Weiwei Jiang
Is Artificial Intelligence Generated Image Detection a Solved Problem?
May 18, 2025



Abstract:The rapid advancement of generative models, such as GANs and Diffusion models, has enabled the creation of highly realistic synthetic images, raising serious concerns about misinformation, deepfakes, and copyright infringement. Although numerous Artificial Intelligence Generated Image (AIGI) detectors have been proposed, often reporting high accuracy, their effectiveness in real-world scenarios remains questionable. To bridge this gap, we introduce AIGIBench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate the robustness and generalization capabilities of state-of-the-art AIGI detectors. AIGIBench simulates real-world challenges through four core tasks: multi-source generalization, robustness to image degradation, sensitivity to data augmentation, and impact of test-time pre-processing. It includes 23 diverse fake image subsets that span both advanced and widely adopted image generation techniques, along with real-world samples collected from social media and AI art platforms. Extensive experiments on 11 advanced detectors demonstrate that, despite their high reported accuracy in controlled settings, these detectors suffer significant performance drops on real-world data, limited benefits from common augmentations, and nuanced effects of pre-processing, highlighting the need for more robust detection strategies. By providing a unified and realistic evaluation framework, AIGIBench offers valuable insights to guide future research toward dependable and generalizable AIGI detection.
SitPose: Real-Time Detection of Sitting Posture and Sedentary Behavior Using Ensemble Learning With Depth Sensor
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:Poor sitting posture can lead to various work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs). Office employees spend approximately 81.8% of their working time seated, and sedentary behavior can result in chronic diseases such as cervical spondylosis and cardiovascular diseases. To address these health concerns, we present SitPose, a sitting posture and sedentary detection system utilizing the latest Kinect depth camera. The system tracks 3D coordinates of bone joint points in real-time and calculates the angle values of related joints. We established a dataset containing six different sitting postures and one standing posture, totaling 33,409 data points, by recruiting 36 participants. We applied several state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms to the dataset and compared their performance in recognizing the sitting poses. Our results show that the ensemble learning model based on the soft voting mechanism achieves the highest F1 score of 98.1%. Finally, we deployed the SitPose system based on this ensemble model to encourage better sitting posture and to reduce sedentary habits.
Real-Time Fall Detection Using Smartphone Accelerometers and WiFi Channel State Information
Dec 13, 2024
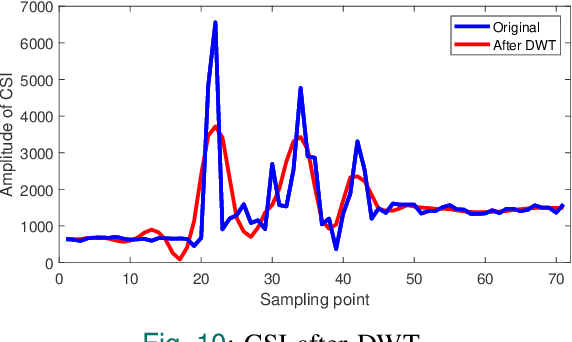
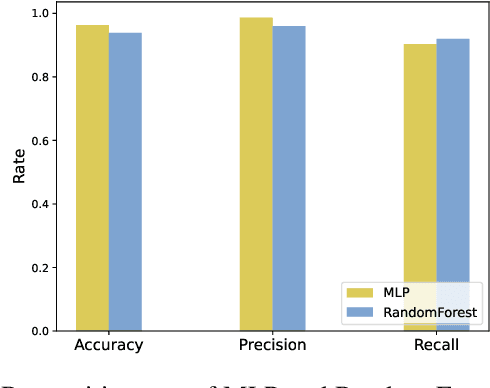
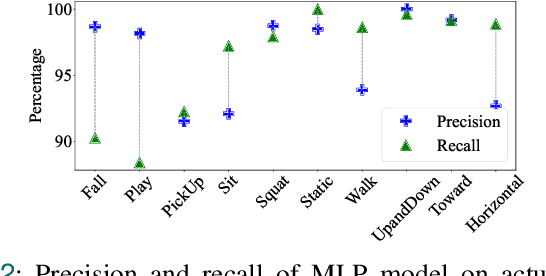
Abstract:In recent years, as the population ages, falls have increasingly posed a significant threat to the health of the elderly. We propose a real-time fall detection system that integrates the inertial measurement unit (IMU) of a smartphone with optimized Wi-Fi channel state information (CSI) for secondary validation. Initially, the IMU distinguishes falls from routine daily activities with minimal computational demand. Subsequently, the CSI is employed for further assessment, which includes evaluating the individual's post-fall mobility. This methodology not only achieves high accuracy but also reduces energy consumption in the smartphone platform. An Android application developed specifically for the purpose issues an emergency alert if the user experiences a fall and is unable to move. Experimental results indicate that the CSI model, based on convolutional neural networks (CNN), achieves a detection accuracy of 99%, \revised{surpassing comparable IMU-only models, and demonstrating significant resilience in distinguishing between falls and non-fall activities.
G-EvoNAS: Evolutionary Neural Architecture Search Based on Network Growth
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:The evolutionary paradigm has been successfully applied to neural network search(NAS) in recent years. Due to the vast search complexity of the global space, current research mainly seeks to repeatedly stack partial architectures to build the entire model or to seek the entire model based on manually designed benchmark modules. The above two methods are attempts to reduce the search difficulty by narrowing the search space. To efficiently search network architecture in the global space, this paper proposes another solution, namely a computationally efficient neural architecture evolutionary search framework based on network growth (G-EvoNAS). The complete network is obtained by gradually deepening different Blocks. The process begins from a shallow network, grows and evolves, and gradually deepens into a complete network, reducing the search complexity in the global space. Then, to improve the ranking accuracy of the network, we reduce the weight coupling of each network in the SuperNet by pruning the SuperNet according to elite groups at different growth stages. The G-EvoNAS is tested on three commonly used image classification datasets, CIFAR10, CIFAR100, and ImageNet, and compared with various state-of-the-art algorithms, including hand-designed networks and NAS networks. Experimental results demonstrate that G-EvoNAS can find a neural network architecture comparable to state-of-the-art designs in 0.2 GPU days.
TS-ENAS:Two-Stage Evolution for Cell-based Network Architecture Search
Oct 14, 2023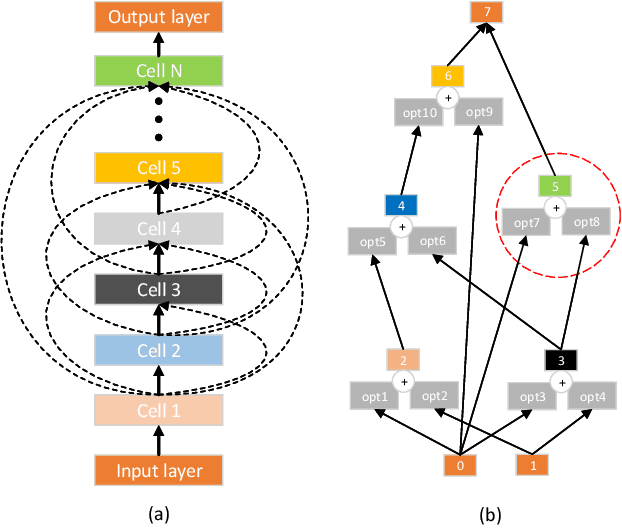
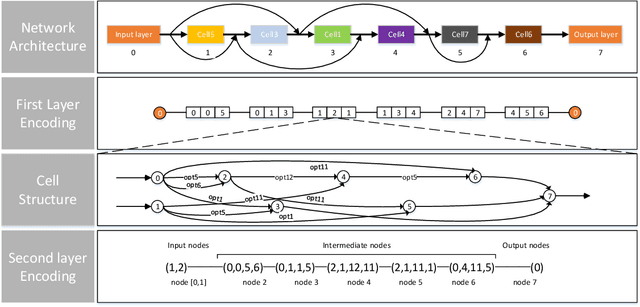
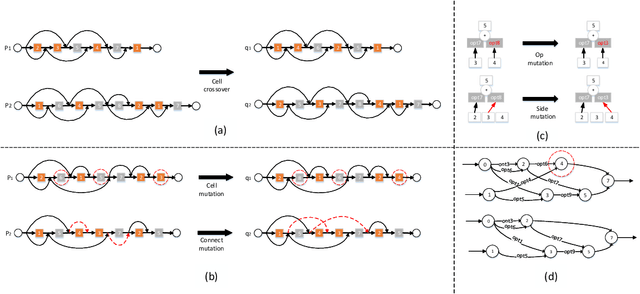
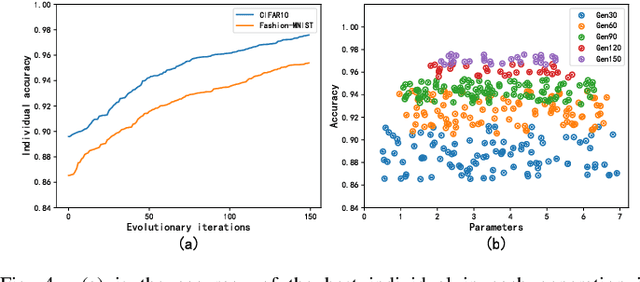
Abstract:Neural network architecture search provides a solution to the automatic design of network structures. However, it is difficult to search the whole network architecture directly. Although using stacked cells to search neural network architectures is an effective way to reduce the complexity of searching, these methods do not able find the global optimal neural network structure since the number of layers, cells and connection methods is fixed. In this paper, we propose a Two-Stage Evolution for cell-based Network Architecture Search(TS-ENAS), including one-stage searching based on stacked cells and second-stage adjusting these cells. In our algorithm, a new cell-based search space and an effective two-stage encoding method are designed to represent cells and neural network structures. In addition, a cell-based weight inheritance strategy is designed to initialize the weight of the network, which significantly reduces the running time of the algorithm. The proposed methods are extensively tested and compared on four image classification dataset, Fashion-MNIST, CIFAR10, CIFAR100 and ImageNet and compared with 22 state-of-the-art algorithms including hand-designed networks and NAS networks. The experimental results show that TS-ENAS can more effectively find the neural network architecture with comparative performance.
3D AGSE-VNet: An Automatic Brain Tumor MRI Data Segmentation Framework
Jul 26, 2021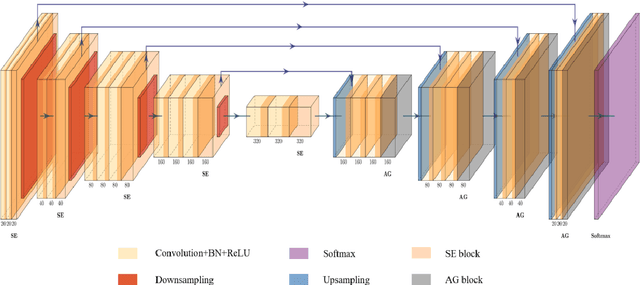
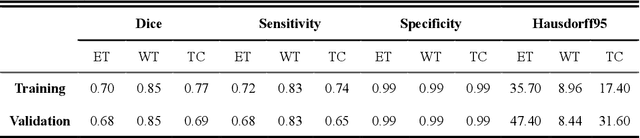
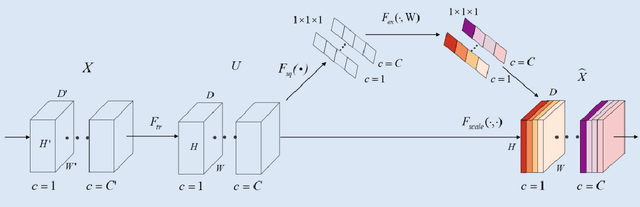
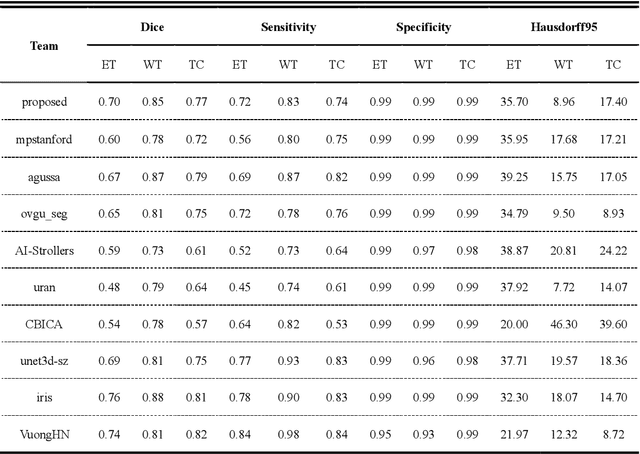
Abstract:Background: Glioma is the most common brain malignant tumor, with a high morbidity rate and a mortality rate of more than three percent, which seriously endangers human health. The main method of acquiring brain tumors in the clinic is MRI. Segmentation of brain tumor regions from multi-modal MRI scan images is helpful for treatment inspection, post-diagnosis monitoring, and effect evaluation of patients. However, the common operation in clinical brain tumor segmentation is still manual segmentation, lead to its time-consuming and large performance difference between different operators, a consistent and accurate automatic segmentation method is urgently needed. Methods: To meet the above challenges, we propose an automatic brain tumor MRI data segmentation framework which is called AGSE-VNet. In our study, the Squeeze and Excite (SE) module is added to each encoder, the Attention Guide Filter (AG) module is added to each decoder, using the channel relationship to automatically enhance the useful information in the channel to suppress the useless information, and use the attention mechanism to guide the edge information and remove the influence of irrelevant information such as noise. Results: We used the BraTS2020 challenge online verification tool to evaluate our approach. The focus of verification is that the Dice scores of the whole tumor (WT), tumor core (TC) and enhanced tumor (ET) are 0.68, 0.85 and 0.70, respectively. Conclusion: Although MRI images have different intensities, AGSE-VNet is not affected by the size of the tumor, and can more accurately extract the features of the three regions, it has achieved impressive results and made outstanding contributions to the clinical diagnosis and treatment of brain tumor patients.
An Evaluation of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models for Drought Prediction using Weather Data
Jul 06, 2021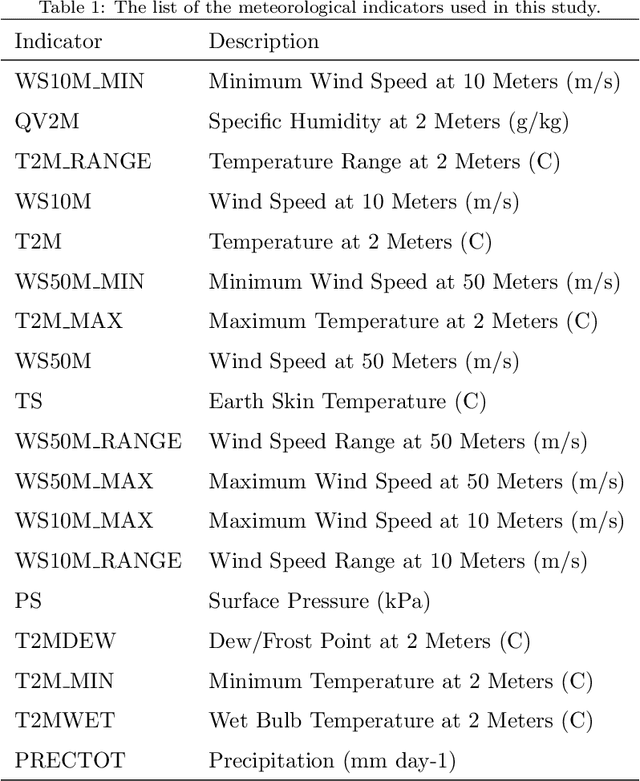
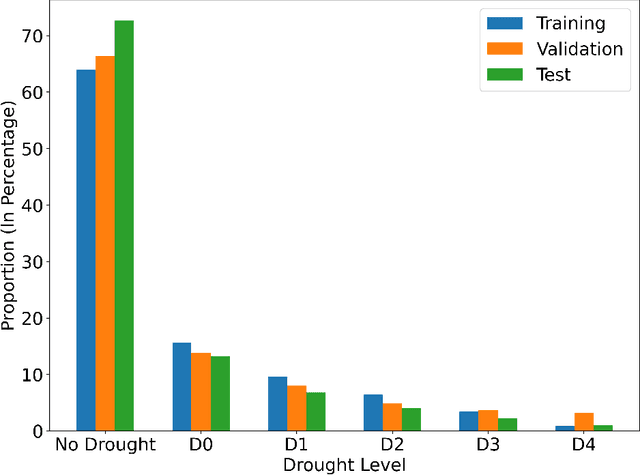
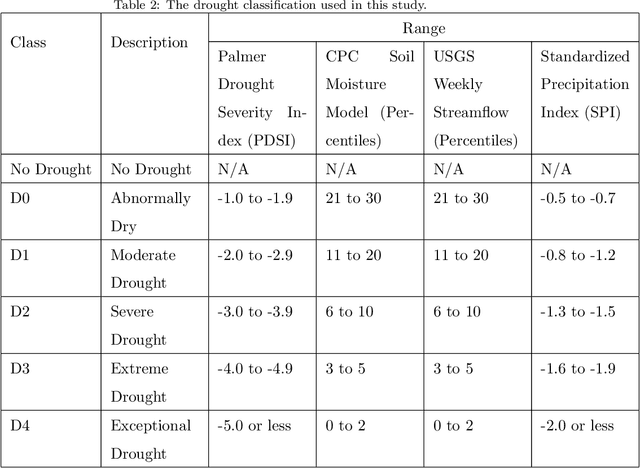
Abstract:Drought is a serious natural disaster that has a long duration and a wide range of influence. To decrease the drought-caused losses, drought prediction is the basis of making the corresponding drought prevention and disaster reduction measures. While this problem has been studied in the literature, it remains unknown whether drought can be precisely predicted or not with machine learning models using weather data. To answer this question, a real-world public dataset is leveraged in this study and different drought levels are predicted using the last 90 days of 18 meteorological indicators as the predictors. In a comprehensive approach, 16 machine learning models and 16 deep learning models are evaluated and compared. The results show no single model can achieve the best performance for all evaluation metrics simultaneously, which indicates the drought prediction problem is still challenging. As benchmarks for further studies, the code and results are publicly available in a Github repository.
Graph-based Deep Learning for Communication Networks: A Survey
Jun 04, 2021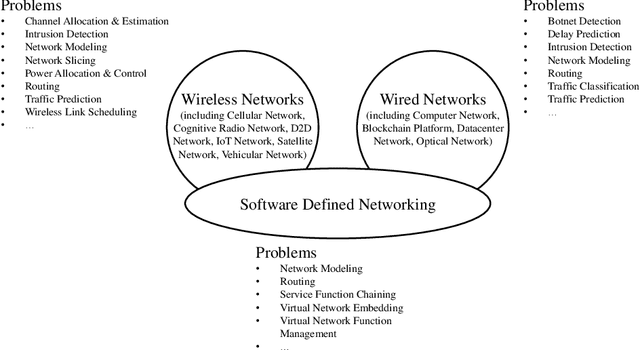

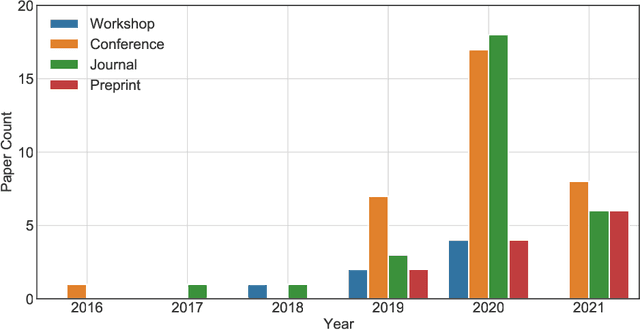
Abstract:Communication networks are important infrastructures in contemporary society. There are still many challenges that are not fully solved and new solutions are proposed continuously in this active research area. In recent years, to model the network topology, graph-based deep learning has achieved state-of-the-art performance in a series of problems in communication networks. In this survey, we review the rapidly growing body of research using different graph-based deep learning models, e.g. graph convolutional and graph attention networks, in various problems from different communication networks, e.g. wireless networks, wired networks, and software-defined networks. We also present a well-organized list of the problem and solution for each study and identify future research directions. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first survey that focuses on the application of graph-based deep learning methods in communication networks. To track the follow-up research, a public GitHub repository is created, where the relevant papers will be updated continuously.
Big Data for Traffic Estimation and Prediction: A Survey of Data and Tools
Mar 18, 2021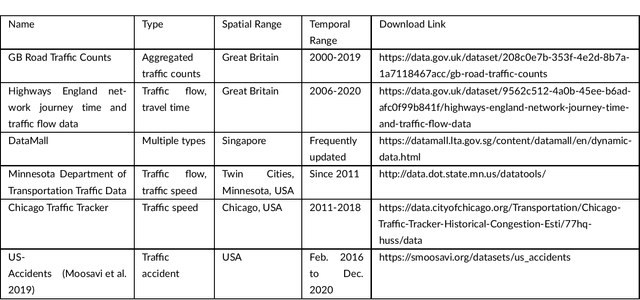
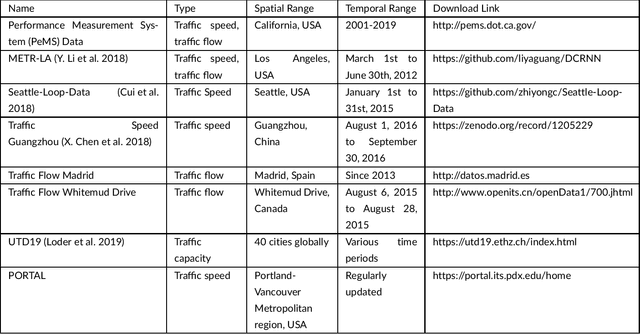
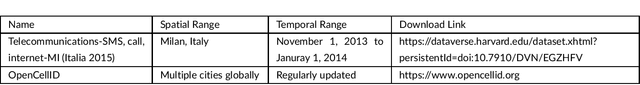
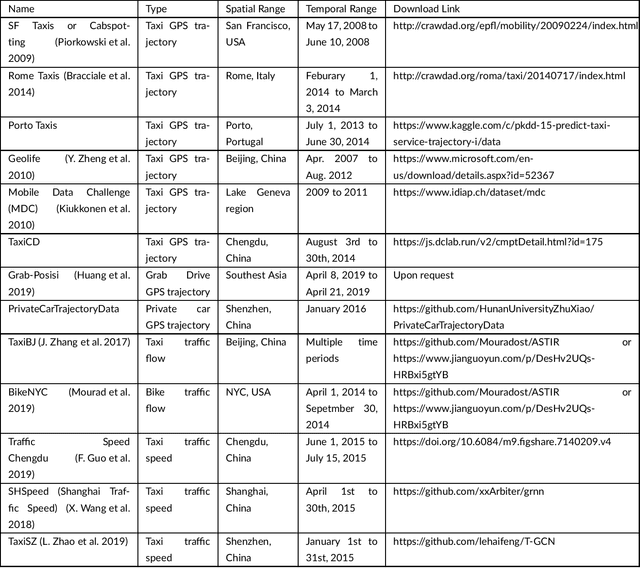
Abstract:Big data has been used widely in many areas including the transportation industry. Using various data sources, traffic states can be well estimated and further predicted for improving the overall operation efficiency. Combined with this trend, this study presents an up-to-date survey of open data and big data tools used for traffic estimation and prediction. Different data types are categorized and the off-the-shelf tools are introduced. To further promote the use of big data for traffic estimation and prediction tasks, challenges and future directions are given for future studies.
Graph Neural Network for Traffic Forecasting: A Survey
Feb 15, 2021
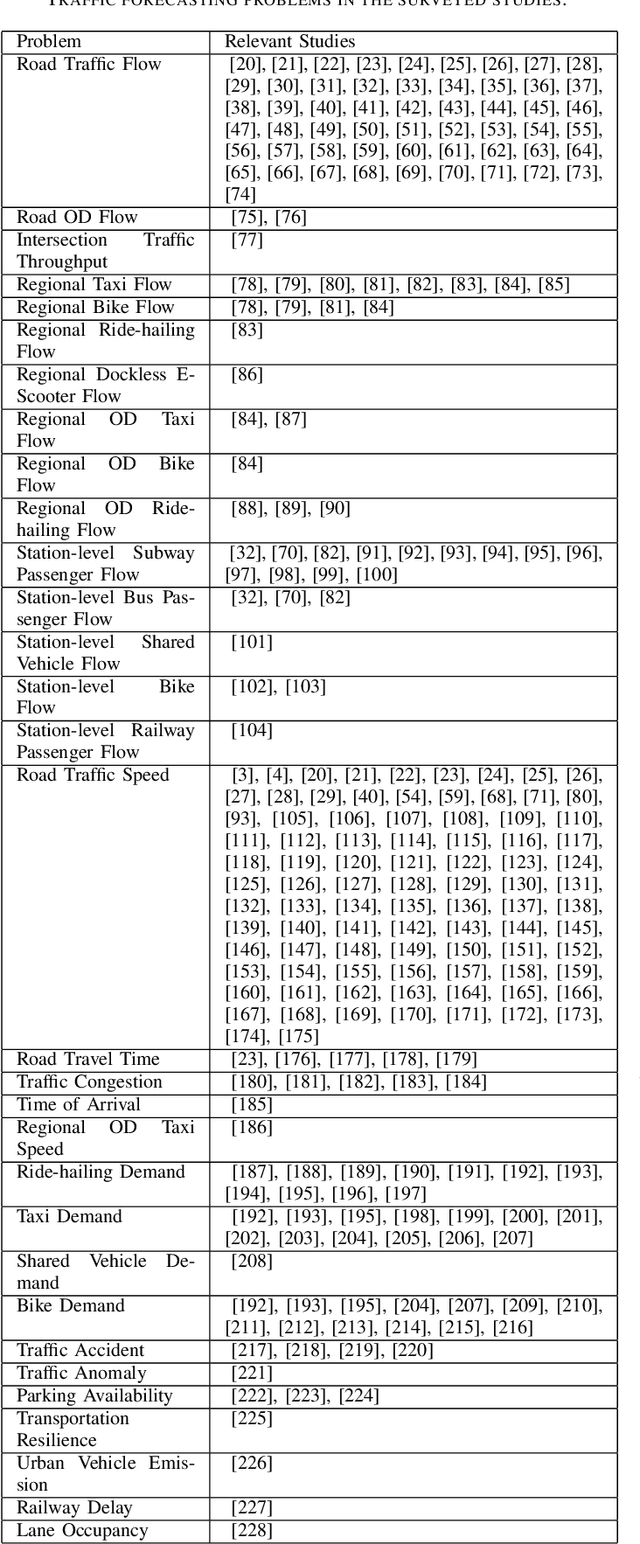
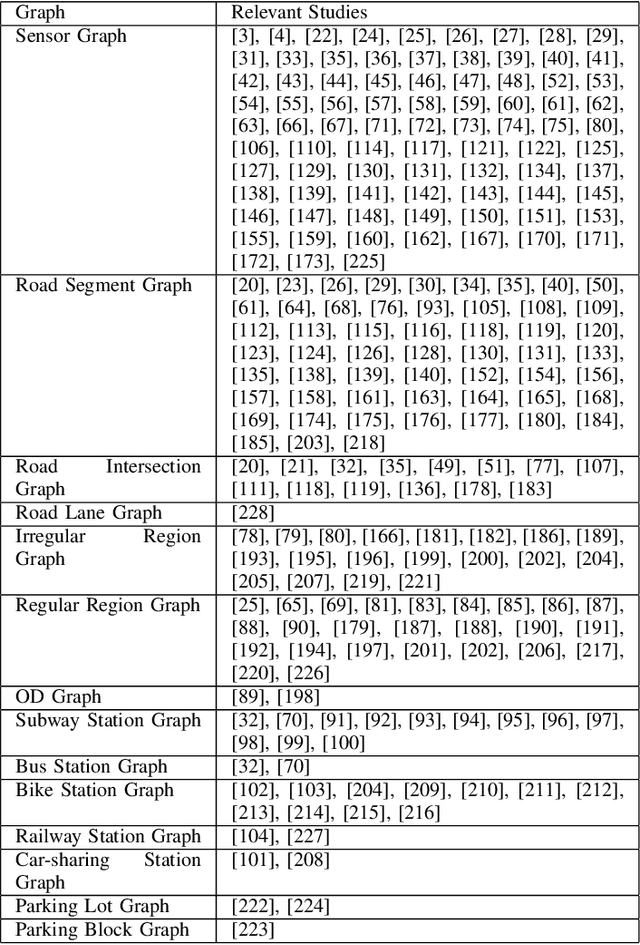
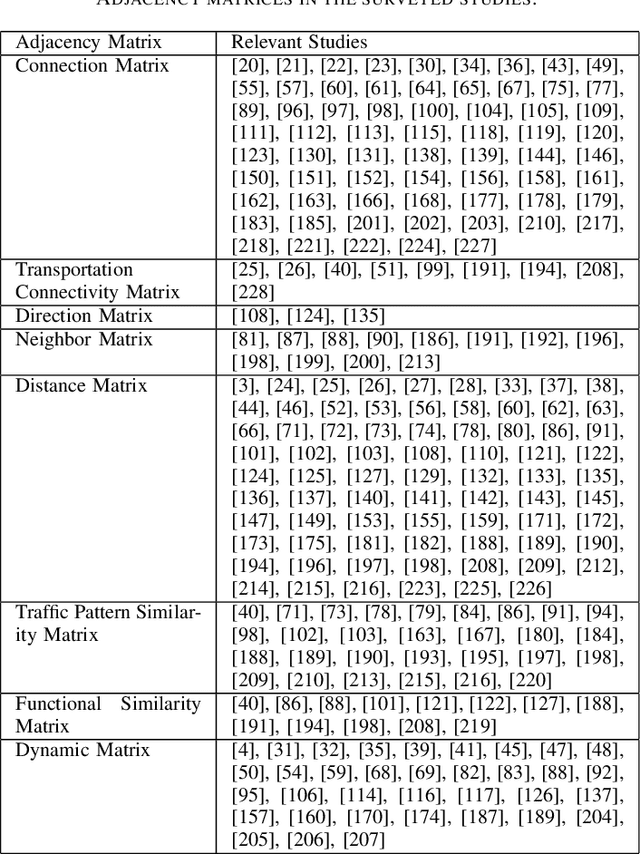
Abstract:Traffic forecasting is important for the success of intelligent transportation systems. Deep learning models, including convolution neural networks and recurrent neural networks, have been extensively applied in traffic forecasting problems to model spatial and temporal dependencies. In recent years, to model the graph structures in transportation systems as well as contextual information, graph neural networks have been introduced and have achieved state-of-the-art performance in a series of traffic forecasting problems. In this survey, we review the rapidly growing body of research using different graph neural networks, e.g. graph convolutional and graph attention networks, in various traffic forecasting problems, e.g. road traffic flow and speed forecasting, passenger flow forecasting in urban rail transit systems, and demand forecasting in ride-hailing platforms. We also present a comprehensive list of open data and source resources for each problem and identify future research directions. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first comprehensive survey that explores the application of graph neural networks for traffic forecasting problems. We have also created a public GitHub repository where the latest papers, open data, and source resources will be updated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge