and manage annotations of large audio corpora while ensuring compliance with the formatting and naming conventions of the annotated output files. In addition, it includes procedures for checking the content of annotations following specific rules are implemented in personalised parsers. Finally, we propose a double-annotation mode, for which Seshat computes automatically an associated inter-annotator agreement with the $\gamma$ measure taking into account the categorisation and segmentation discrepancies.
The Zero Resource Speech Challenge 2019: TTS without T
Apr 25, 2019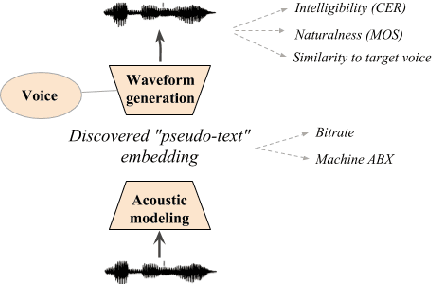
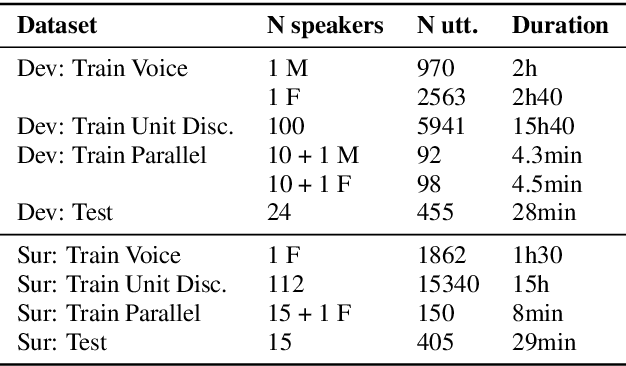
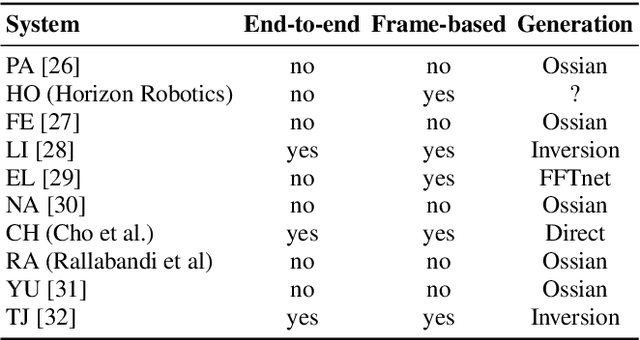
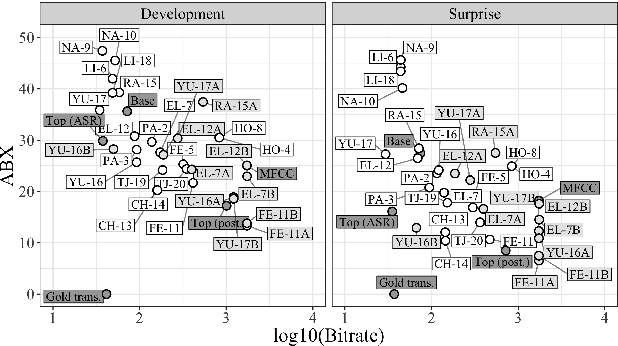
Abstract:We present the Zero Resource Speech Challenge 2019, which proposes to build a speech synthesizer without any text or phonetic labels: hence, TTS without T (text-to-speech without text). We provide raw audio for a target voice in an unknown language (the Voice dataset), but no alignment, text or labels. Participants must discover subword units in an unsupervised way (using the Unit Discovery dataset) and align them to the voice recordings in a way that works best for the purpose of synthesizing novel utterances from novel speakers, similar to the target speaker's voice. We describe the metrics used for evaluation, a baseline system consisting of unsupervised subword unit discovery plus a standard TTS system, and a topline TTS using gold phoneme transcriptions. We present an overview of the 19 submitted systems from 11 teams and discuss the main results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge