Xinmei Huang
LLMIdxAdvis: Resource-Efficient Index Advisor Utilizing Large Language Model
Mar 10, 2025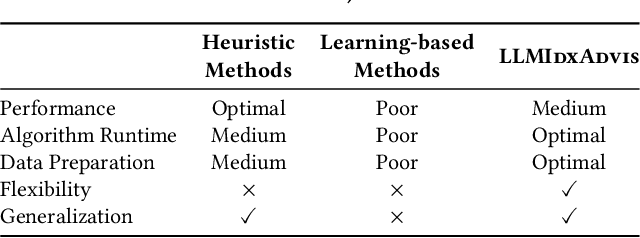
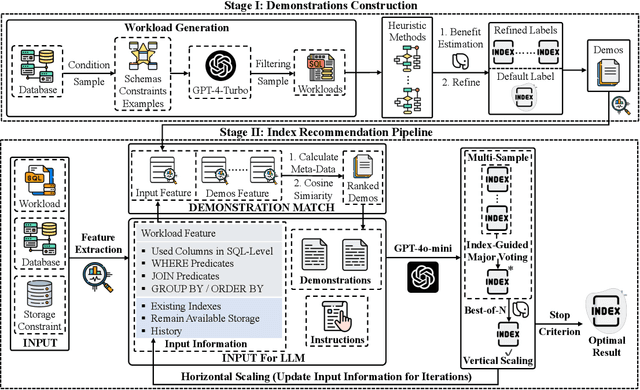

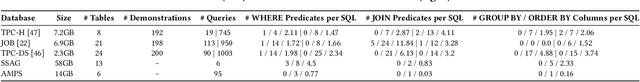
Abstract:Index recommendation is essential for improving query performance in database management systems (DBMSs) through creating an optimal set of indexes under specific constraints. Traditional methods, such as heuristic and learning-based approaches, are effective but face challenges like lengthy recommendation time, resource-intensive training, and poor generalization across different workloads and database schemas. To address these issues, we propose LLMIdxAdvis, a resource-efficient index advisor that uses large language models (LLMs) without extensive fine-tuning. LLMIdxAdvis frames index recommendation as a sequence-to-sequence task, taking target workload, storage constraint, and corresponding database environment as input, and directly outputting recommended indexes. It constructs a high-quality demonstration pool offline, using GPT-4-Turbo to synthesize diverse SQL queries and applying integrated heuristic methods to collect both default and refined labels. During recommendation, these demonstrations are ranked to inject database expertise via in-context learning. Additionally, LLMIdxAdvis extracts workload features involving specific column statistical information to strengthen LLM's understanding, and introduces a novel inference scaling strategy combining vertical scaling (via ''Index-Guided Major Voting'' and Best-of-N) and horizontal scaling (through iterative ''self-optimization'' with database feedback) to enhance reliability. Experiments on 3 OLAP and 2 real-world benchmarks reveal that LLMIdxAdvis delivers competitive index recommendation with reduced runtime, and generalizes effectively across different workloads and database schemas.
OmniSQL: Synthesizing High-quality Text-to-SQL Data at Scale
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Text-to-SQL, the task of translating natural language questions into SQL queries, plays a crucial role in enabling non-experts to interact with databases. While recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced text-to-SQL performance, existing approaches face notable limitations in real-world text-to-SQL applications. Prompting-based methods often depend on closed-source LLMs, which are expensive, raise privacy concerns, and lack customization. Fine-tuning-based methods, on the other hand, suffer from poor generalizability due to the limited coverage of publicly available training data. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel and scalable text-to-SQL data synthesis framework for automatically synthesizing large-scale, high-quality, and diverse datasets without extensive human intervention. Using this framework, we introduce SynSQL-2.5M, the first million-scale text-to-SQL dataset, containing 2.5 million samples spanning over 16,000 synthetic databases. Each sample includes a database, SQL query, natural language question, and chain-of-thought (CoT) solution. Leveraging SynSQL-2.5M, we develop OmniSQL, a powerful open-source text-to-SQL model available in three sizes: 7B, 14B, and 32B. Extensive evaluations across nine datasets demonstrate that OmniSQL achieves state-of-the-art performance, matching or surpassing leading closed-source and open-source LLMs, including GPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3, despite its smaller size. We release all code, datasets, and models to support further research.
LLMTune: Accelerate Database Knob Tuning with Large Language Models
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Database knob tuning is a critical challenge in the database community, aiming to optimize knob values to enhance database performance for specific workloads. DBMS often feature hundreds of tunable knobs, posing a significant challenge for DBAs to recommend optimal configurations. Consequently, many machine learning-based tuning methods have been developed to automate this process. Despite the introduction of various optimizers, practical applications have unveiled a new problem: they typically require numerous workload runs to achieve satisfactory performance, a process that is both time-consuming and resource-intensive. This inefficiency largely stems from the optimal configuration often being substantially different from the default setting, necessitating multiple iterations during tuning. Recognizing this, we argue that an effective starting point could significantly reduce redundant exploration in less efficient areas, thereby potentially speeding up the tuning process for the optimizers. Based on this assumption, we introduce LLMTune, a large language model-based configuration generator designed to produce an initial, high-quality configuration for new workloads. These generated configurations can then serve as starting points for various base optimizers, accelerating their tuning processes. To obtain training data for LLMTune's supervised fine-tuning, we have devised a new automatic data generation framework capable of efficiently creating a large number of <workload, configuration> pairs. We have conducted thorough experiments to evaluate LLMTune's effectiveness with different workloads, such as TPC-H and JOB. In comparison to leading methods, LLMTune demonstrates a quicker ability to identify superior configurations. For instance, with the challenging TPC-H workload, our LLMTune achieves a significant 15.6x speed-up ratio in finding the best-performing configurations.
Chain of Thought Prompting Elicits Knowledge Augmentation
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:The knowledge-augmented deep learning paradigm refers to a paradigm in which domain knowledge is identified and integrated into deep models. Conventional methods typically employ task-specific approaches to gather external knowledge from various sources. In contrast, large language models are extensively pre-trained and can serve as a comprehensive source of external knowledge. In this paper, we propose CoT-KA, a Chain-of-Thought-based method that augments knowledge for deep learning. CoT-KA avoids the need for additional knowledge retrieval or knowledge reasoning models, as required in conventional augmentation methods. Our results demonstrate that CoT-KA outperforms both pure CoT-based methods and the non-augmented method across the majority of eleven publicly available benchmarks for various reasoning tasks.
FC-KBQA: A Fine-to-Coarse Composition Framework for Knowledge Base Question Answering
Jun 26, 2023



Abstract:The generalization problem on KBQA has drawn considerable attention. Existing research suffers from the generalization issue brought by the entanglement in the coarse-grained modeling of the logical expression, or inexecutability issues due to the fine-grained modeling of disconnected classes and relations in real KBs. We propose a Fine-to-Coarse Composition framework for KBQA (FC-KBQA) to both ensure the generalization ability and executability of the logical expression. The main idea of FC-KBQA is to extract relevant fine-grained knowledge components from KB and reformulate them into middle-grained knowledge pairs for generating the final logical expressions. FC-KBQA derives new state-of-the-art performance on GrailQA and WebQSP, and runs 4 times faster than the baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge