William R. Jarnagin
Comparing the Effects of Persistence Barcodes Aggregation and Feature Concatenation on Medical Imaging
May 29, 2025



Abstract:In medical image analysis, feature engineering plays an important role in the design and performance of machine learning models. Persistent homology (PH), from the field of topological data analysis (TDA), demonstrates robustness and stability to data perturbations and addresses the limitation from traditional feature extraction approaches where a small change in input results in a large change in feature representation. Using PH, we store persistent topological and geometrical features in the form of the persistence barcode whereby large bars represent global topological features and small bars encapsulate geometrical information of the data. When multiple barcodes are computed from 2D or 3D medical images, two approaches can be used to construct the final topological feature vector in each dimension: aggregating persistence barcodes followed by featurization or concatenating topological feature vectors derived from each barcode. In this study, we conduct a comprehensive analysis across diverse medical imaging datasets to compare the effects of the two aforementioned approaches on the performance of classification models. The results of this analysis indicate that feature concatenation preserves detailed topological information from individual barcodes, yields better classification performance and is therefore a preferred approach when conducting similar experiments.
The Medical Segmentation Decathlon
Jun 10, 2021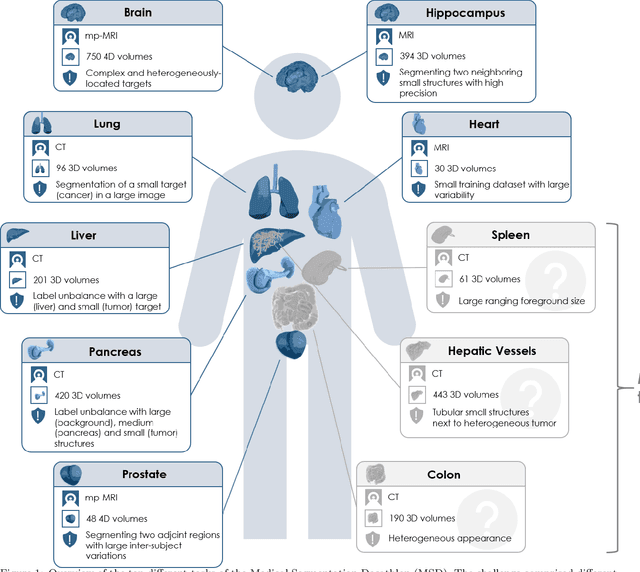
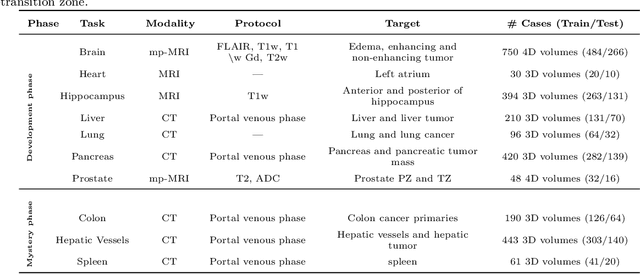
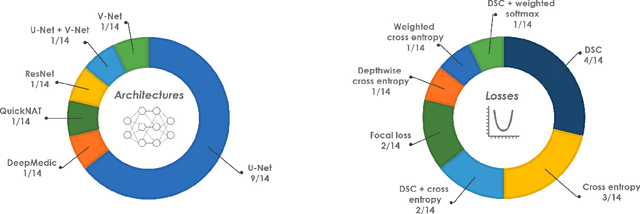
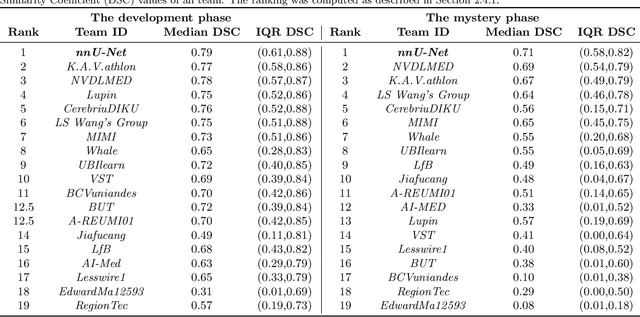
Abstract:International challenges have become the de facto standard for comparative assessment of image analysis algorithms given a specific task. Segmentation is so far the most widely investigated medical image processing task, but the various segmentation challenges have typically been organized in isolation, such that algorithm development was driven by the need to tackle a single specific clinical problem. We hypothesized that a method capable of performing well on multiple tasks will generalize well to a previously unseen task and potentially outperform a custom-designed solution. To investigate the hypothesis, we organized the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) - a biomedical image analysis challenge, in which algorithms compete in a multitude of both tasks and modalities. The underlying data set was designed to explore the axis of difficulties typically encountered when dealing with medical images, such as small data sets, unbalanced labels, multi-site data and small objects. The MSD challenge confirmed that algorithms with a consistent good performance on a set of tasks preserved their good average performance on a different set of previously unseen tasks. Moreover, by monitoring the MSD winner for two years, we found that this algorithm continued generalizing well to a wide range of other clinical problems, further confirming our hypothesis. Three main conclusions can be drawn from this study: (1) state-of-the-art image segmentation algorithms are mature, accurate, and generalize well when retrained on unseen tasks; (2) consistent algorithmic performance across multiple tasks is a strong surrogate of algorithmic generalizability; (3) the training of accurate AI segmentation models is now commoditized to non AI experts.
Towards Unsupervised Cancer Subtyping: Predicting Prognosis Using A Histologic Visual Dictionary
Mar 12, 2019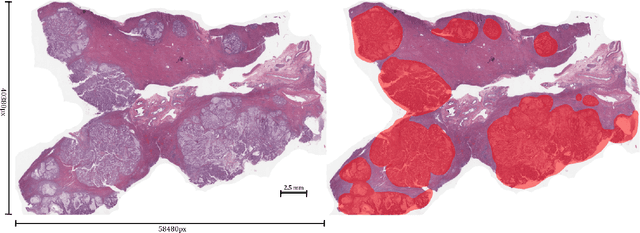
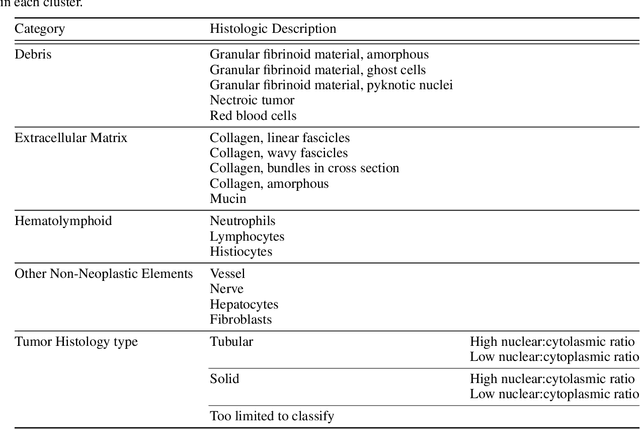
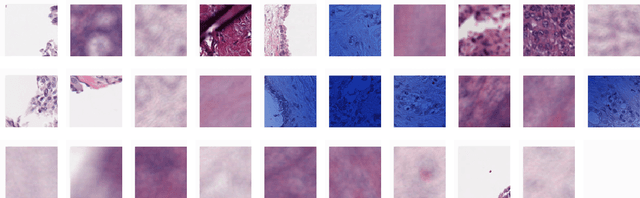
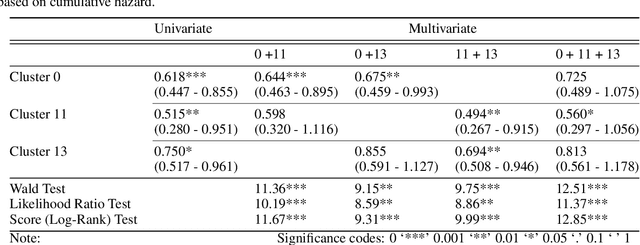
Abstract:Unlike common cancers, such as those of the prostate and breast, tumor grading in rare cancers is difficult and largely undefined because of small sample sizes, the sheer volume of time needed to undertake on such a task, and the inherent difficulty of extracting human-observed patterns. One of the most challenging examples is intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), a primary liver cancer arising from the biliary system, for which there is well-recognized tumor heterogeneity and no grading paradigm or prognostic biomarkers. In this paper, we propose a new unsupervised deep convolutional autoencoder-based clustering model that groups together cellular and structural morphologies of tumor in 246 ICC digitized whole slides, based on visual similarity. From this visual dictionary of histologic patterns, we use the clusters as covariates to train Cox-proportional hazard survival models. In univariate analysis, three clusters were significantly associated with recurrence-free survival. Combinations of these clusters were significant in multivariate analysis. In a multivariate analysis of all clusters, five showed significance to recurrence-free survival, however the overall model was not measured to be significant. Finally, a pathologist assigned clinical terminology to the significant clusters in the visual dictionary and found evidence supporting the hypothesis that collagen-enriched fibrosis plays a role in disease severity. These results offer insight into the future of cancer subtyping and show that computational pathology can contribute to disease prognostication, especially in rare cancers.
A large annotated medical image dataset for the development and evaluation of segmentation algorithms
Feb 25, 2019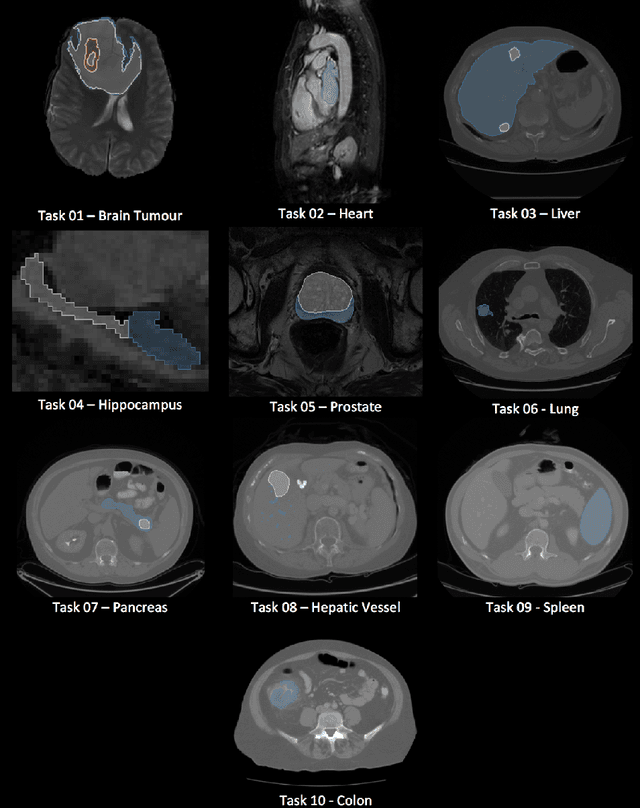

Abstract:Semantic segmentation of medical images aims to associate a pixel with a label in a medical image without human initialization. The success of semantic segmentation algorithms is contingent on the availability of high-quality imaging data with corresponding labels provided by experts. We sought to create a large collection of annotated medical image datasets of various clinically relevant anatomies available under open source license to facilitate the development of semantic segmentation algorithms. Such a resource would allow: 1) objective assessment of general-purpose segmentation methods through comprehensive benchmarking and 2) open and free access to medical image data for any researcher interested in the problem domain. Through a multi-institutional effort, we generated a large, curated dataset representative of several highly variable segmentation tasks that was used in a crowd-sourced challenge - the Medical Segmentation Decathlon held during the 2018 Medical Image Computing and Computer Aided Interventions Conference in Granada, Spain. Here, we describe these ten labeled image datasets so that these data may be effectively reused by the research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge