Ulisses Braga-Neto
Convolution Operator Network for Forward and Inverse Problems (FI-Conv): Application to Plasma Turbulence Simulations
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:We propose the Convolutional Operator Network for Forward and Inverse Problems (FI-Conv), a framework capable of predicting system evolution and estimating parameters in complex spatio-temporal dynamics, such as turbulence. FI-Conv is built on a U-Net architecture, in which most convolutional layers are replaced by ConvNeXt V2 blocks. This design preserves U-Net performance on inputs with high-frequency variations while maintaining low computational complexity. FI-Conv uses an initial state, PDE parameters, and evolution time as input to predict the system future state. As a representative example of a system exhibiting complex dynamics, we evaluate the performance of FI-Conv on the task of predicting turbulent plasma fields governed by the Hasegawa-Wakatani (HW) equations. The HW system models two-dimensional electrostatic drift-wave turbulence and exhibits strongly nonlinear behavior, making accurate approximation and long-term prediction particularly challenging. Using an autoregressive forecasting procedure, FI-Conv achieves accurate forward prediction of the plasma state evolution over short times (t ~ 3) and captures the statistic properties of derived physical quantities of interest over longer times (t ~ 100). Moreover, we develop a gradient-descent-based inverse estimation method that accurately infers PDE parameters from plasma state evolution data, without modifying the trained model weights. Collectively, our results demonstrate that FI-Conv can be an effective alternative to existing physics-informed machine learning methods for systems with complex spatio-temporal dynamics.
Free-RBF-KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks with Adaptive Radial Basis Functions for Efficient Function Learning
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) have shown strong potential for efficiently approximating complex nonlinear functions. However, the original KAN formulation relies on B-spline basis functions, which incur substantial computational overhead due to De Boor's algorithm. To address this limitation, recent work has explored alternative basis functions such as radial basis functions (RBFs) that can improve computational efficiency and flexibility. Yet, standard RBF-KANs often sacrifice accuracy relative to the original KAN design. In this work, we propose Free-RBF-KAN, a RBF-based KAN architecture that incorporates adaptive learning grids and trainable smoothness to close this performance gap. Our method employs freely learnable RBF shapes that dynamically align grid representations with activation patterns, enabling expressive and adaptive function approximation. Additionally, we treat smoothness as a kernel parameter optimized jointly with network weights, without increasing computational complexity. We provide a general universality proof for RBF-KANs, which encompasses our Free-RBF-KAN formulation. Through a broad set of experiments, including multiscale function approximation, physics-informed machine learning, and PDE solution operator learning, Free-RBF-KAN achieves accuracy comparable to the original B-spline-based KAN while delivering faster training and inference. These results highlight Free-RBF-KAN as a compelling balance between computational efficiency and adaptive resolution, particularly for high-dimensional structured modeling tasks.
BumpNet: A Sparse Neural Network Framework for Learning PDE Solutions
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:We introduce BumpNet, a sparse neural network framework for PDE numerical solution and operator learning. BumpNet is based on meshless basis function expansion, in a similar fashion to radial-basis function (RBF) networks. Unlike RBF networks, the basis functions in BumpNet are constructed from ordinary sigmoid activation functions. This enables the efficient use of modern training techniques optimized for such networks. All parameters of the basis functions, including shape, location, and amplitude, are fully trainable. Model parsimony and h-adaptivity are effectively achieved through dynamically pruning basis functions during training. BumpNet is a general framework that can be combined with existing neural architectures for learning PDE solutions: here, we propose Bump-PINNs (BumpNet with physics-informed neural networks) for solving general PDEs; Bump-EDNN (BumpNet with evolutionary deep neural networks) to solve time-evolution PDEs; and Bump-DeepONet (BumpNet with deep operator networks) for PDE operator learning. Bump-PINNs are trained using the same collocation-based approach used by PINNs, Bump-EDNN uses a BumpNet only in the spatial domain and uses EDNNs to advance the solution in time, while Bump-DeepONets employ a BumpNet regression network as the trunk network of a DeepONet. Extensive numerical experiments demonstrate the efficiency and accuracy of the proposed architecture.
In-Context Multi-Operator Learning with DeepOSets
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:In-context Learning (ICL) is the remarkable capability displayed by some machine learning models to learn from examples in a prompt, without any further weight updates. ICL had originally been thought to emerge from the self-attention mechanism in autoregressive transformer architectures. DeepOSets is a non-autoregressive, non-attention based neural architecture that combines set learning via the DeepSets architecture with operator learning via Deep Operator Networks (DeepONets). In a previous study, DeepOSets was shown to display ICL capabilities in supervised learning problems. In this paper, we show that the DeepOSets architecture, with the appropriate modifications, is a multi-operator in-context learner that can recover the solution operator of a new PDE, not seen during training, from example pairs of parameter and solution placed in a user prompt, without any weight updates. Furthermore, we show that DeepOSets is a universal uniform approximator over a class of continuous operators, which we believe is the first result of its kind in the literature of scientific machine learning. This means that a single DeepOSets architecture exists that approximates in-context any continuous operator in the class to any fixed desired degree accuracy, given an appropriate number of examples in the prompt. Experiments with Poisson and reaction-diffusion forward and inverse boundary-value problems demonstrate the ability of the proposed model to use in-context examples to predict accurately the solutions corresponding to parameter queries for PDEs not seen during training.
Generalized Resubstitution for Regression Error Estimation
Oct 23, 2024Abstract:We propose generalized resubstitution error estimators for regression, a broad family of estimators, each corresponding to a choice of empirical probability measures and loss function. The usual sum of squares criterion is a special case corresponding to the standard empirical probability measure and the quadratic loss. Other choices of empirical probability measure lead to more general estimators with superior bias and variance properties. We prove that these error estimators are consistent under broad assumptions. In addition, procedures for choosing the empirical measure based on the method of moments and maximum pseudo-likelihood are proposed and investigated. Detailed experimental results using polynomial regression demonstrate empirically the superior finite-sample bias and variance properties of the proposed estimators. The R code for the experiments is provided.
DeepOSets: Non-Autoregressive In-Context Learning of Supervised Learning Operators
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:We introduce DeepSets Operator Networks (DeepOSets), an efficient, non-autoregressive neural network architecture for in-context operator learning. In-context learning allows a trained machine learning model to learn from a user prompt without further training. DeepOSets adds in-context learning capabilities to Deep Operator Networks (DeepONets) by combining it with the DeepSets architecture. As the first non-autoregressive model for in-context operator learning, DeepOSets allow the user prompt to be processed in parallel, leading to significant computational savings. Here, we present the application of DeepOSets in the problem of learning supervised learning algorithms, which are operators mapping a finite-dimensional space of labeled data into an infinite-dimensional hypothesis space of prediction functions. In an empirical comparison with a popular autoregressive (transformer-based) model for in-context learning of the least-squares linear regression algorithm, DeepOSets reduced the number of model weights by several orders of magnitude and required a fraction of training and inference time. Furthermore, DeepOSets proved to be less sensitive to noise, outperforming the transformer model in noisy settings.
Label Propagation Training Schemes for Physics-Informed Neural Networks and Gaussian Processes
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes a semi-supervised methodology for training physics-informed machine learning methods. This includes self-training of physics-informed neural networks and physics-informed Gaussian processes in isolation, and the integration of the two via co-training. We demonstrate via extensive numerical experiments how these methods can ameliorate the issue of propagating information forward in time, which is a common failure mode of physics-informed machine learning.
Characteristics-Informed Neural Networks for Forward and Inverse Hyperbolic Problems
Dec 28, 2022
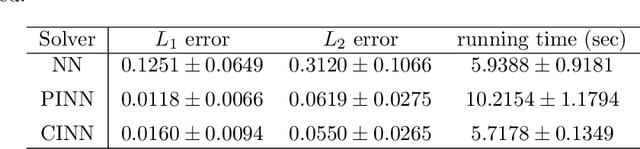

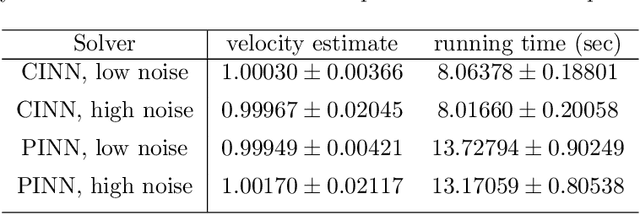
Abstract:We propose characteristic-informed neural networks (CINN), a simple and efficient machine learning approach for solving forward and inverse problems involving hyperbolic PDEs. Like physics-informed neural networks (PINN), CINN is a meshless machine learning solver with universal approximation capabilities. Unlike PINN, which enforces a PDE softly via a multi-part loss function, CINN encodes the characteristics of the PDE in a general-purpose deep neural network trained with the usual MSE data-fitting regression loss and standard deep learning optimization methods. This leads to faster training and can avoid well-known pathologies of gradient descent optimization of multi-part PINN loss functions. If the characteristic ODEs can be solved exactly, which is true in important cases, the output of a CINN is an exact solution of the PDE, even at initialization, preventing the occurrence of non-physical outputs. Otherwise, the ODEs must be solved approximately, but the CINN is still trained only using a data-fitting loss function. The performance of CINN is assessed empirically in forward and inverse linear hyperbolic problems. These preliminary results indicate that CINN is able to improve on the accuracy of the baseline PINN, while being nearly twice as fast to train and avoiding non-physical solutions. Future extensions to hyperbolic PDE systems and nonlinear PDEs are also briefly discussed.
Plastic Contaminant Detection in Aerial Imagery of Cotton Fields with Deep Learning
Dec 14, 2022



Abstract:Plastic shopping bags that get carried away from the side of roads and tangled on cotton plants can end up at cotton gins if not removed before the harvest. Such bags may not only cause problem in the ginning process but might also get embodied in cotton fibers reducing its quality and marketable value. Therefore, it is required to detect, locate, and remove the bags before cotton is harvested. Manually detecting and locating these bags in cotton fields is labor intensive, time-consuming and a costly process. To solve these challenges, we present application of four variants of YOLOv5 (YOLOv5s, YOLOv5m, YOLOv5l and YOLOv5x) for detecting plastic shopping bags using Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS)-acquired RGB (Red, Green, and Blue) images. We also show fixed effect model tests of color of plastic bags as well as YOLOv5-variant on average precision (AP), mean average precision (mAP@50) and accuracy. In addition, we also demonstrate the effect of height of plastic bags on the detection accuracy. It was found that color of bags had significant effect (p < 0.001) on accuracy across all the four variants while it did not show any significant effect on the AP with YOLOv5m (p = 0.10) and YOLOv5x (p = 0.35) at 95% confidence level. Similarly, YOLOv5-variant did not show any significant effect on the AP (p = 0.11) and accuracy (p = 0.73) of white bags, but it had significant effects on the AP (p = 0.03) and accuracy (p = 0.02) of brown bags including on the mAP@50 (p = 0.01) and inference speed (p < 0.0001). Additionally, height of plastic bags had significant effect (p < 0.0001) on overall detection accuracy. The findings reported in this paper can be useful in speeding up removal of plastic bags from cotton fields before harvest and thereby reducing the amount of contaminants that end up at cotton gins.
Assessing The Performance of YOLOv5 Algorithm for Detecting Volunteer Cotton Plants in Corn Fields at Three Different Growth Stages
Jul 31, 2022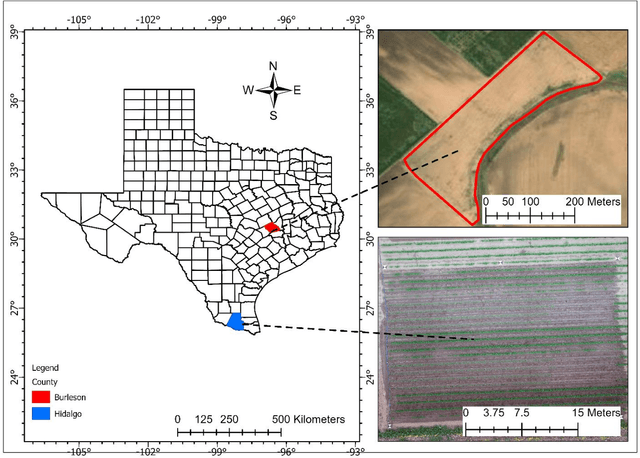
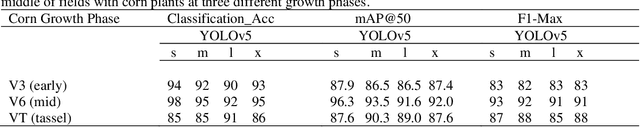


Abstract:The boll weevil (Anthonomus grandis L.) is a serious pest that primarily feeds on cotton plants. In places like Lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas, due to sub-tropical climatic conditions, cotton plants can grow year-round and therefore the left-over seeds from the previous season during harvest can continue to grow in the middle of rotation crops like corn (Zea mays L.) and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.). These feral or volunteer cotton (VC) plants when reach the pinhead squaring phase (5-6 leaf stage) can act as hosts for the boll weevil pest. The Texas Boll Weevil Eradication Program (TBWEP) employs people to locate and eliminate VC plants growing by the side of roads or fields with rotation crops but the ones growing in the middle of fields remain undetected. In this paper, we demonstrate the application of computer vision (CV) algorithm based on You Only Look Once version 5 (YOLOv5) for detecting VC plants growing in the middle of corn fields at three different growth stages (V3, V6, and VT) using unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) remote sensing imagery. All the four variants of YOLOv5 (s, m, l, and x) were used and their performances were compared based on classification accuracy, mean average precision (mAP), and F1-score. It was found that YOLOv5s could detect VC plants with a maximum classification accuracy of 98% and mAP of 96.3 % at the V6 stage of corn while YOLOv5s and YOLOv5m resulted in the lowest classification accuracy of 85% and YOLOv5m and YOLOv5l had the least mAP of 86.5% at the VT stage on images of size 416 x 416 pixels. The developed CV algorithm has the potential to effectively detect and locate VC plants growing in the middle of corn fields as well as expedite the management aspects of TBWEP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge