Xingzhuo Guo
Consistent World Models via Foresight Diffusion
May 22, 2025Abstract:Diffusion and flow-based models have enabled significant progress in generation tasks across various modalities and have recently found applications in world modeling. However, unlike typical generation tasks that encourage sample diversity, world models entail different sources of uncertainty and require consistent samples aligned with the ground-truth trajectory, which is a limitation we empirically observe in diffusion models. We argue that a key bottleneck in learning consistent diffusion-based world models lies in the suboptimal predictive ability, which we attribute to the entanglement of condition understanding and target denoising within shared architectures and co-training schemes. To address this, we propose Foresight Diffusion (ForeDiff), a diffusion-based world modeling framework that enhances consistency by decoupling condition understanding from target denoising. ForeDiff incorporates a separate deterministic predictive stream to process conditioning inputs independently of the denoising stream, and further leverages a pretrained predictor to extract informative representations that guide generation. Extensive experiments on robot video prediction and scientific spatiotemporal forecasting show that ForeDiff improves both predictive accuracy and sample consistency over strong baselines, offering a promising direction for diffusion-based world models.
Dynamical Diffusion: Learning Temporal Dynamics with Diffusion Models
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as powerful generative frameworks by progressively adding noise to data through a forward process and then reversing this process to generate realistic samples. While these models have achieved strong performance across various tasks and modalities, their application to temporal predictive learning remains underexplored. Existing approaches treat predictive learning as a conditional generation problem, but often fail to fully exploit the temporal dynamics inherent in the data, leading to challenges in generating temporally coherent sequences. To address this, we introduce Dynamical Diffusion (DyDiff), a theoretically sound framework that incorporates temporally aware forward and reverse processes. Dynamical Diffusion explicitly models temporal transitions at each diffusion step, establishing dependencies on preceding states to better capture temporal dynamics. Through the reparameterization trick, Dynamical Diffusion achieves efficient training and inference similar to any standard diffusion model. Extensive experiments across scientific spatiotemporal forecasting, video prediction, and time series forecasting demonstrate that Dynamical Diffusion consistently improves performance in temporal predictive tasks, filling a crucial gap in existing methodologies. Code is available at this repository: https://github.com/thuml/dynamical-diffusion.
Diffusion Tuning: Transferring Diffusion Models via Chain of Forgetting
Jun 02, 2024
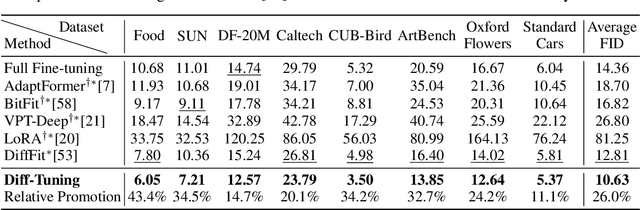
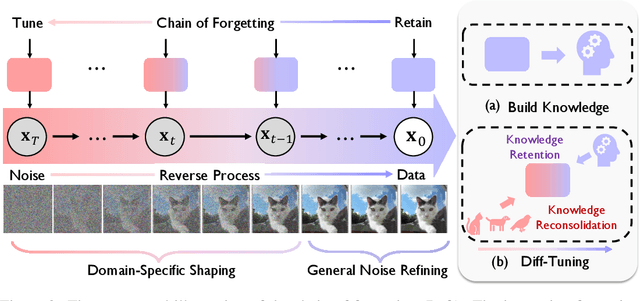
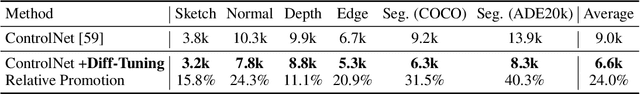
Abstract:Diffusion models have significantly advanced the field of generative modeling. However, training a diffusion model is computationally expensive, creating a pressing need to adapt off-the-shelf diffusion models for downstream generation tasks. Current fine-tuning methods focus on parameter-efficient transfer learning but overlook the fundamental transfer characteristics of diffusion models. In this paper, we investigate the transferability of diffusion models and observe a monotonous chain of forgetting trend of transferability along the reverse process. Based on this observation and novel theoretical insights, we present Diff-Tuning, a frustratingly simple transfer approach that leverages the chain of forgetting tendency. Diff-Tuning encourages the fine-tuned model to retain the pre-trained knowledge at the end of the denoising chain close to the generated data while discarding the other noise side. We conduct comprehensive experiments to evaluate Diff-Tuning, including the transfer of pre-trained Diffusion Transformer models to eight downstream generations and the adaptation of Stable Diffusion to five control conditions with ControlNet. Diff-Tuning achieves a 26% improvement over standard fine-tuning and enhances the convergence speed of ControlNet by 24%. Notably, parameter-efficient transfer learning techniques for diffusion models can also benefit from Diff-Tuning.
CogDPM: Diffusion Probabilistic Models via Cognitive Predictive Coding
May 03, 2024Abstract:Predictive Coding (PC) is a theoretical framework in cognitive science suggesting that the human brain processes cognition through spatiotemporal prediction of the visual world. Existing studies have developed spatiotemporal prediction neural networks based on the PC theory, emulating its two core mechanisms: Correcting predictions from residuals and hierarchical learning. However, these models do not show the enhancement of prediction skills on real-world forecasting tasks and ignore the Precision Weighting mechanism of PC theory. The precision weighting mechanism posits that the brain allocates more attention to signals with lower precision, contributing to the cognitive ability of human brains. This work introduces the Cognitive Diffusion Probabilistic Models (CogDPM), which demonstrate the connection between diffusion probabilistic models and PC theory. CogDPM features a precision estimation method based on the hierarchical sampling capabilities of diffusion models and weight the guidance with precision weights estimated by the inherent property of diffusion models. We experimentally show that the precision weights effectively estimate the data predictability. We apply CogDPM to real-world prediction tasks using the United Kindom precipitation and ERA surface wind datasets. Our results demonstrate that CogDPM outperforms both existing domain-specific operational models and general deep prediction models by providing more proficient forecasting.
On the Embedding Collapse when Scaling up Recommendation Models
Oct 06, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in deep foundation models have led to a promising trend of developing large recommendation models to leverage vast amounts of available data. However, we experiment to scale up existing recommendation models and observe that the enlarged models do not improve satisfactorily. In this context, we investigate the embedding layers of enlarged models and identify a phenomenon of embedding collapse, which ultimately hinders scalability, wherein the embedding matrix tends to reside in a low-dimensional subspace. Through empirical and theoretical analysis, we demonstrate that the feature interaction module specific to recommendation models has a two-sided effect. On the one hand, the interaction restricts embedding learning when interacting with collapsed embeddings, exacerbating the collapse issue. On the other hand, feature interaction is crucial in mitigating the fitting of spurious features, thereby improving scalability. Based on this analysis, we propose a simple yet effective multi-embedding design incorporating embedding-set-specific interaction modules to capture diverse patterns and reduce collapse. Extensive experiments demonstrate that this proposed design provides consistent scalability for various recommendation models.
Decoupled Training: Return of Frustratingly Easy Multi-Domain Learning
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:Multi-domain learning (MDL) aims to train a model with minimal average risk across multiple overlapping but non-identical domains. To tackle the challenges of dataset bias and domain domination, numerous MDL approaches have been proposed from the perspectives of seeking commonalities by aligning distributions to reduce domain gap or reserving differences by implementing domain-specific towers, gates, and even experts. MDL models are becoming more and more complex with sophisticated network architectures or loss functions, introducing extra parameters and enlarging computation costs. In this paper, we propose a frustratingly easy and hyperparameter-free multi-domain learning method named Decoupled Training(D-Train). D-Train is a tri-phase general-to-specific training strategy that first pre-trains on all domains to warm up a root model, then post-trains on each domain by splitting into multi heads, and finally fine-tunes the heads by fixing the backbone, enabling decouple training to achieve domain independence. Despite its extraordinary simplicity and efficiency, D-Train performs remarkably well in extensive evaluations of various datasets from standard benchmarks to applications of satellite imagery and recommender systems.
CLIPood: Generalizing CLIP to Out-of-Distributions
Feb 02, 2023



Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization, where the model needs to handle distribution shifts from training, is a major challenge of machine learning. Recently, contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) models have shown impressive zero-shot ability, revealing a promising path toward OOD generalization. However, to boost upon zero-shot performance, further adaptation of CLIP on downstream tasks is indispensable but undesirably degrades OOD generalization ability. In this paper, we aim at generalizing CLIP to out-of-distribution test data on downstream tasks. Beyond the two canonical OOD situations, domain shift and open class, we tackle a more general but difficult in-the-wild setting where both OOD situations may occur on the unseen test data. We propose CLIPood, a simple fine-tuning method that can adapt CLIP models to all OOD situations. To exploit semantic relations between classes from the text modality, CLIPood introduces a new training objective, margin metric softmax (MMS), with class adaptive margins for fine-tuning. Moreover, to incorporate both the pre-trained zero-shot model and the fine-tuned task-adaptive model, CLIPood proposes a new Beta moving average (BMA) to maintain a temporal ensemble according to Beta distribution. Experiments on diverse datasets with different OOD scenarios show that CLIPood consistently outperforms existing generalization techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge