Wuyue Lu
Learning Priors for Non Rigid SfM from Casual Videos
Apr 10, 2024Abstract:We tackle the long-standing challenge of reconstructing 3D structures and camera positions from videos. The problem is particularly hard when objects are transformed in a non-rigid way. Current approaches to this problem make unrealistic assumptions or require a long optimization time. We present TracksTo4D, a novel deep learning-based approach that enables inferring 3D structure and camera positions from dynamic content originating from in-the-wild videos using a single feed-forward pass on a sparse point track matrix. To achieve this, we leverage recent advances in 2D point tracking and design an equivariant neural architecture tailored for directly processing 2D point tracks by leveraging their symmetries. TracksTo4D is trained on a dataset of in-the-wild videos utilizing only the 2D point tracks extracted from the videos, without any 3D supervision. Our experiments demonstrate that TracksTo4D generalizes well to unseen videos of unseen semantic categories at inference time, producing equivalent results to state-of-the-art methods while significantly reducing the runtime compared to other baselines.
SlotDiffusion: Object-Centric Generative Modeling with Diffusion Models
May 18, 2023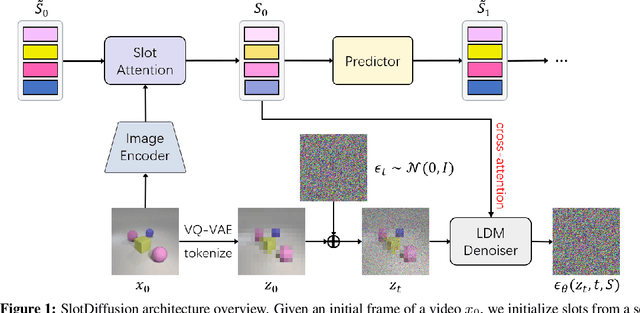
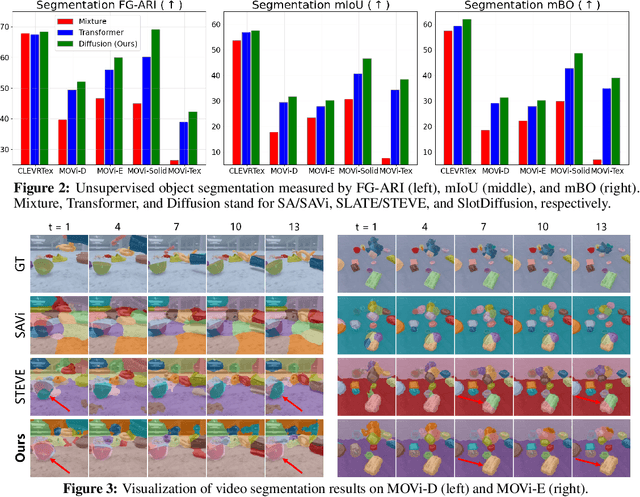
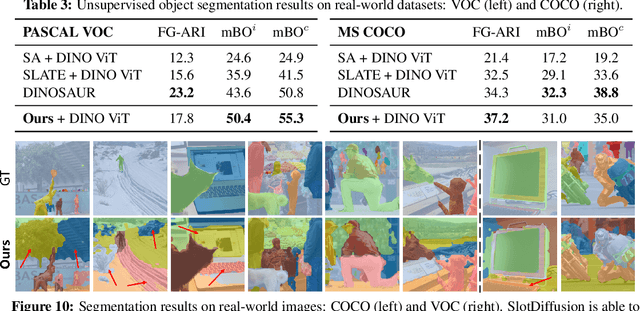
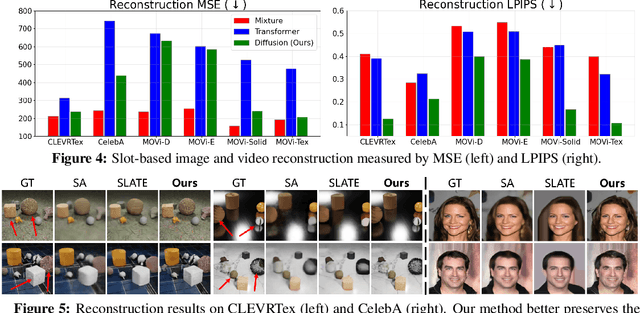
Abstract:Object-centric learning aims to represent visual data with a set of object entities (a.k.a. slots), providing structured representations that enable systematic generalization. Leveraging advanced architectures like Transformers, recent approaches have made significant progress in unsupervised object discovery. In addition, slot-based representations hold great potential for generative modeling, such as controllable image generation and object manipulation in image editing. However, current slot-based methods often produce blurry images and distorted objects, exhibiting poor generative modeling capabilities. In this paper, we focus on improving slot-to-image decoding, a crucial aspect for high-quality visual generation. We introduce SlotDiffusion -- an object-centric Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) designed for both image and video data. Thanks to the powerful modeling capacity of LDMs, SlotDiffusion surpasses previous slot models in unsupervised object segmentation and visual generation across six datasets. Furthermore, our learned object features can be utilized by existing object-centric dynamics models, improving video prediction quality and downstream temporal reasoning tasks. Finally, we demonstrate the scalability of SlotDiffusion to unconstrained real-world datasets such as PASCAL VOC and COCO, when integrated with self-supervised pre-trained image encoders.
Neuromuscular Control of the Face-Head-Neck Biomechanical Complex With Learning-Based Expression Transfer From Images and Videos
Nov 12, 2021

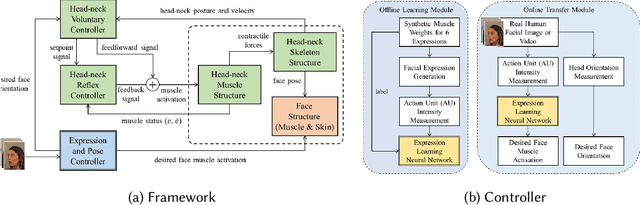
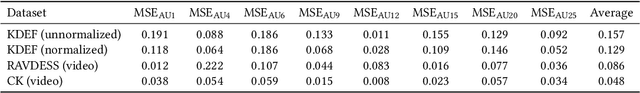
Abstract:The transfer of facial expressions from people to 3D face models is a classic computer graphics problem. In this paper, we present a novel, learning-based approach to transferring facial expressions and head movements from images and videos to a biomechanical model of the face-head-neck complex. Leveraging the Facial Action Coding System (FACS) as an intermediate representation of the expression space, we train a deep neural network to take in FACS Action Units (AUs) and output suitable facial muscle and jaw activation signals for the musculoskeletal model. Through biomechanical simulation, the activations deform the facial soft tissues, thereby transferring the expression to the model. Our approach has advantages over previous approaches. First, the facial expressions are anatomically consistent as our biomechanical model emulates the relevant anatomy of the face, head, and neck. Second, by training the neural network using data generated from the biomechanical model itself, we eliminate the manual effort of data collection for expression transfer. The success of our approach is demonstrated through experiments involving the transfer onto our face-head-neck model of facial expressions and head poses from a range of facial images and videos.
Deep Active Lesion Segmentation
Aug 21, 2019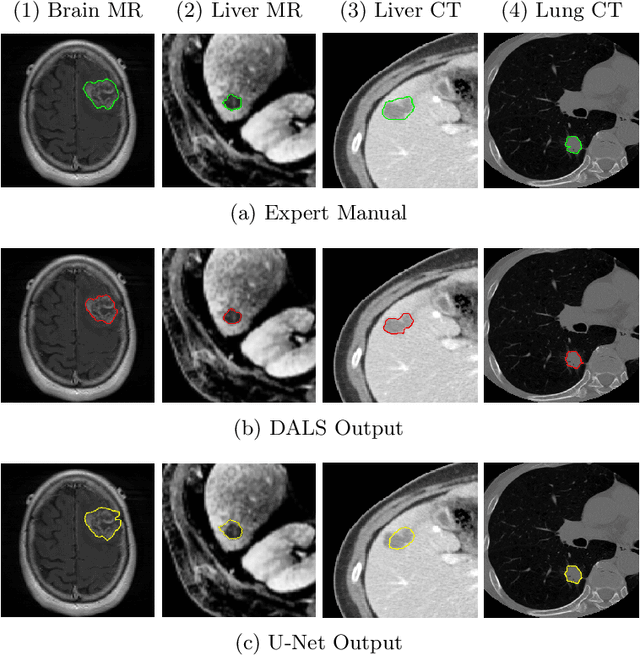
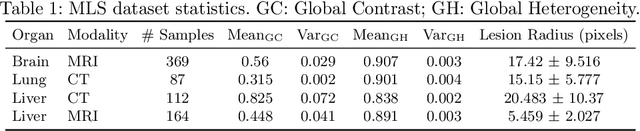
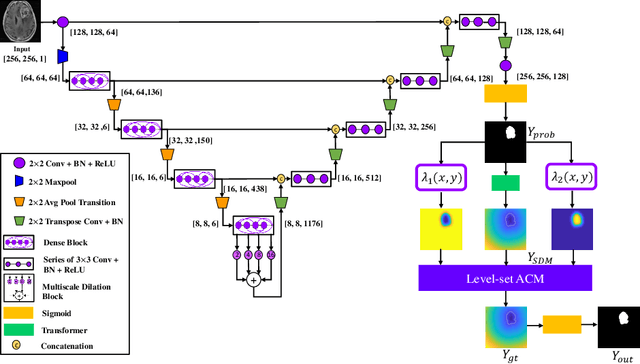
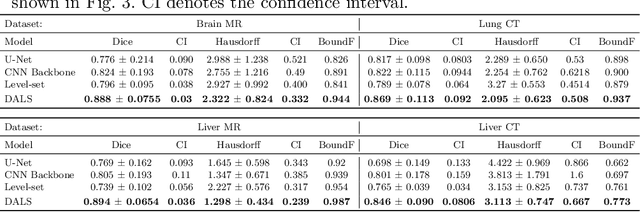
Abstract:Lesion segmentation is an important problem in computer-assisted diagnosis that remains challenging due to the prevalence of low contrast, irregular boundaries that are unamenable to shape priors. We introduce Deep Active Lesion Segmentation (DALS), a fully automated segmentation framework for that leverages the powerful nonlinear feature extraction abilities of fully Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and the precise boundary delineation abilities of Active Contour Models (ACMs). Our DALS framework benefits from an improved level-set ACM formulation with a per-pixel-parameterized energy functional and a novel multiscale encoder-decoder CNN that learns an initialization probability map along with parameter maps for the ACM. We evaluate our lesion segmentation model on a new Multiorgan Lesion Segmentation (MLS) dataset that contains images of various organs, including brain, liver, and lung, across different imaging modalities---MR and CT. Our results demonstrate favorable performance compared to competing methods, especially for small training datasets.
* Accepted to Machine Learning in Medical Imaging (MLMI 2019)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge