Vitor Cerqueira
Grasynda: Graph-based Synthetic Time Series Generation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Data augmentation is a crucial tool in time series forecasting, especially for deep learning architectures that require a large training sample size to generalize effectively. However, extensive datasets are not always available in real-world scenarios. Although many data augmentation methods exist, their limitations include the use of transformations that do not adequately preserve data properties. This paper introduces Grasynda, a novel graph-based approach for synthetic time series generation that: (1) converts univariate time series into a network structure using a graph representation, where each state is a node and each transition is represented as a directed edge; and (2) encodes their temporal dynamics in a transition probability matrix. We performed an extensive evaluation of Grasynda as a data augmentation method for time series forecasting. We use three neural network variations on six benchmark datasets. The results indicate that Grasynda consistently outperforms other time series data augmentation methods, including ones used in state-of-the-art time series foundation models. The method and all experiments are publicly available.
N-BEATS-MOE: N-BEATS with a Mixture-of-Experts Layer for Heterogeneous Time Series Forecasting
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Deep learning approaches are increasingly relevant for time series forecasting tasks. Methods such as N-BEATS, which is built on stacks of multilayer perceptrons (MLPs) blocks, have achieved state-of-the-art results on benchmark datasets and competitions. N-BEATS is also more interpretable relative to other deep learning approaches, as it decomposes forecasts into different time series components, such as trend and seasonality. In this work, we present N-BEATS-MOE, an extension of N-BEATS based on a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) layer. N-BEATS-MOE employs a dynamic block weighting strategy based on a gating network which allows the model to better adapt to the characteristics of each time series. We also hypothesize that the gating mechanism provides additional interpretability by identifying which expert is most relevant for each series. We evaluate our method across 12 benchmark datasets against several approaches, achieving consistent improvements on several datasets, especially those composed of heterogeneous time series.
L-GTA: Latent Generative Modeling for Time Series Augmentation
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Data augmentation is gaining importance across various aspects of time series analysis, from forecasting to classification and anomaly detection tasks. We introduce the Latent Generative Transformer Augmentation (L-GTA) model, a generative approach using a transformer-based variational recurrent autoencoder. This model uses controlled transformations within the latent space of the model to generate new time series that preserve the intrinsic properties of the original dataset. L-GTA enables the application of diverse transformations, ranging from simple jittering to magnitude warping, and combining these basic transformations to generate more complex synthetic time series datasets. Our evaluation of several real-world datasets demonstrates the ability of L-GTA to produce more reliable, consistent, and controllable augmented data. This translates into significant improvements in predictive accuracy and similarity measures compared to direct transformation methods.
ModelRadar: Aspect-based Forecast Evaluation
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Accurate evaluation of forecasting models is essential for ensuring reliable predictions. Current practices for evaluating and comparing forecasting models focus on summarising performance into a single score, using metrics such as SMAPE. While convenient, averaging performance over all samples dilutes relevant information about model behavior under varying conditions. This limitation is especially problematic for time series forecasting, where multiple layers of averaging--across time steps, horizons, and multiple time series in a dataset--can mask relevant performance variations. We address this limitation by proposing ModelRadar, a framework for evaluating univariate time series forecasting models across multiple aspects, such as stationarity, presence of anomalies, or forecasting horizons. We demonstrate the advantages of this framework by comparing 24 forecasting methods, including classical approaches and different machine learning algorithms. NHITS, a state-of-the-art neural network architecture, performs best overall but its superiority varies with forecasting conditions. For instance, concerning the forecasting horizon, we found that NHITS (and also other neural networks) only outperforms classical approaches for multi-step ahead forecasting. Another relevant insight is that classical approaches such as ETS or Theta are notably more robust in the presence of anomalies. These and other findings highlight the importance of aspect-based model evaluation for both practitioners and researchers. ModelRadar is available as a Python package.
CapyMOA: Efficient Machine Learning for Data Streams in Python
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:CapyMOA is an open-source library designed for efficient machine learning on streaming data. It provides a structured framework for real-time learning and evaluation, featuring a flexible data representation. CapyMOA includes an extensible architecture that allows integration with external frameworks such as MOA and PyTorch, facilitating hybrid learning approaches that combine traditional online algorithms with deep learning techniques. By emphasizing adaptability, scalability, and usability, CapyMOA allows researchers and practitioners to tackle dynamic learning challenges across various domains.
Cherry-Picking in Time Series Forecasting: How to Select Datasets to Make Your Model Shine
Dec 19, 2024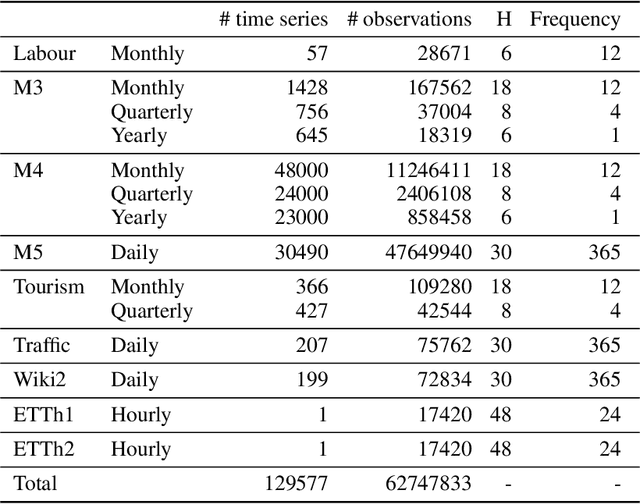
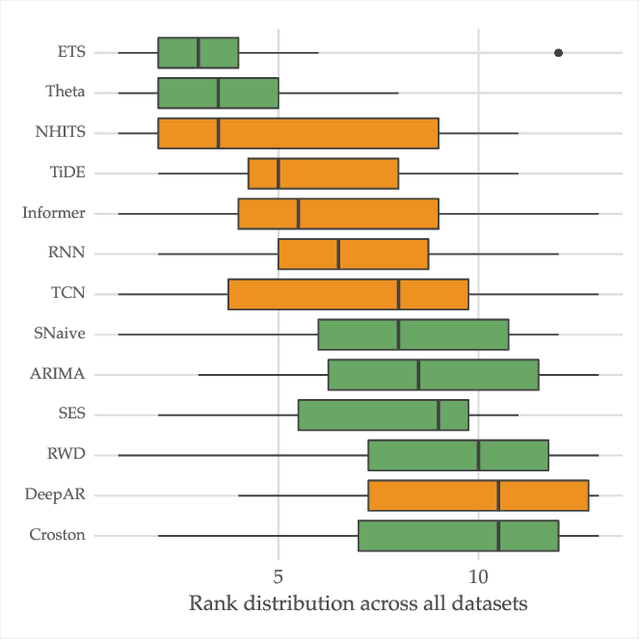
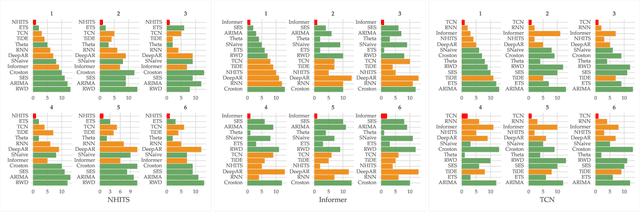

Abstract:The importance of time series forecasting drives continuous research and the development of new approaches to tackle this problem. Typically, these methods are introduced through empirical studies that frequently claim superior accuracy for the proposed approaches. Nevertheless, concerns are rising about the reliability and generalizability of these results due to limitations in experimental setups. This paper addresses a critical limitation: the number and representativeness of the datasets used. We investigate the impact of dataset selection bias, particularly the practice of cherry-picking datasets, on the performance evaluation of forecasting methods. Through empirical analysis with a diverse set of benchmark datasets, our findings reveal that cherry-picking datasets can significantly distort the perceived performance of methods, often exaggerating their effectiveness. Furthermore, our results demonstrate that by selectively choosing just four datasets - what most studies report - 46% of methods could be deemed best in class, and 77% could rank within the top three. Additionally, recent deep learning-based approaches show high sensitivity to dataset selection, whereas classical methods exhibit greater robustness. Finally, our results indicate that, when empirically validating forecasting algorithms on a subset of the benchmarks, increasing the number of datasets tested from 3 to 6 reduces the risk of incorrectly identifying an algorithm as the best one by approximately 40%. Our study highlights the critical need for comprehensive evaluation frameworks that more accurately reflect real-world scenarios. Adopting such frameworks will ensure the development of robust and reliable forecasting methods.
Meta-learning and Data Augmentation for Stress Testing Forecasting Models
Jun 24, 2024



Abstract:The effectiveness of univariate forecasting models is often hampered by conditions that cause them stress. A model is considered to be under stress if it shows a negative behaviour, such as higher-than-usual errors or increased uncertainty. Understanding the factors that cause stress to forecasting models is important to improve their reliability, transparency, and utility. This paper addresses this problem by contributing with a novel framework called MAST (Meta-learning and data Augmentation for Stress Testing). The proposed approach aims to model and characterize stress in univariate time series forecasting models, focusing on conditions where they exhibit large errors. In particular, MAST is a meta-learning approach that predicts the probability that a given model will perform poorly on a given time series based on a set of statistical time series features. MAST also encompasses a novel data augmentation technique based on oversampling to improve the metadata concerning stress. We conducted experiments using three benchmark datasets that contain a total of 49.794 time series to validate the performance of MAST. The results suggest that the proposed approach is able to identify conditions that lead to large errors. The method and experiments are publicly available in a repository.
Forecasting with Deep Learning: Beyond Average of Average of Average Performance
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Accurate evaluation of forecasting models is essential for ensuring reliable predictions. Current practices for evaluating and comparing forecasting models focus on summarising performance into a single score, using metrics such as SMAPE. We hypothesize that averaging performance over all samples dilutes relevant information about the relative performance of models. Particularly, conditions in which this relative performance is different than the overall accuracy. We address this limitation by proposing a novel framework for evaluating univariate time series forecasting models from multiple perspectives, such as one-step ahead forecasting versus multi-step ahead forecasting. We show the advantages of this framework by comparing a state-of-the-art deep learning approach with classical forecasting techniques. While classical methods (e.g. ARIMA) are long-standing approaches to forecasting, deep neural networks (e.g. NHITS) have recently shown state-of-the-art forecasting performance in benchmark datasets. We conducted extensive experiments that show NHITS generally performs best, but its superiority varies with forecasting conditions. For instance, concerning the forecasting horizon, NHITS only outperforms classical approaches for multi-step ahead forecasting. Another relevant insight is that, when dealing with anomalies, NHITS is outperformed by methods such as Theta. These findings highlight the importance of aspect-based model evaluation.
Lag Selection for Univariate Time Series Forecasting using Deep Learning: An Empirical Study
May 18, 2024



Abstract:Most forecasting methods use recent past observations (lags) to model the future values of univariate time series. Selecting an adequate number of lags is important for training accurate forecasting models. Several approaches and heuristics have been devised to solve this task. However, there is no consensus about what the best approach is. Besides, lag selection procedures have been developed based on local models and classical forecasting techniques such as ARIMA. We bridge this gap in the literature by carrying out an extensive empirical analysis of different lag selection methods. We focus on deep learning methods trained in a global approach, i.e., on datasets comprising multiple univariate time series. The experiments were carried out using three benchmark databases that contain a total of 2411 univariate time series. The results indicate that the lag size is a relevant parameter for accurate forecasts. In particular, excessively small or excessively large lag sizes have a considerable negative impact on forecasting performance. Cross-validation approaches show the best performance for lag selection, but this performance is comparable with simple heuristics.
Time Series Data Augmentation as an Imbalanced Learning Problem
Apr 29, 2024



Abstract:Recent state-of-the-art forecasting methods are trained on collections of time series. These methods, often referred to as global models, can capture common patterns in different time series to improve their generalization performance. However, they require large amounts of data that might not be readily available. Besides this, global models sometimes fail to capture relevant patterns unique to a particular time series. In these cases, data augmentation can be useful to increase the sample size of time series datasets. The main contribution of this work is a novel method for generating univariate time series synthetic samples. Our approach stems from the insight that the observations concerning a particular time series of interest represent only a small fraction of all observations. In this context, we frame the problem of training a forecasting model as an imbalanced learning task. Oversampling strategies are popular approaches used to deal with the imbalance problem in machine learning. We use these techniques to create synthetic time series observations and improve the accuracy of forecasting models. We carried out experiments using 7 different databases that contain a total of 5502 univariate time series. We found that the proposed solution outperforms both a global and a local model, thus providing a better trade-off between these two approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge