Kholoud Alghamdi
Exploring and Eliciting Needs and Preferences from Editors for Wikidata Recommendations
Dec 04, 2022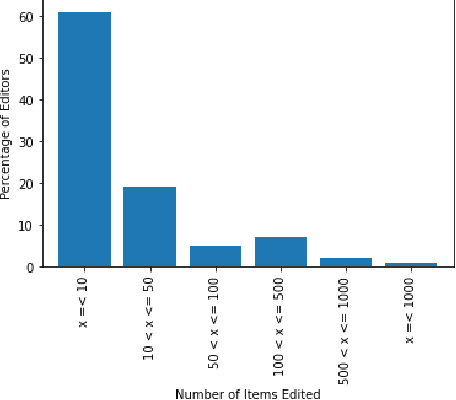


Abstract:Wikidata is an open knowledge graph created, managed, and maintained collaboratively by a global community of volunteers. As it continues to grow, it faces substantial editor engagement challenges, including acquiring new editors to tackle an increasing workload and retaining existing editors. Experiences from other online communities and peer-production systems, including Wikipedia, suggest that recommending tasks to editors could help with both. Our aim with this paper is to elicit the user requirements for a Wikidata recommendations system. We conduct a mixed-methods study with a thematic analysis of in-depth interviews with 31 Wikidata editors and three Wikimedia managers, complemented by a quantitative analysis of edit records of 3,740 Wikidata editors. The insights gained from the study help us outline design requirements for the Wikidata recommender system. We conclude with a discussion of the implications of this work and directions for future work.
Knowledge Graphs Evolution and Preservation -- A Technical Report from ISWS 2019
Dec 22, 2020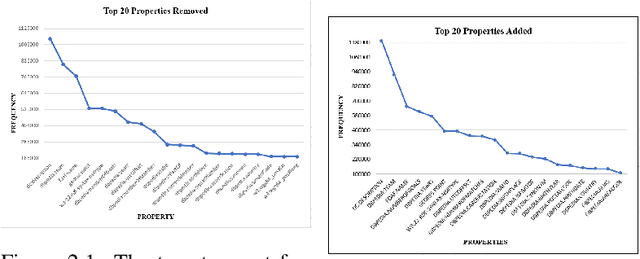
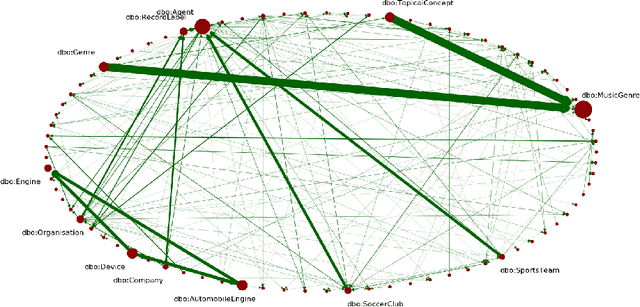

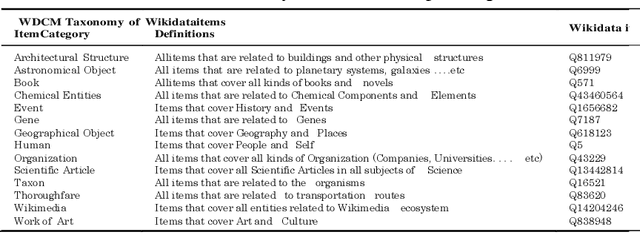
Abstract:One of the grand challenges discussed during the Dagstuhl Seminar "Knowledge Graphs: New Directions for Knowledge Representation on the Semantic Web" and described in its report is that of a: "Public FAIR Knowledge Graph of Everything: We increasingly see the creation of knowledge graphs that capture information about the entirety of a class of entities. [...] This grand challenge extends this further by asking if we can create a knowledge graph of "everything" ranging from common sense concepts to location based entities. This knowledge graph should be "open to the public" in a FAIR manner democratizing this mass amount of knowledge." Although linked open data (LOD) is one knowledge graph, it is the closest realisation (and probably the only one) to a public FAIR Knowledge Graph (KG) of everything. Surely, LOD provides a unique testbed for experimenting and evaluating research hypotheses on open and FAIR KG. One of the most neglected FAIR issues about KGs is their ongoing evolution and long term preservation. We want to investigate this problem, that is to understand what preserving and supporting the evolution of KGs means and how these problems can be addressed. Clearly, the problem can be approached from different perspectives and may require the development of different approaches, including new theories, ontologies, metrics, strategies, procedures, etc. This document reports a collaborative effort performed by 9 teams of students, each guided by a senior researcher as their mentor, attending the International Semantic Web Research School (ISWS 2019). Each team provides a different perspective to the problem of knowledge graph evolution substantiated by a set of research questions as the main subject of their investigation. In addition, they provide their working definition for KG preservation and evolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge