Valentina Anita Carriero
Procedural Knowledge Ontology (PKO)
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Processes, workflows and guidelines are core to ensure the correct functioning of industrial companies: for the successful operations of factory lines, machinery or services, often industry operators rely on their past experience and know-how. The effect is that this Procedural Knowledge (PK) remains tacit and, as such, difficult to exploit efficiently and effectively. This paper presents PKO, the Procedural Knowledge Ontology, which enables the explicit modeling of procedures and their executions, by reusing and extending existing ontologies. PKO is built on requirements collected from three heterogeneous industrial use cases and can be exploited by any AI and data-driven tools that rely on a shared and interoperable representation to support the governance of PK throughout its life cycle. We describe its structure and design methodology, and outline its relevance, quality, and impact by discussing applications leveraging PKO for PK elicitation and exploitation.
Human Evaluation of Procedural Knowledge Graph Extraction from Text with Large Language Models
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:Procedural Knowledge is the know-how expressed in the form of sequences of steps needed to perform some tasks. Procedures are usually described by means of natural language texts, such as recipes or maintenance manuals, possibly spread across different documents and systems, and their interpretation and subsequent execution is often left to the reader. Representing such procedures in a Knowledge Graph (KG) can be the basis to build digital tools to support those users who need to apply or execute them. In this paper, we leverage Large Language Model (LLM) capabilities and propose a prompt engineering approach to extract steps, actions, objects, equipment and temporal information from a textual procedure, in order to populate a Procedural KG according to a pre-defined ontology. We evaluate the KG extraction results by means of a user study, in order to qualitatively and quantitatively assess the perceived quality and usefulness of the LLM-extracted procedural knowledge. We show that LLMs can produce outputs of acceptable quality and we assess the subjective perception of AI by human evaluators.
OntoChat: a Framework for Conversational Ontology Engineering using Language Models
Mar 09, 2024Abstract:Ontology engineering (OE) in large projects poses a number of challenges arising from the heterogeneous backgrounds of the various stakeholders, domain experts, and their complex interactions with ontology designers. This multi-party interaction often creates systematic ambiguities and biases from the elicitation of ontology requirements, which directly affect the design, evaluation and may jeopardise the target reuse. Meanwhile, current OE methodologies strongly rely on manual activities (e.g., interviews, discussion pages). After collecting evidence on the most crucial OE activities, we introduce OntoChat, a framework for conversational ontology engineering that supports requirement elicitation, analysis, and testing. By interacting with a conversational agent, users can steer the creation of user stories and the extraction of competency questions, while receiving computational support to analyse the overall requirements and test early versions of the resulting ontologies. We evaluate OntoChat by replicating the engineering of the Music Meta Ontology, and collecting preliminary metrics on the effectiveness of each component from users. We release all code at https://github.com/King-s-Knowledge-Graph-Lab/OntoChat.
The Music Meta Ontology: a flexible semantic model for the interoperability of music metadata
Nov 07, 2023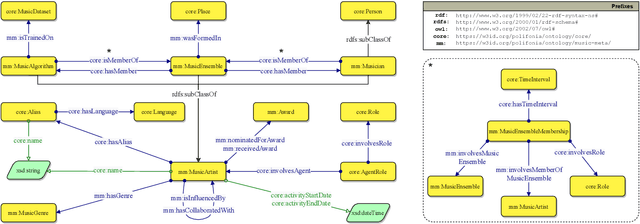
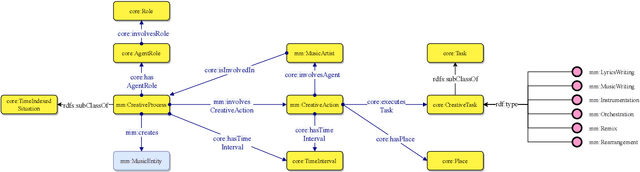
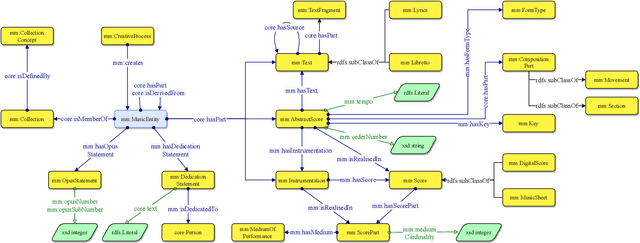

Abstract:The semantic description of music metadata is a key requirement for the creation of music datasets that can be aligned, integrated, and accessed for information retrieval and knowledge discovery. It is nonetheless an open challenge due to the complexity of musical concepts arising from different genres, styles, and periods -- standing to benefit from a lingua franca to accommodate various stakeholders (musicologists, librarians, data engineers, etc.). To initiate this transition, we introduce the Music Meta ontology, a rich and flexible semantic model to describe music metadata related to artists, compositions, performances, recordings, and links. We follow eXtreme Design methodologies and best practices for data engineering, to reflect the perspectives and the requirements of various stakeholders into the design of the model, while leveraging ontology design patterns and accounting for provenance at different levels (claims, links). After presenting the main features of Music Meta, we provide a first evaluation of the model, alignments to other schema (Music Ontology, DOREMUS, Wikidata), and support for data transformation.
Extraction of common conceptual components from multiple ontologies
Jun 24, 2021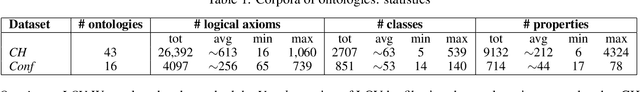
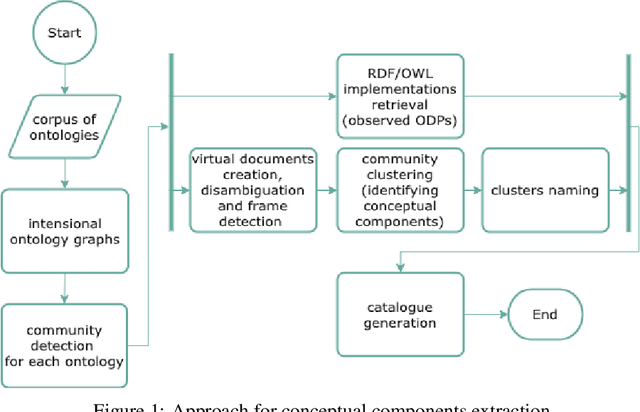
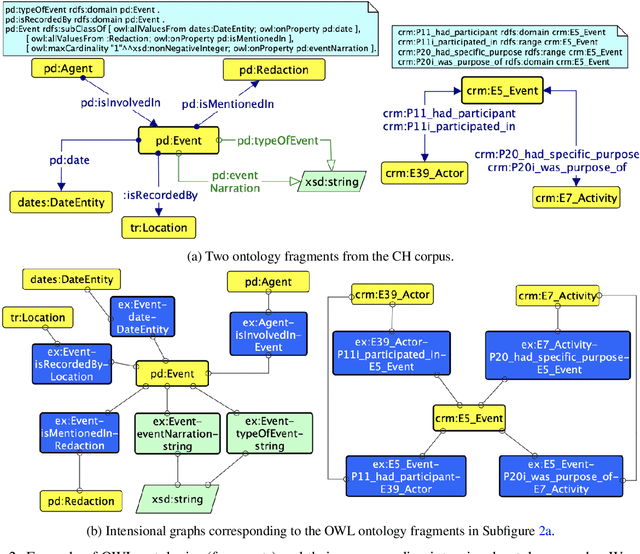
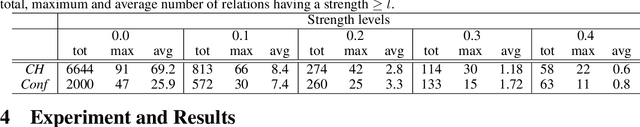
Abstract:We describe a novel method for identifying and extracting conceptual components from domain ontologies, which are used to understand and compare them. The method is applied to two corpora of ontologies in the Cultural Heritage and Conference domain, respectively. The results, which show good quality, are evaluated by manual inspection and by correlation with datasets and tool performance from the ontology alignment evaluation initiative.
An Ontology Design Pattern for representing Recurrent Situations
Jan 01, 2021
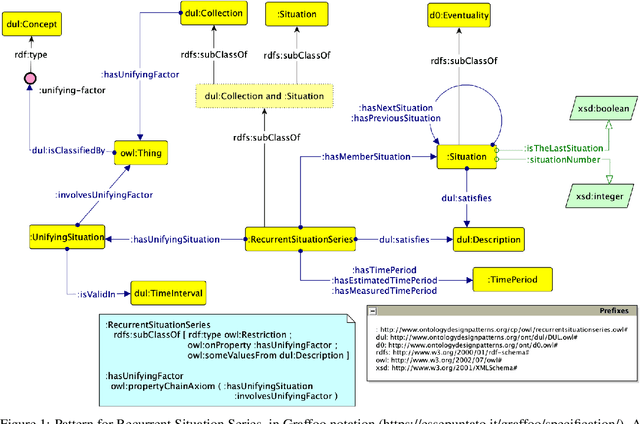
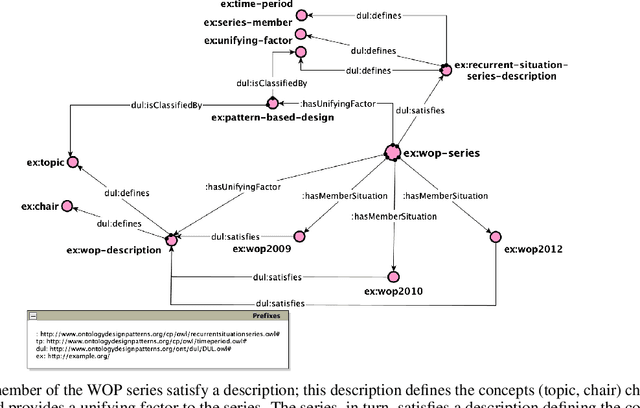
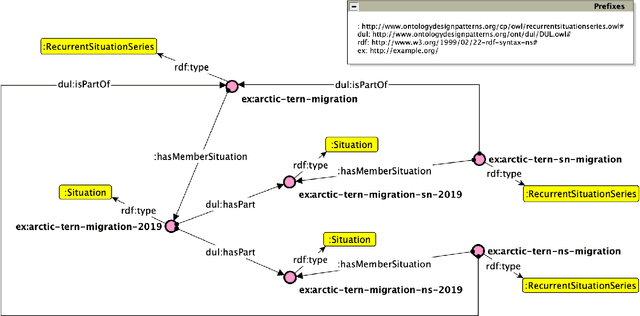
Abstract:In this paper, we present an Ontology Design Pattern for representing situations that recur at regular periods and share some invariant factors, which unify them conceptually: we refer to this set of recurring situations as recurrent situation series. The proposed pattern appears to be foundational, since it can be generalised for modelling the top-level domain-independent concept of recurrence, which is strictly associated with invariance. The pattern reuses other foundational patterns such as Collection, Description and Situation, Classification, Sequence. Indeed, a recurrent situation series is formalised as both a collection of situations occurring regularly over time and unified according to some properties that are common to all the members, and a situation itself, which provides a relational context to its members that satisfy a reference description. Besides including some exemplifying instances of this pattern, we show how it has been implemented and specialised to model recurrent cultural events and ceremonies in ArCo, the Knowledge Graph of Italian cultural heritage.
Knowledge Graphs Evolution and Preservation -- A Technical Report from ISWS 2019
Dec 22, 2020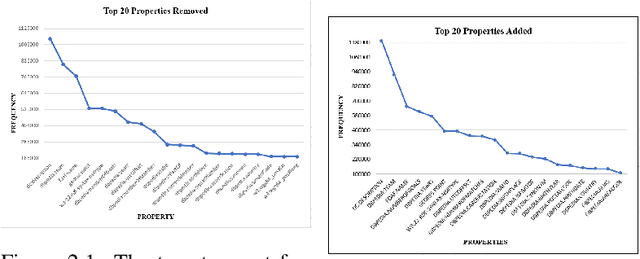

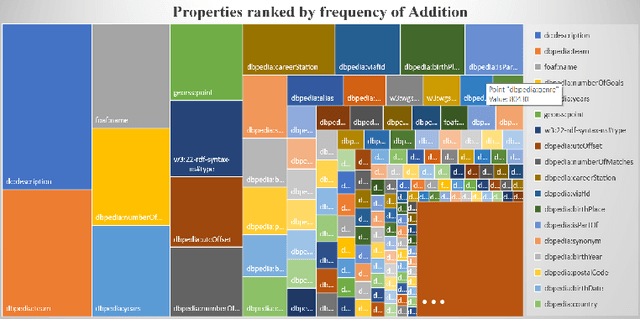
Abstract:One of the grand challenges discussed during the Dagstuhl Seminar "Knowledge Graphs: New Directions for Knowledge Representation on the Semantic Web" and described in its report is that of a: "Public FAIR Knowledge Graph of Everything: We increasingly see the creation of knowledge graphs that capture information about the entirety of a class of entities. [...] This grand challenge extends this further by asking if we can create a knowledge graph of "everything" ranging from common sense concepts to location based entities. This knowledge graph should be "open to the public" in a FAIR manner democratizing this mass amount of knowledge." Although linked open data (LOD) is one knowledge graph, it is the closest realisation (and probably the only one) to a public FAIR Knowledge Graph (KG) of everything. Surely, LOD provides a unique testbed for experimenting and evaluating research hypotheses on open and FAIR KG. One of the most neglected FAIR issues about KGs is their ongoing evolution and long term preservation. We want to investigate this problem, that is to understand what preserving and supporting the evolution of KGs means and how these problems can be addressed. Clearly, the problem can be approached from different perspectives and may require the development of different approaches, including new theories, ontologies, metrics, strategies, procedures, etc. This document reports a collaborative effort performed by 9 teams of students, each guided by a senior researcher as their mentor, attending the International Semantic Web Research School (ISWS 2019). Each team provides a different perspective to the problem of knowledge graph evolution substantiated by a set of research questions as the main subject of their investigation. In addition, they provide their working definition for KG preservation and evolution.
The Landscape of Ontology Reuse Approaches
Nov 25, 2020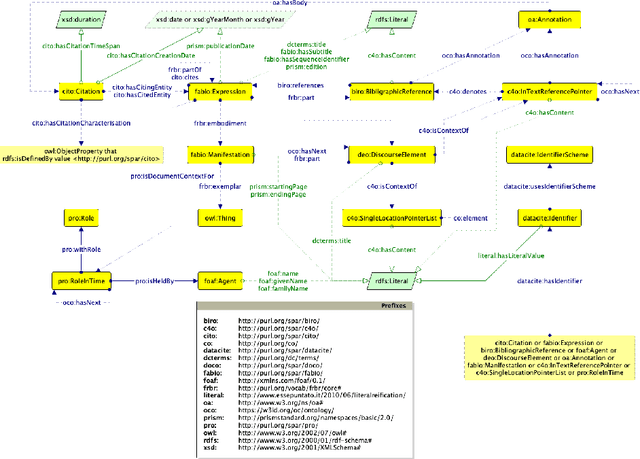
Abstract:Ontology reuse aims to foster interoperability and facilitate knowledge reuse. Several approaches are typically evaluated by ontology engineers when bootstrapping a new project. However, current practices are often motivated by subjective, case-by-case decisions, which hamper the definition of a recommended behaviour. In this chapter we argue that to date there are no effective solutions for supporting developers' decision-making process when deciding on an ontology reuse strategy. The objective is twofold: (i) to survey current approaches to ontology reuse, presenting motivations, strategies, benefits and limits, and (ii) to analyse two representative approaches and discuss their merits.
Pattern-based design applied to cultural heritage knowledge graphs
Nov 18, 2019



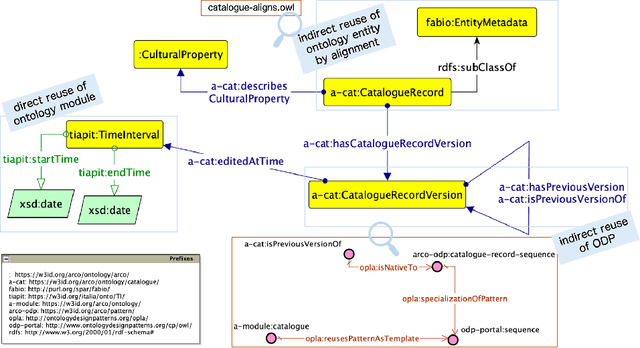
Abstract:Ontology Design Patterns (ODPs) have become an established and recognised practice for guaranteeing good quality ontology engineering. There are several ODP repositories where ODPs are shared as well as ontology design methodologies recommending their reuse. Performing rigorous testing is recommended as well for supporting ontology maintenance and validating the resulting resource against its motivating requirements. Nevertheless, it is less than straightforward to find guidelines on how to apply such methodologies for developing domain-specific knowledge graphs. ArCo is the knowledge graph of Italian Cultural Heritage and has been developed by using eXtreme Design (XD), an ODP- and test-driven methodology. During its development, XD has been adapted to the need of the CH domain e.g. gathering requirements from an open, diverse community of consumers, a new ODP has been defined and many have been specialised to address specific CH requirements. This paper presents ArCo and describes how to apply XD to the development and validation of a CH knowledge graph, also detailing the (intellectual) process implemented for matching the encountered modelling problems to ODPs. Relevant contributions also include a novel web tool for supporting unit-testing of knowledge graphs, a rigorous evaluation of ArCo, and a discussion of methodological lessons learned during ArCo development.
ArCo: the Italian Cultural Heritage Knowledge Graph
May 07, 2019



Abstract:ArCo is the Italian Cultural Heritage knowledge graph, consisting of a network of seven vocabularies and 169 million triples about 820 thousand cultural entities. It is distributed jointly with a SPARQL endpoint, a software for converting catalogue records to RDF, and a rich suite of documentation material (testing, evaluation, how-to, examples, etc.). ArCo is based on the official General Catalogue of the Italian Ministry of Cultural Heritage and Activities (MiBAC) - and its associated encoding regulations - which collects and validates the catalogue records of (ideally) all Italian Cultural Heritage properties (excluding libraries and archives), contributed by CH administrators from all over Italy. We present its structure, design methods and tools, its growing community, and delineate its importance, quality, and impact.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge