Wentao Tan
ChartMaster: Advancing Chart-to-Code Generation with Real-World Charts and Chart Similarity Reinforcement Learning
Aug 25, 2025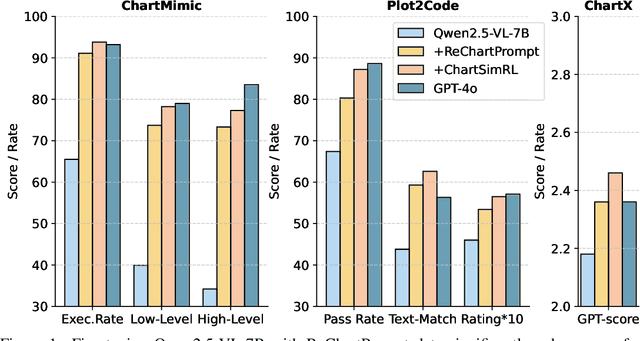

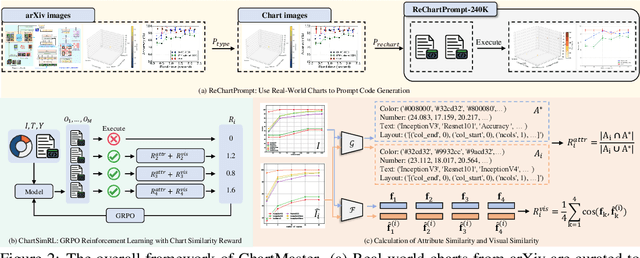

Abstract:The chart-to-code generation task requires MLLMs to convert chart images into executable code. This task faces two major challenges: limited data diversity and insufficient maintenance of visual consistency between generated and original charts during training. Existing datasets mainly rely on seed data to prompt GPT models for code generation, resulting in homogeneous samples. To address this, we propose ReChartPrompt, which leverages real-world, human-designed charts from arXiv papers as prompts instead of synthetic seeds. Using the diverse styles and rich content of arXiv charts, we construct ReChartPrompt-240K, a large-scale and highly diverse dataset. Another challenge is that although SFT effectively improve code understanding, it often fails to ensure that generated charts are visually consistent with the originals. To address this, we propose ChartSimRL, a GRPO-based reinforcement learning algorithm guided by a novel chart similarity reward. This reward consists of attribute similarity, which measures the overlap of chart attributes such as layout and color between the generated and original charts, and visual similarity, which assesses similarity in texture and other overall visual features using convolutional neural networks. Unlike traditional text-based rewards such as accuracy or format rewards, our reward considers the multimodal nature of the chart-to-code task and effectively enhances the model's ability to accurately reproduce charts. By integrating ReChartPrompt and ChartSimRL, we develop the ChartMaster model, which achieves state-of-the-art results among 7B-parameter models and even rivals GPT-4o on various chart-to-code generation benchmarks. All resources are available at https://github.com/WentaoTan/ChartMaster.
Modeling Thousands of Human Annotators for Generalizable Text-to-Image Person Re-identification
Mar 13, 2025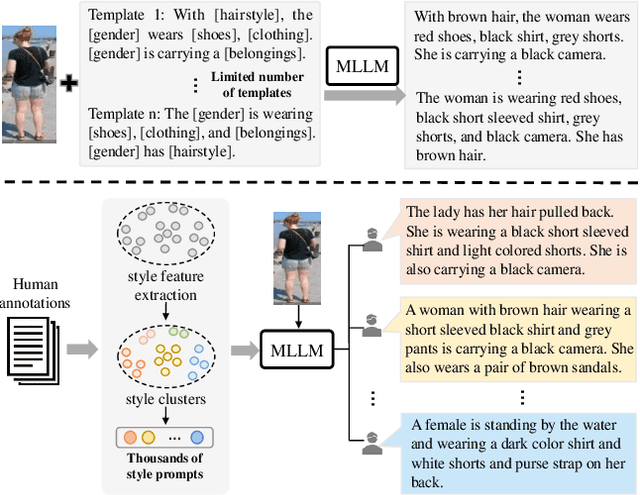
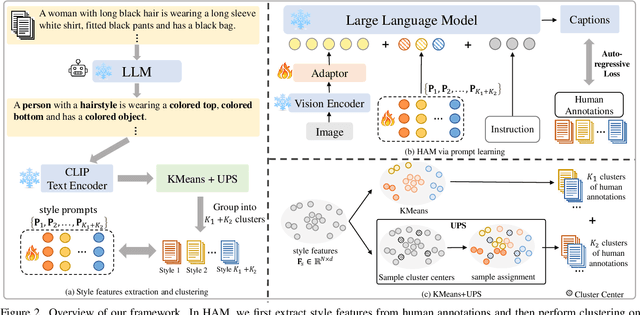
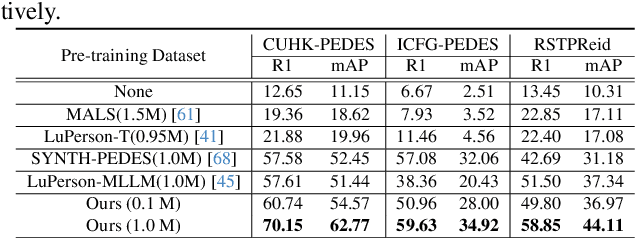
Abstract:Text-to-image person re-identification (ReID) aims to retrieve the images of an interested person based on textual descriptions. One main challenge for this task is the high cost in manually annotating large-scale databases, which affects the generalization ability of ReID models. Recent works handle this problem by leveraging Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to describe pedestrian images automatically. However, the captions produced by MLLMs lack diversity in description styles. To address this issue, we propose a Human Annotator Modeling (HAM) approach to enable MLLMs to mimic the description styles of thousands of human annotators. Specifically, we first extract style features from human textual descriptions and perform clustering on them. This allows us to group textual descriptions with similar styles into the same cluster. Then, we employ a prompt to represent each of these clusters and apply prompt learning to mimic the description styles of different human annotators. Furthermore, we define a style feature space and perform uniform sampling in this space to obtain more diverse clustering prototypes, which further enriches the diversity of the MLLM-generated captions. Finally, we adopt HAM to automatically annotate a massive-scale database for text-to-image ReID. Extensive experiments on this database demonstrate that it significantly improves the generalization ability of ReID models.
Beyond Human Data: Aligning Multimodal Large Language Models by Iterative Self-Evolution
Dec 20, 2024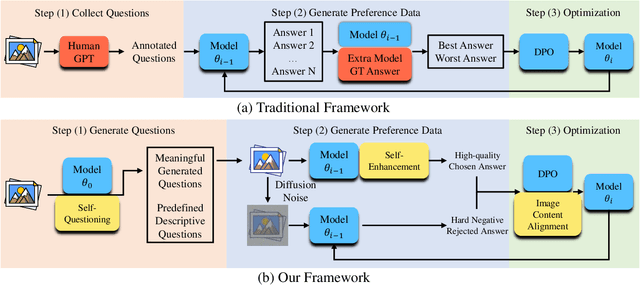

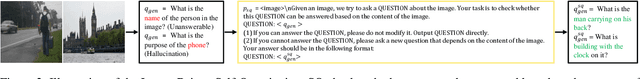

Abstract:Human preference alignment can greatly enhance Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), but collecting high-quality preference data is costly. A promising solution is the self-evolution strategy, where models are iteratively trained on data they generate. However, current techniques still rely on human- or GPT-annotated data and sometimes require additional models or ground truth answers. To address these issues, we propose a novel multimodal self-evolution framework that enables the model to autonomously generate high-quality questions and answers using only unannotated images. First, we implement an image-driven self-questioning mechanism, allowing the model to create and evaluate questions based on image content, regenerating them if they are irrelevant or unanswerable. This sets a strong foundation for answer generation. Second, we introduce an answer self-enhancement technique, starting with image captioning to improve answer quality. We also use corrupted images to generate rejected answers, forming distinct preference pairs for optimization. Finally, we incorporate an image content alignment loss function alongside Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) loss to reduce hallucinations, ensuring the model focuses on image content. Experiments show that our framework performs competitively with methods using external information, offering a more efficient and scalable approach to MLLMs.
Harnessing the Power of MLLMs for Transferable Text-to-Image Person ReID
May 08, 2024



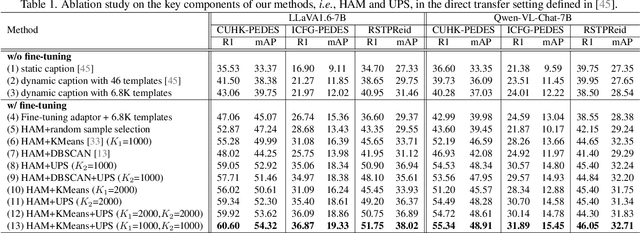
Abstract:Text-to-image person re-identification (ReID) retrieves pedestrian images according to textual descriptions. Manually annotating textual descriptions is time-consuming, restricting the scale of existing datasets and therefore the generalization ability of ReID models. As a result, we study the transferable text-to-image ReID problem, where we train a model on our proposed large-scale database and directly deploy it to various datasets for evaluation. We obtain substantial training data via Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Moreover, we identify and address two key challenges in utilizing the obtained textual descriptions. First, an MLLM tends to generate descriptions with similar structures, causing the model to overfit specific sentence patterns. Thus, we propose a novel method that uses MLLMs to caption images according to various templates. These templates are obtained using a multi-turn dialogue with a Large Language Model (LLM). Therefore, we can build a large-scale dataset with diverse textual descriptions. Second, an MLLM may produce incorrect descriptions. Hence, we introduce a novel method that automatically identifies words in a description that do not correspond with the image. This method is based on the similarity between one text and all patch token embeddings in the image. Then, we mask these words with a larger probability in the subsequent training epoch, alleviating the impact of noisy textual descriptions. The experimental results demonstrate that our methods significantly boost the direct transfer text-to-image ReID performance. Benefiting from the pre-trained model weights, we also achieve state-of-the-art performance in the traditional evaluation settings.
Decoupled Prototype Learning for Reliable Test-Time Adaptation
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:Test-time adaptation (TTA) is a task that continually adapts a pre-trained source model to the target domain during inference. One popular approach involves fine-tuning model with cross-entropy loss according to estimated pseudo-labels. However, its performance is significantly affected by noisy pseudo-labels. This study reveals that minimizing the classification error of each sample causes the cross-entropy loss's vulnerability to label noise. To address this issue, we propose a novel Decoupled Prototype Learning (DPL) method that features prototype-centric loss computation. First, we decouple the optimization of class prototypes. For each class prototype, we reduce its distance with positive samples and enlarge its distance with negative samples in a contrastive manner. This strategy prevents the model from overfitting to noisy pseudo-labels. Second, we propose a memory-based strategy to enhance DPL's robustness for the small batch sizes often encountered in TTA. We update each class's pseudo-feature from a memory in a momentum manner and insert an additional DPL loss. Finally, we introduce a consistency regularization-based approach to leverage samples with unconfident pseudo-labels. This approach transfers feature styles of samples with unconfident pseudo-labels to those with confident pseudo-labels. Thus, more reliable samples for TTA are created. The experimental results demonstrate that our methods achieve state-of-the-art performance on domain generalization benchmarks, and reliably improve the performance of self-training-based methods on image corruption benchmarks. The code will be released.
Style Interleaved Learning for Generalizable Person Re-identification
Jul 07, 2022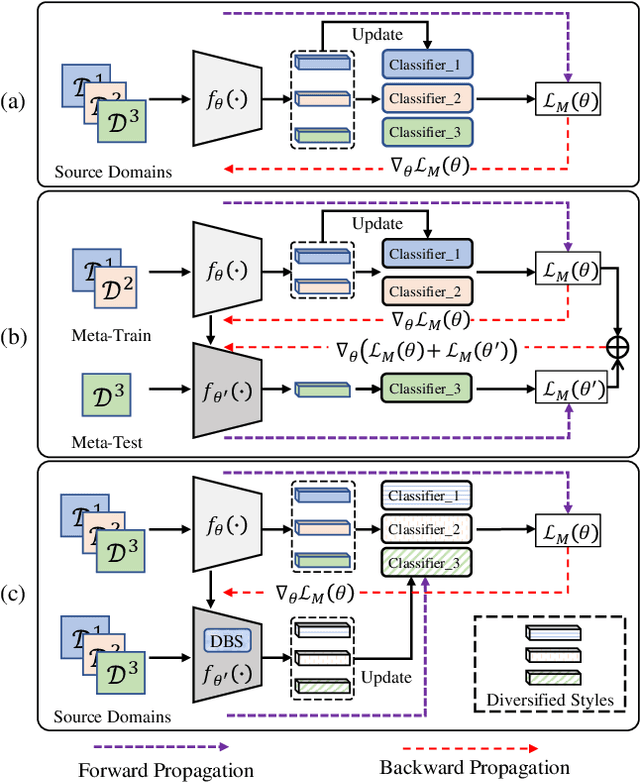
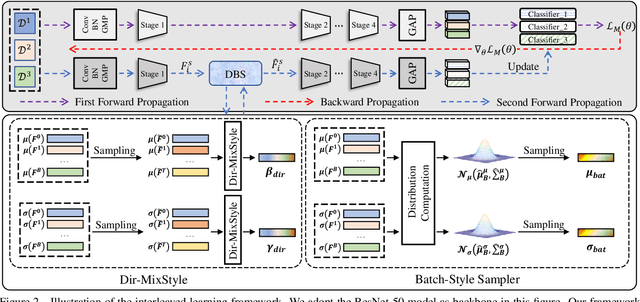
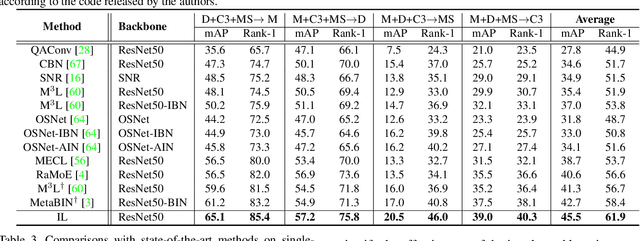
Abstract:Domain generalization (DG) for person re-identification (ReID) is a challenging problem, as there is no access to target domain data permitted during the training process. Most existing DG ReID methods employ the same features for the updating of the feature extractor and classifier parameters. This common practice causes the model to overfit to existing feature styles in the source domain, resulting in sub-optimal generalization ability on target domains even if meta-learning is used. To solve this problem, we propose a novel style interleaved learning framework. Unlike conventional learning strategies, interleaved learning incorporates two forward propagations and one backward propagation for each iteration. We employ the features of interleaved styles to update the feature extractor and classifiers using different forward propagations, which helps the model avoid overfitting to certain domain styles. In order to fully explore the advantages of style interleaved learning, we further propose a novel feature stylization approach to diversify feature styles. This approach not only mixes the feature styles of multiple training samples, but also samples new and meaningful feature styles from batch-level style distribution. Extensive experimental results show that our model consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on large-scale benchmarks for DG ReID, yielding clear advantages in computational efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/WentaoTan/Interleaved-Learning.
Uncertainty-aware Clustering for Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Object Re-identification
Aug 22, 2021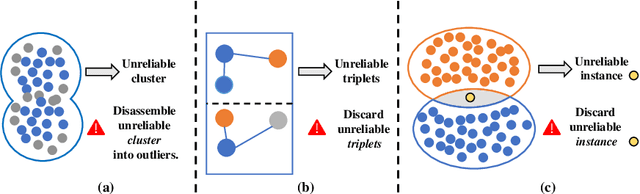
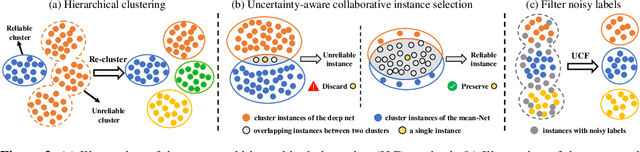
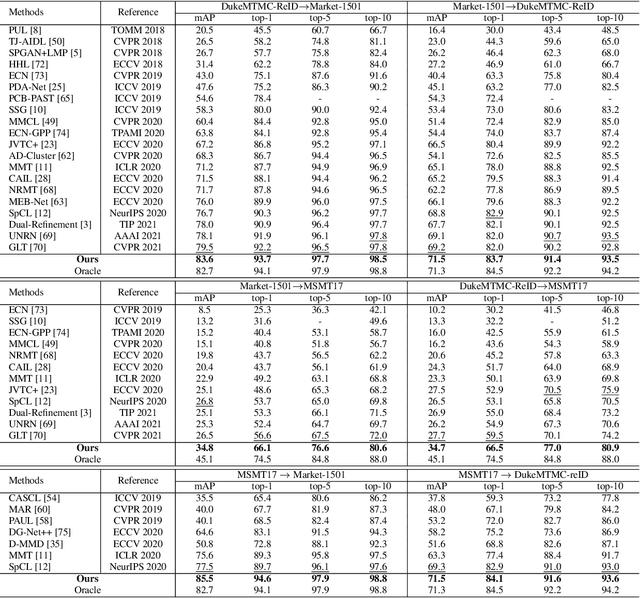
Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptive (UDA) object re-identification (Re-ID) aims at adapting a model trained on a labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain. State-of-the-art object Re-ID approaches adopt clustering algorithms to generate pseudo-labels for the unlabeled target domain. However, the inevitable label noise caused by the clustering procedure significantly degrades the discriminative power of Re-ID model. To address this problem, we propose an uncertainty-aware clustering framework (UCF) for UDA tasks. First, a novel hierarchical clustering scheme is proposed to promote clustering quality. Second, an uncertainty-aware collaborative instance selection method is introduced to select images with reliable labels for model training. Combining both techniques effectively reduces the impact of noisy labels. In addition, we introduce a strong baseline that features a compact contrastive loss. Our UCF method consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance in multiple UDA tasks for object Re-ID, and significantly reduces the gap between unsupervised and supervised Re-ID performance. In particular, the performance of our unsupervised UCF method in the MSMT17$\to$Market1501 task is better than that of the fully supervised setting on Market1501. The code of UCF is available at https://github.com/Wang-pengfei/UCF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge