Xi Gu
Modeling Users' Behavior Sequences with Hierarchical Explainable Network for Cross-domain Fraud Detection
Jan 04, 2022



Abstract:With the explosive growth of the e-commerce industry, detecting online transaction fraud in real-world applications has become increasingly important to the development of e-commerce platforms. The sequential behavior history of users provides useful information in differentiating fraudulent payments from regular ones. Recently, some approaches have been proposed to solve this sequence-based fraud detection problem. However, these methods usually suffer from two problems: the prediction results are difficult to explain and the exploitation of the internal information of behaviors is insufficient. To tackle the above two problems, we propose a Hierarchical Explainable Network (HEN) to model users' behavior sequences, which could not only improve the performance of fraud detection but also make the inference process interpretable. Meanwhile, as e-commerce business expands to new domains, e.g., new countries or new markets, one major problem for modeling user behavior in fraud detection systems is the limitation of data collection, e.g., very few data/labels available. Thus, in this paper, we further propose a transfer framework to tackle the cross-domain fraud detection problem, which aims to transfer knowledge from existing domains (source domains) with enough and mature data to improve the performance in the new domain (target domain). Our proposed method is a general transfer framework that could not only be applied upon HEN but also various existing models in the Embedding & MLP paradigm. Based on 90 transfer task experiments, we also demonstrate that our transfer framework could not only contribute to the cross-domain fraud detection task with HEN, but also be universal and expandable for various existing models.
Neural Hierarchical Factorization Machines for User's Event Sequence Analysis
Dec 31, 2021



Abstract:Many prediction tasks of real-world applications need to model multi-order feature interactions in user's event sequence for better detection performance. However, existing popular solutions usually suffer two key issues: 1) only focusing on feature interactions and failing to capture the sequence influence; 2) only focusing on sequence information, but ignoring internal feature relations of each event, thus failing to extract a better event representation. In this paper, we consider a two-level structure for capturing the hierarchical information over user's event sequence: 1) learning effective feature interactions based event representation; 2) modeling the sequence representation of user's historical events. Experimental results on both industrial and public datasets clearly demonstrate that our model achieves significantly better performance compared with state-of-the-art baselines.
A Light-Weight Object Detection Framework with FPA Module for Optical Remote Sensing Imagery
Sep 07, 2020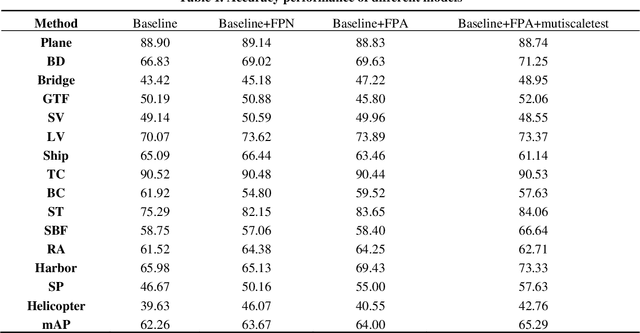
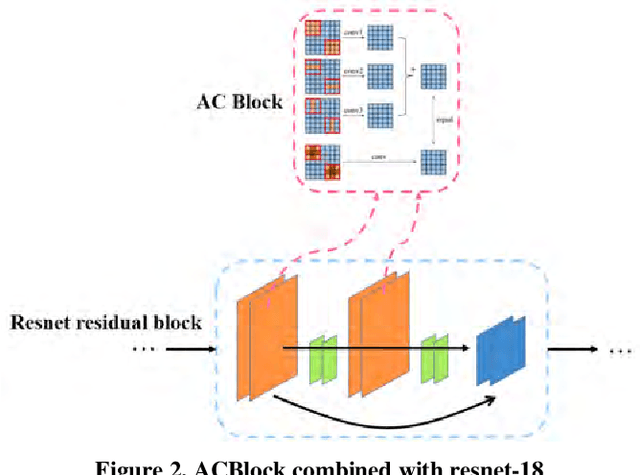
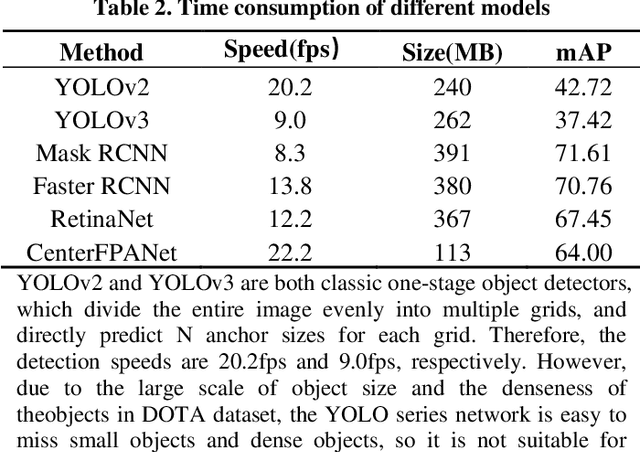
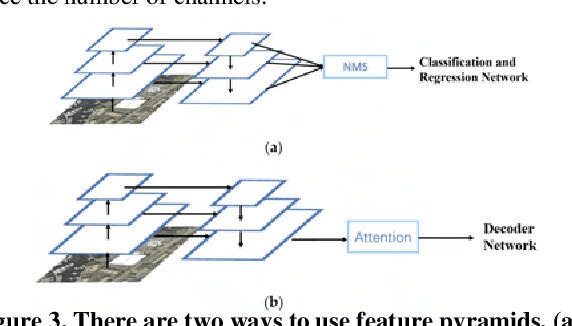
Abstract:With the development of remote sensing technology, the acquisition of remote sensing images is easier and easier, which provides sufficient data resources for the task of detecting remote sensing objects. However, how to detect objects quickly and accurately from many complex optical remote sensing images is a challenging hot issue. In this paper, we propose an efficient anchor free object detector, CenterFPANet. To pursue speed, we use a lightweight backbone and introduce the asymmetric revolution block. To improve the accuracy, we designed the FPA module, which links the feature maps of different levels, and introduces the attention mechanism to dynamically adjust the weights of each level of feature maps, which solves the problem of detection difficulty caused by large size range of remote sensing objects. This strategy can improve the accuracy of remote sensing image object detection without reducing the detection speed. On the DOTA dataset, CenterFPANet mAP is 64.00%, and FPS is 22.2, which is close to the accuracy of the anchor-based methods currently used and much faster than them. Compared with Faster RCNN, mAP is 6.76% lower but 60.87% faster. All in all, CenterFPANet achieves a balance between speed and accuracy in large-scale optical remote sensing object detection.
Differentiating Features for Scene Segmentation Based on Dedicated Attention Mechanisms
Nov 19, 2019



Abstract:Semantic segmentation is a challenge in scene parsing. It requires both context information and rich spatial information. In this paper, we differentiate features for scene segmentation based on dedicated attention mechanisms (DF-DAM), and two attention modules are proposed to optimize the high-level and low-level features in the encoder, respectively. Specifically, we use the high-level and low-level features of ResNet as the source of context information and spatial information, respectively, and optimize them with attention fusion module and 2D position attention module, respectively. For attention fusion module, we adopt dual channel weight to selectively adjust the channel map for the highest two stage features of ResNet, and fuse them to get context information. For 2D position attention module, we use the context information obtained by attention fusion module to assist the selection of the lowest-stage features of ResNet as supplementary spatial information. Finally, the two sets of information obtained by the two modules are simply fused to obtain the prediction. We evaluate our approach on Cityscapes and PASCAL VOC 2012 datasets. In particular, there aren't complicated and redundant processing modules in our architecture, which greatly reduces the complexity, and we achieving 82.3% Mean IoU on PASCAL VOC 2012 test dataset without pre-training on MS-COCO dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge