Xiaoxiao Hu
An Exceptional Dataset For Rare Pancreatic Tumor Segmentation
Jan 29, 2025Abstract:Pancreatic NEuroendocrine Tumors (pNETs) are very rare endocrine neoplasms that account for less than 5% of all pancreatic malignancies, with an incidence of only 1-1.5 cases per 100,000. Early detection of pNETs is critical for improving patient survival, but the rarity of pNETs makes segmenting them from CT a very challenging problem. So far, there has not been a dataset specifically for pNETs available to researchers. To address this issue, we propose a pNETs dataset, a well-annotated Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography (CECT) dataset focused exclusively on Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors, containing data from 469 patients. This is the first dataset solely dedicated to pNETs, distinguishing it from previous collections. Additionally, we provide the baseline detection networks with a new slice-wise weight loss function designed for the UNet-based model, improving the overall pNET segmentation performance. We hope that our dataset can enhance the understanding and diagnosis of pNET Tumors within the medical community, facilitate the development of more accurate diagnostic tools, and ultimately improve patient outcomes and advance the field of oncology.
ScreenMark: Watermarking Arbitrary Visual Content on Screen
Sep 05, 2024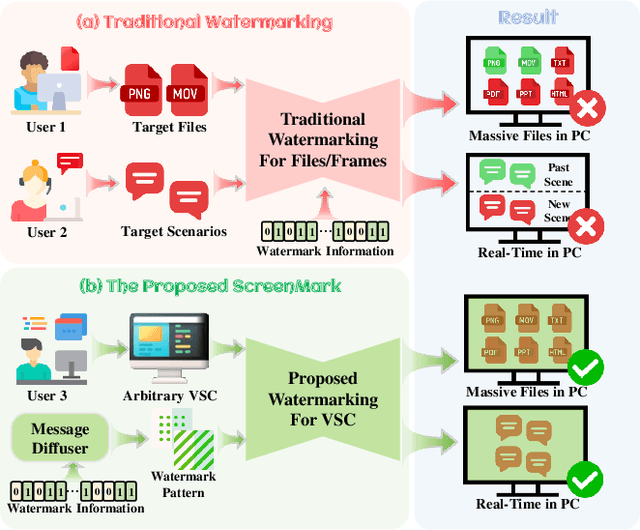
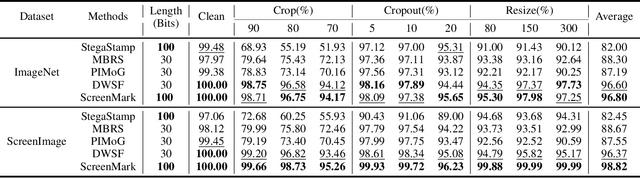
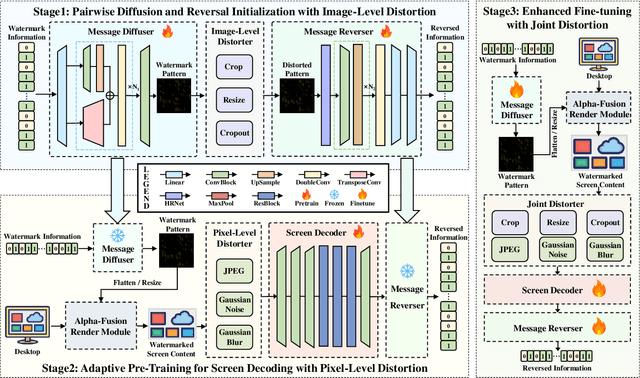
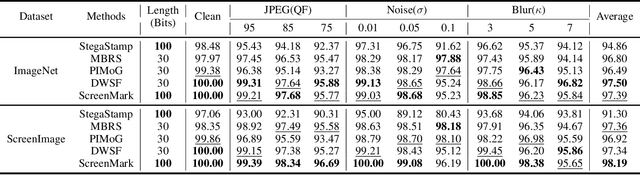
Abstract:Digital watermarking has demonstrated its effectiveness in protecting multimedia content. However, existing watermarking are predominantly tailored for specific media types, rendering them less effective for the protection of content displayed on computer screens, which is often multimodal and dynamic. Visual Screen Content (VSC), is particularly susceptible to theft and leakage via screenshots, a vulnerability that current watermarking methods fail to adequately address.To tackle these challenges, we propose ScreenMark, a robust and practical watermarking method designed specifically for arbitrary VSC protection. ScreenMark utilizes a three-stage progressive watermarking framework. Initially, inspired by diffusion principles, we initialize the mutual transformation between regular watermark information and irregular watermark patterns. Subsequently, these patterns are integrated with screen content using a pre-multiplication alpha blending technique, supported by a pre-trained screen decoder for accurate watermark retrieval. The progressively complex distorter enhances the robustness of the watermark in real-world screenshot scenarios. Finally, the model undergoes fine-tuning guided by a joint-level distorter to ensure optimal performance.To validate the effectiveness of ScreenMark, we compiled a dataset comprising 100,000 screenshots from various devices and resolutions. Extensive experiments across different datasets confirm the method's superior robustness, imperceptibility, and practical applicability.
From Covert Hiding to Visual Editing: Robust Generative Video Steganography
Jan 01, 2024



Abstract:Traditional video steganography methods are based on modifying the covert space for embedding, whereas we propose an innovative approach that embeds secret message within semantic feature for steganography during the video editing process. Although existing traditional video steganography methods display a certain level of security and embedding capacity, they lack adequate robustness against common distortions in online social networks (OSNs). In this paper, we introduce an end-to-end robust generative video steganography network (RoGVS), which achieves visual editing by modifying semantic feature of videos to embed secret message. We employ face-swapping scenario to showcase the visual editing effects. We first design a secret message embedding module to adaptively hide secret message into the semantic feature of videos. Extensive experiments display that the proposed RoGVS method applied to facial video datasets demonstrate its superiority over existing video and image steganography techniques in terms of both robustness and capacity.
The Color Clifford Hardy Signal: Application to Color Edge Detection and Optical Flow
Aug 12, 2023
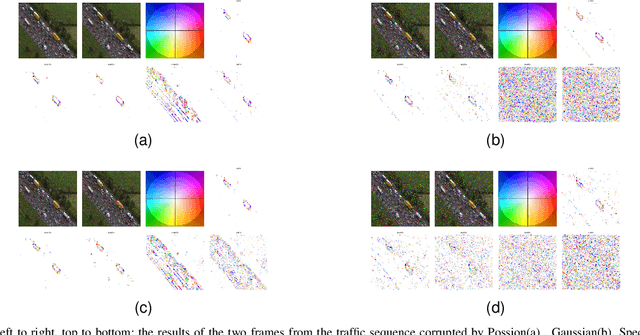


Abstract:This paper introduces the idea of the color Clifford Hardy signal, which can be used to process color images. As a complex analytic function's high-dimensional analogue, the color Clifford Hardy signal inherits many desirable qualities of analyticity. A crucial tool for getting the color and structural data is the local feature representation of a color image in the color Clifford Hardy signal. By looking at the extended Cauchy-Riemann equations in the high-dimensional space, it is possible to see the connection between the different parts of the color Clifford Hardy signal. Based on the distinctive and important local amplitude and local phase generated by the color Clifford Hardy signal, we propose five methods to identify the edges of color images with relation to a certain color. To prove the superiority of the offered methodologies, numerous comparative studies employing image quality assessment criteria are used. Specifically by using the multi-scale structure of the color Clifford Hardy signal, the proposed approaches are resistant to a variety of noises. In addition, a color optical flow detection method with anti-noise ability is provided as an example of application.
DRAW: Defending Camera-shooted RAW against Image Manipulation
Jul 31, 2023



Abstract:RAW files are the initial measurement of scene radiance widely used in most cameras, and the ubiquitously-used RGB images are converted from RAW data through Image Signal Processing (ISP) pipelines. Nowadays, digital images are risky of being nefariously manipulated. Inspired by the fact that innate immunity is the first line of body defense, we propose DRAW, a novel scheme of defending images against manipulation by protecting their sources, i.e., camera-shooted RAWs. Specifically, we design a lightweight Multi-frequency Partial Fusion Network (MPF-Net) friendly to devices with limited computing resources by frequency learning and partial feature fusion. It introduces invisible watermarks as protective signal into the RAW data. The protection capability can not only be transferred into the rendered RGB images regardless of the applied ISP pipeline, but also is resilient to post-processing operations such as blurring or compression. Once the image is manipulated, we can accurately identify the forged areas with a localization network. Extensive experiments on several famous RAW datasets, e.g., RAISE, FiveK and SIDD, indicate the effectiveness of our method. We hope that this technique can be used in future cameras as an option for image protection, which could effectively restrict image manipulation at the source.
No way to crop: On robust image crop localization
Oct 12, 2021



Abstract:Previous image forensics schemes for crop detection are only limited on predicting whether an image has been cropped. This paper presents a novel scheme for image crop localization using robust watermarking. We further extend our scheme to detect tampering attack on the attacked image. We demonstrate that our scheme is the first to provide high-accuracy and robust image crop localization. Besides, the accuracy of tamper detection is comparable to many state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge