Wenhe Jia
Deep Learning Technique for Human Parsing: A Survey and Outlook
Jan 01, 2023Abstract:Human parsing aims to partition humans in image or video into multiple pixel-level semantic parts. In the last decade, it has gained significantly increased interest in the computer vision community and has been utilized in a broad range of practical applications, from security monitoring, to social media, to visual special effects, just to name a few. Although deep learning-based human parsing solutions have made remarkable achievements, many important concepts, existing challenges, and potential research directions are still confusing. In this survey, we comprehensively review three core sub-tasks: single human parsing, multiple human parsing, and video human parsing, by introducing their respective task settings, background concepts, relevant problems and applications, representative literature, and datasets. We also present quantitative performance comparisons of the reviewed methods on benchmark datasets. Additionally, to promote sustainable development of the community, we put forward a transformer-based human parsing framework, providing a high-performance baseline for follow-up research through universal, concise, and extensible solutions. Finally, we point out a set of under-investigated open issues in this field and suggest new directions for future study. We also provide a regularly updated project page, to continuously track recent developments in this fast-advancing field: https://github.com/soeaver/awesome-human-parsing.
UV R-CNN: Stable and Efficient Dense Human Pose Estimation
Nov 04, 2022Abstract:Dense pose estimation is a dense 3D prediction task for instance-level human analysis, aiming to map human pixels from an RGB image to a 3D surface of the human body. Due to a large amount of surface point regression, the training process appears to be easy to collapse compared to other region-based human instance analyzing tasks. By analyzing the loss formulation of the existing dense pose estimation model, we introduce a novel point regression loss function, named Dense Points} loss to stable the training progress, and a new balanced loss weighting strategy to handle the multi-task losses. With the above novelties, we propose a brand new architecture, named UV R-CNN. Without auxiliary supervision and external knowledge from other tasks, UV R-CNN can handle many complicated issues in dense pose model training progress, achieving 65.0% $AP_{gps}$ and 66.1% $AP_{gpsm}$ on the DensePose-COCO validation subset with ResNet-50-FPN feature extractor, competitive among the state-of-the-art dense human pose estimation methods.
TIVE: A Toolbox for Identifying Video Instance Segmentation Errors
Oct 17, 2022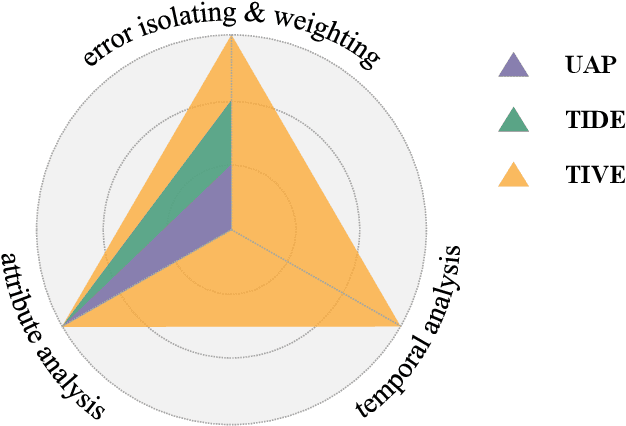
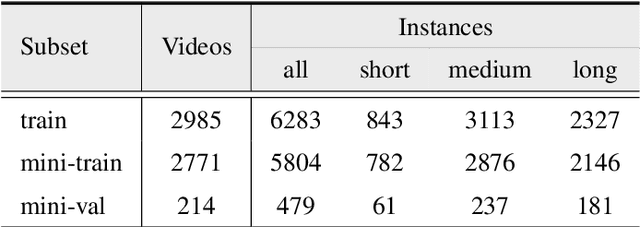
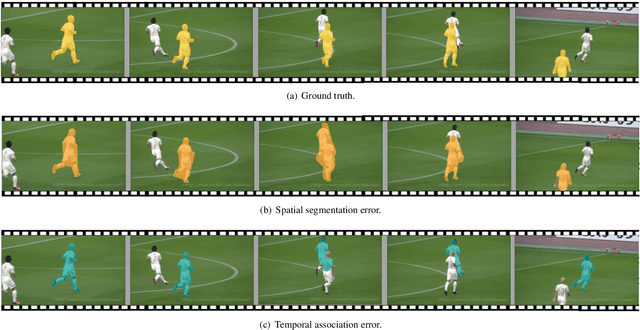
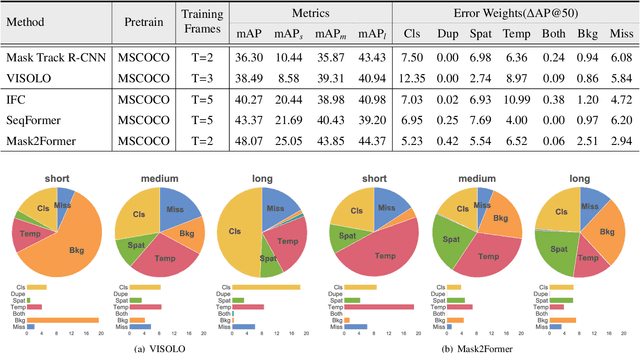
Abstract:Since first proposed, Video Instance Segmentation(VIS) task has attracted vast researchers' focus on architecture modeling to boost performance. Though great advances achieved in online and offline paradigms, there are still insufficient means to identify model errors and distinguish discrepancies between methods, as well approaches that correctly reflect models' performance in recognizing object instances of various temporal lengths remain barely available. More importantly, as the fundamental model abilities demanded by the task, spatial segmentation and temporal association are still understudied in both evaluation and interaction mechanisms. In this paper, we introduce TIVE, a Toolbox for Identifying Video instance segmentation Errors. By directly operating output prediction files, TIVE defines isolated error types and weights each type's damage to mAP, for the purpose of distinguishing model characters. By decomposing localization quality in spatial-temporal dimensions, model's potential drawbacks on spatial segmentation and temporal association can be revealed. TIVE can also report mAP over instance temporal length for real applications. We conduct extensive experiments by the toolbox to further illustrate how spatial segmentation and temporal association affect each other. We expect the analysis of TIVE can give the researchers more insights, guiding the community to promote more meaningful explorations for video instance segmentation. The proposed toolbox is available at https://github.com/wenhe-jia/TIVE.
Renovating Parsing R-CNN for Accurate Multiple Human Parsing
Sep 20, 2020



Abstract:Multiple human parsing aims to segment various human parts and associate each part with the corresponding instance simultaneously. This is a very challenging task due to the diverse human appearance, semantic ambiguity of different body parts, and complex background. Through analysis of multiple human parsing task, we observe that human-centric global perception and accurate instance-level parsing scoring are crucial for obtaining high-quality results. But the most state-of-the-art methods have not paid enough attention to these issues. To reverse this phenomenon, we present Renovating Parsing R-CNN (RP R-CNN), which introduces a global semantic enhanced feature pyramid network and a parsing re-scoring network into the existing high-performance pipeline. The proposed RP R-CNN adopts global semantic representation to enhance multi-scale features for generating human parsing maps, and regresses a confidence score to represent its quality. Extensive experiments show that RP R-CNN performs favorably against state-of-the-art methods on CIHP and MHP-v2 datasets. Code and models are available at https://github.com/soeaver/RP-R-CNN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge