Vladimir Iashin
Video Object Segmentation-Aware Audio Generation
Sep 30, 2025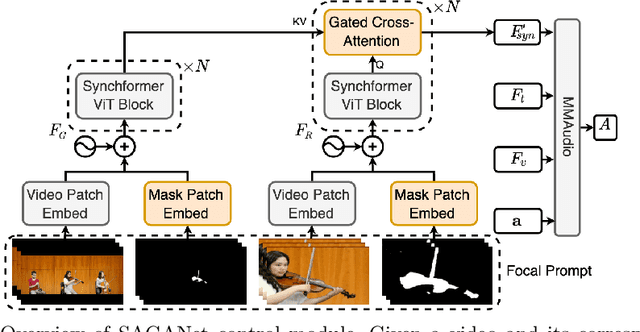



Abstract:Existing multimodal audio generation models often lack precise user control, which limits their applicability in professional Foley workflows. In particular, these models focus on the entire video and do not provide precise methods for prioritizing a specific object within a scene, generating unnecessary background sounds, or focusing on the wrong objects. To address this gap, we introduce the novel task of video object segmentation-aware audio generation, which explicitly conditions sound synthesis on object-level segmentation maps. We present SAGANet, a new multimodal generative model that enables controllable audio generation by leveraging visual segmentation masks along with video and textual cues. Our model provides users with fine-grained and visually localized control over audio generation. To support this task and further research on segmentation-aware Foley, we propose Segmented Music Solos, a benchmark dataset of musical instrument performance videos with segmentation information. Our method demonstrates substantial improvements over current state-of-the-art methods and sets a new standard for controllable, high-fidelity Foley synthesis. Code, samples, and Segmented Music Solos are available at https://saganet.notion.site
Temporally Aligned Audio for Video with Autoregression
Sep 20, 2024Abstract:We introduce V-AURA, the first autoregressive model to achieve high temporal alignment and relevance in video-to-audio generation. V-AURA uses a high-framerate visual feature extractor and a cross-modal audio-visual feature fusion strategy to capture fine-grained visual motion events and ensure precise temporal alignment. Additionally, we propose VisualSound, a benchmark dataset with high audio-visual relevance. VisualSound is based on VGGSound, a video dataset consisting of in-the-wild samples extracted from YouTube. During the curation, we remove samples where auditory events are not aligned with the visual ones. V-AURA outperforms current state-of-the-art models in temporal alignment and semantic relevance while maintaining comparable audio quality. Code, samples, VisualSound and models are available at https://v-aura.notion.site
Synchformer: Efficient Synchronization from Sparse Cues
Jan 29, 2024



Abstract:Our objective is audio-visual synchronization with a focus on 'in-the-wild' videos, such as those on YouTube, where synchronization cues can be sparse. Our contributions include a novel audio-visual synchronization model, and training that decouples feature extraction from synchronization modelling through multi-modal segment-level contrastive pre-training. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in both dense and sparse settings. We also extend synchronization model training to AudioSet a million-scale 'in-the-wild' dataset, investigate evidence attribution techniques for interpretability, and explore a new capability for synchronization models: audio-visual synchronizability.
Sparse in Space and Time: Audio-visual Synchronisation with Trainable Selectors
Oct 13, 2022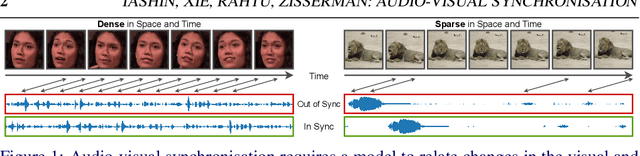
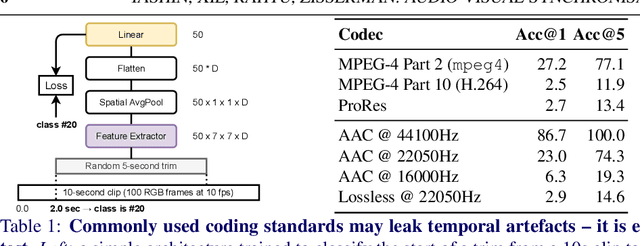
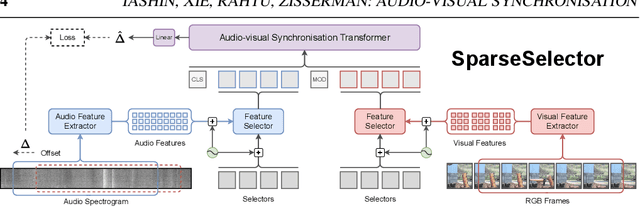
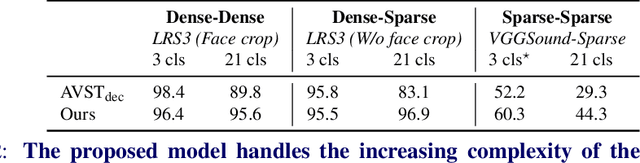
Abstract:The objective of this paper is audio-visual synchronisation of general videos 'in the wild'. For such videos, the events that may be harnessed for synchronisation cues may be spatially small and may occur only infrequently during a many seconds-long video clip, i.e. the synchronisation signal is 'sparse in space and time'. This contrasts with the case of synchronising videos of talking heads, where audio-visual correspondence is dense in both time and space. We make four contributions: (i) in order to handle longer temporal sequences required for sparse synchronisation signals, we design a multi-modal transformer model that employs 'selectors' to distil the long audio and visual streams into small sequences that are then used to predict the temporal offset between streams. (ii) We identify artefacts that can arise from the compression codecs used for audio and video and can be used by audio-visual models in training to artificially solve the synchronisation task. (iii) We curate a dataset with only sparse in time and space synchronisation signals; and (iv) the effectiveness of the proposed model is shown on both dense and sparse datasets quantitatively and qualitatively. Project page: v-iashin.github.io/SparseSync
Taming Visually Guided Sound Generation
Oct 17, 2021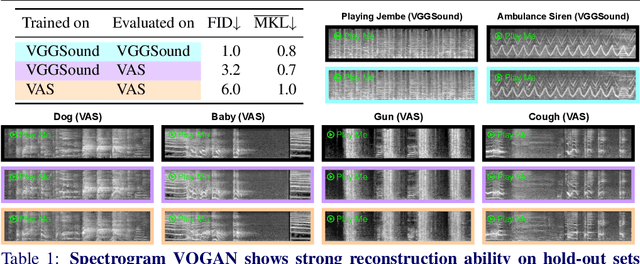
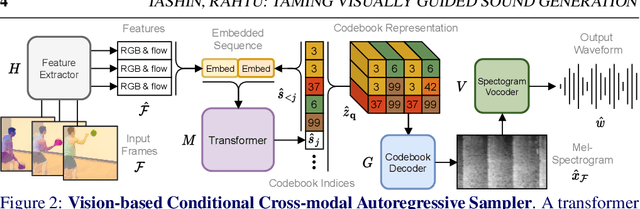
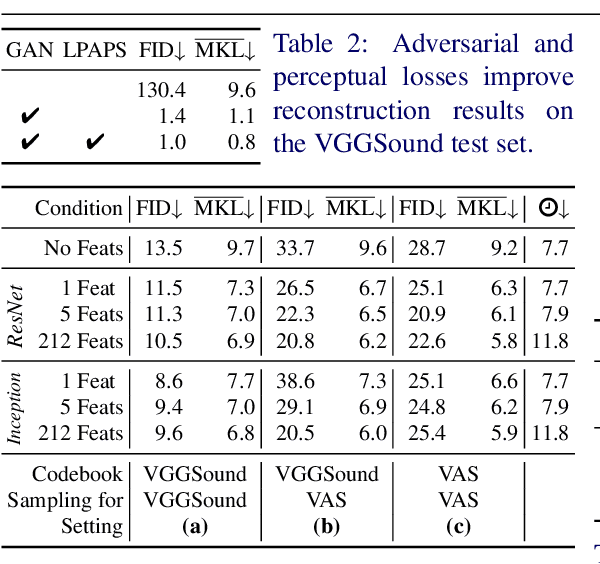
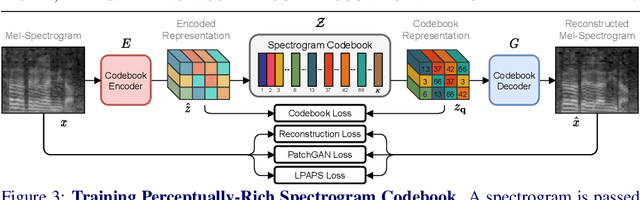
Abstract:Recent advances in visually-induced audio generation are based on sampling short, low-fidelity, and one-class sounds. Moreover, sampling 1 second of audio from the state-of-the-art model takes minutes on a high-end GPU. In this work, we propose a single model capable of generating visually relevant, high-fidelity sounds prompted with a set of frames from open-domain videos in less time than it takes to play it on a single GPU. We train a transformer to sample a new spectrogram from the pre-trained spectrogram codebook given the set of video features. The codebook is obtained using a variant of VQGAN trained to produce a compact sampling space with a novel spectrogram-based perceptual loss. The generated spectrogram is transformed into a waveform using a window-based GAN that significantly speeds up generation. Considering the lack of metrics for automatic evaluation of generated spectrograms, we also build a family of metrics called FID and MKL. These metrics are based on a novel sound classifier, called Melception, and designed to evaluate the fidelity and relevance of open-domain samples. Both qualitative and quantitative studies are conducted on small- and large-scale datasets to evaluate the fidelity and relevance of generated samples. We also compare our model to the state-of-the-art and observe a substantial improvement in quality, size, and computation time. Code, demo, and samples: v-iashin.github.io/SpecVQGAN
Multi-modal estimation of the properties of containers and their content: survey and evaluation
Jul 27, 2021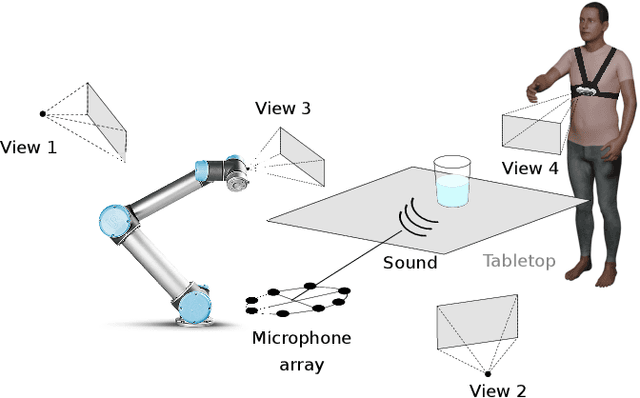
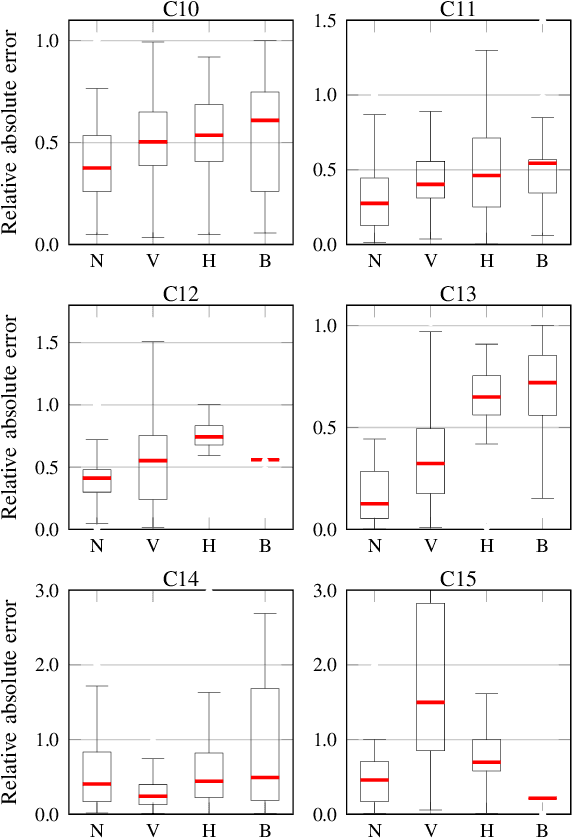
Abstract:Acoustic and visual sensing can support the contactless estimation of the weight of a container and the amount of its content when the container is manipulated by a person. However, transparencies (both of the container and of the content) and the variability of materials, shapes and sizes make this problem challenging. In this paper, we present an open benchmarking framework and an in-depth comparative analysis of recent methods that estimate the capacity of a container, as well as the type, mass, and amount of its content. These methods use learned and handcrafted features, such as mel-frequency cepstrum coefficients, zero-crossing rate, spectrograms, with different types of classifiers to estimate the type and amount of the content with acoustic data, and geometric approaches with visual data to determine the capacity of the container. Results on a newly distributed dataset show that audio alone is a strong modality and methods achieves a weighted average F1-score up to 81% and 97% for content type and level classification, respectively. Estimating the container capacity with vision-only approaches and filling mass with multi-modal, multi-stage algorithms reaches up to 65% weighted average capacity and mass scores.
Top-1 CORSMAL Challenge 2020 Submission: Filling Mass Estimation Using Multi-modal Observations of Human-robot Handovers
Dec 02, 2020
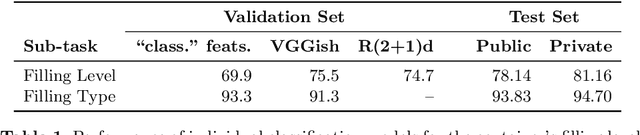
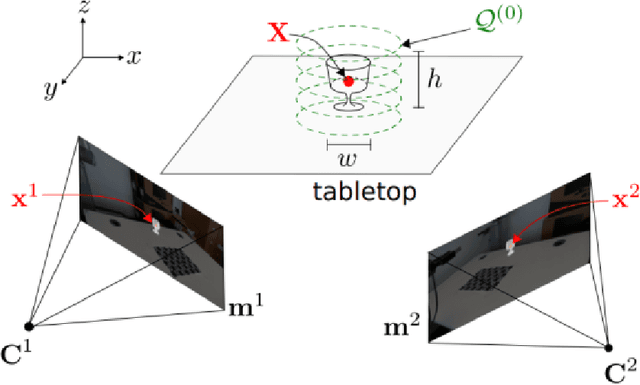
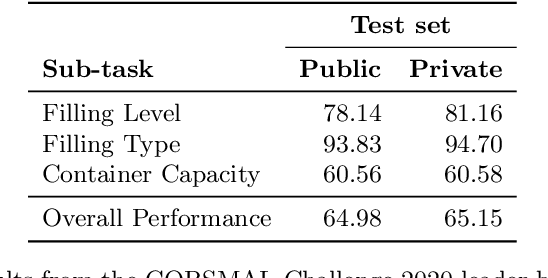
Abstract:Human-robot object handover is a key skill for the future of human-robot collaboration. CORSMAL 2020 Challenge focuses on the perception part of this problem: the robot needs to estimate the filling mass of a container held by a human. Although there are powerful methods in image processing and audio processing individually, answering such a problem requires processing data from multiple sensors together. The appearance of the container, the sound of the filling, and the depth data provide essential information. We propose a multi-modal method to predict three key indicators of the filling mass: filling type, filling level, and container capacity. These indicators are then combined to estimate the filling mass of a container. Our method obtained Top-1 overall performance among all submissions to CORSMAL 2020 Challenge on both public and private subsets while showing no evidence of overfitting. Our source code is publicly available: https://github.com/v-iashin/CORSMAL
A Better Use of Audio-Visual Cues: Dense Video Captioning with Bi-modal Transformer
May 17, 2020
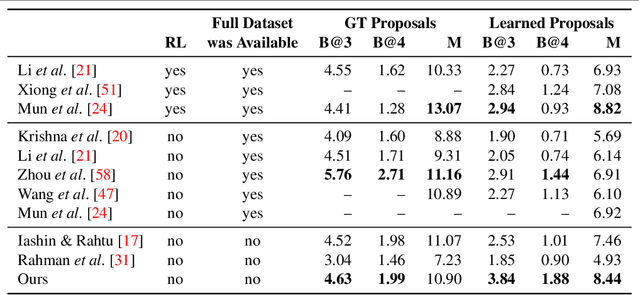
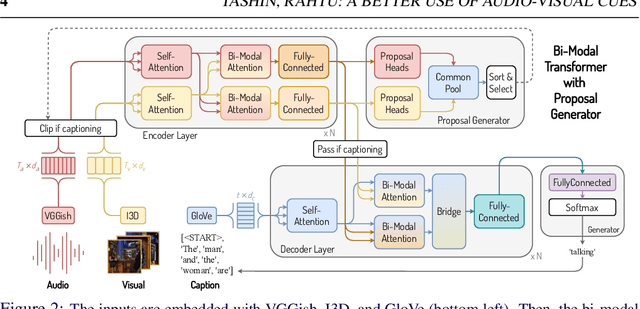
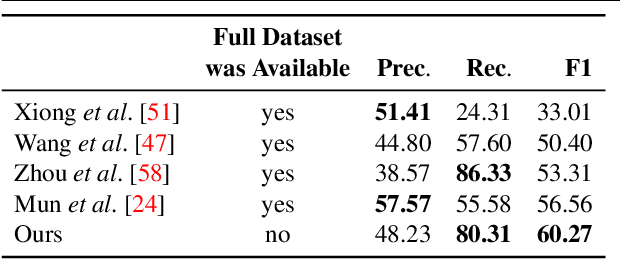
Abstract:Dense video captioning aims to localize and describe important events in untrimmed videos. Existing methods mainly tackle this task by exploiting only visual features, while completely neglecting the audio track. Only a few prior works have utilized both modalities, yet they show poor results or demonstrate the importance on a dataset with a specific domain. In this paper, we introduce Bi-modal Transformer which generalizes the Transformer architecture for a bi-modal input. We show the effectiveness of the proposed model with audio and visual modalities on the dense video captioning task, yet the module is capable to input any two modalities in a sequence-to-sequence task. We show that the pre-training a bi-modal encoder along with a bi-modal decoder for captioning can be used as a feature extractor for a simple proposal generation module. The performance is demonstrated on a challenging ActivityNet Captions dataset where our model achieves outstanding performance.
Multi-modal Dense Video Captioning
Mar 17, 2020
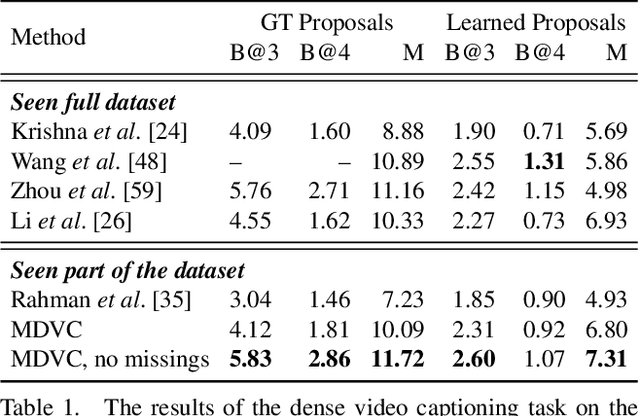
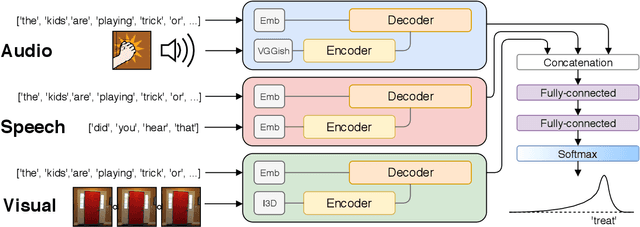
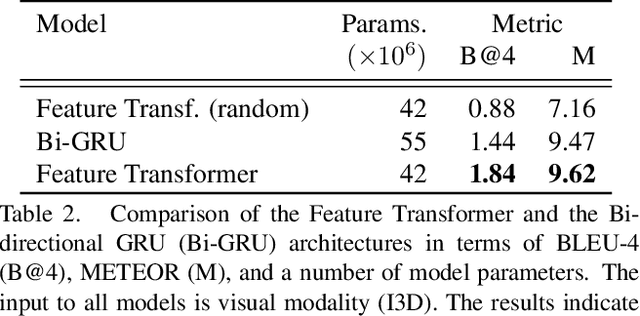
Abstract:Dense video captioning is a task of localizing interesting events from an untrimmed video and producing textual description (captions) for each localized event. Most of the previous works in dense video captioning are solely based on visual information and completely ignore the audio track. However, audio, and speech, in particular, are vital cues for a human observer in understanding an environment. In this paper, we present a new dense video captioning approach that is able to utilize any number of modalities for event description. Specifically, we show how audio and speech modalities may improve a dense video captioning model. We apply automatic speech recognition (ASR) system to obtain a temporally aligned textual description of the speech (similar to subtitles) and treat it as a separate input alongside video frames and the corresponding audio track. We formulate the captioning task as a machine translation problem and utilize recently proposed Transformer architecture to convert multi-modal input data into textual descriptions. We demonstrate the performance of our model on ActivityNet Captions dataset. The ablation studies indicate a considerable contribution from audio and speech components suggesting that these modalities contain substantial complementary information to video frames. Furthermore, we provide an in-depth analysis of the ActivityNet Caption results by leveraging the category tags obtained from original YouTube videos. The program code of our method and evaluations will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge