Tolga Çukur
NeuroSSM: Multiscale Differential State-Space Modeling for Context-Aware fMRI Analysis
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Accurate fMRI analysis requires sensitivity to temporal structure across multiple scales, as BOLD signals encode cognitive processes that emerge from fast transient dynamics to slower, large-scale fluctuations. Existing deep learning (DL) approaches to temporal modeling face challenges in jointly capturing these dynamics over long fMRI time series. Among current DL models, transformers address long-range dependencies by explicitly modeling pairwise interactions through attention, but the associated quadratic computational cost limits effective integration of temporal dependencies across long fMRI sequences. Selective state-space models (SSMs) instead model long-range temporal dependencies implicitly through latent state evolution in a dynamical system, enabling efficient propagation of dependencies over time. However, recent SSM-based approaches for fMRI commonly operate on derived functional connectivity representations and employ single-scale temporal processing. These design choices constrain the ability to jointly represent fast transient dynamics and slower global trends within a single model. We propose NeuroSSM, a selective state-space architecture designed for end-to-end analysis of raw BOLD signals in fMRI time series. NeuroSSM addresses the above limitations through two complementary design components: a multiscale state-space backbone that captures fast and slow dynamics concurrently, and a parallel differencing branch that increases sensitivity to transient state changes. Experiments on clinical and non-clinical datasets demonstrate that NeuroSSM achieves competitive performance and efficiency against state-of-the-art fMRI analysis methods.
A Tutorial on MRI Reconstruction: From Modern Methods to Clinical Implications
Jul 22, 2025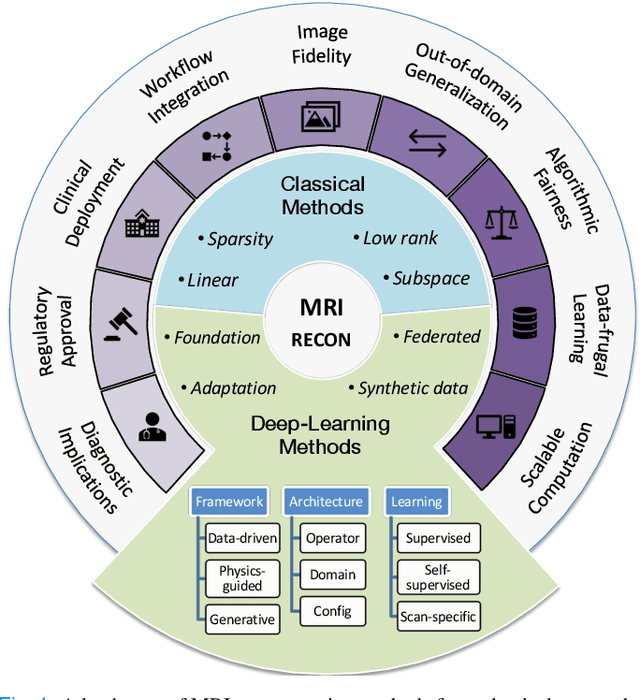
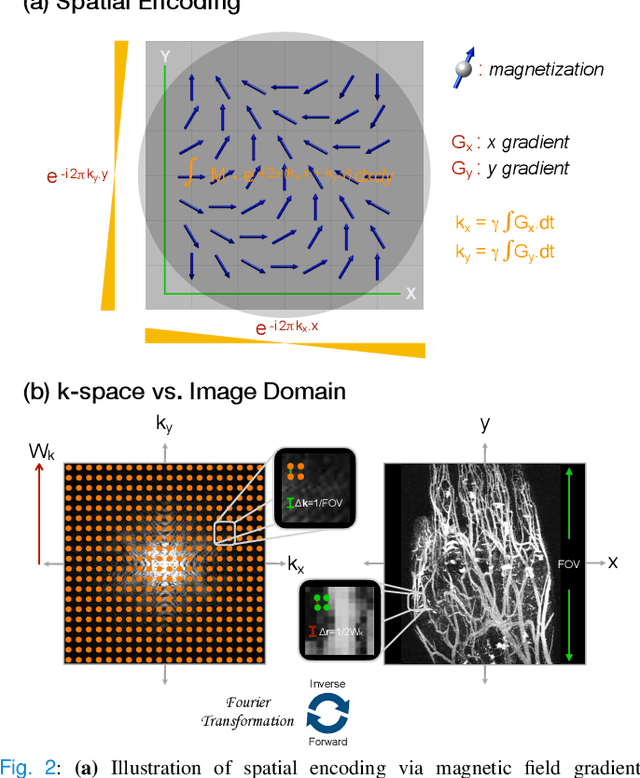
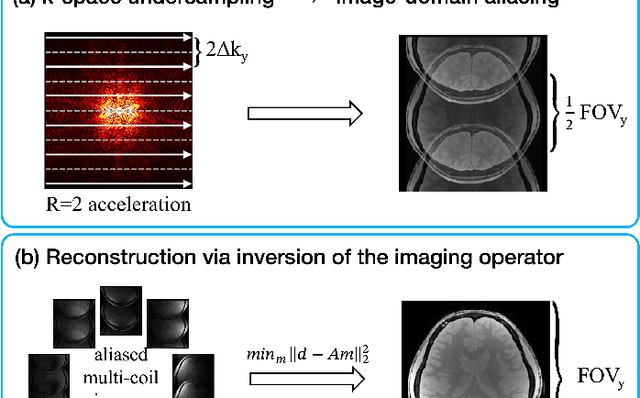
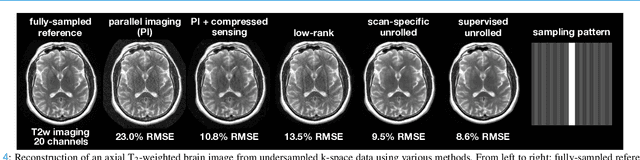
Abstract:MRI is an indispensable clinical tool, offering a rich variety of tissue contrasts to support broad diagnostic and research applications. Clinical exams routinely acquire multiple structural sequences that provide complementary information for differential diagnosis, while research protocols often incorporate advanced functional, diffusion, spectroscopic, and relaxometry sequences to capture multidimensional insights into tissue structure and composition. However, these capabilities come at the cost of prolonged scan times, which reduce patient throughput, increase susceptibility to motion artifacts, and may require trade-offs in image quality or diagnostic scope. Over the last two decades, advances in image reconstruction algorithms--alongside improvements in hardware and pulse sequence design--have made it possible to accelerate acquisitions while preserving diagnostic quality. Central to this progress is the ability to incorporate prior information to regularize the solutions to the reconstruction problem. In this tutorial, we overview the basics of MRI reconstruction and highlight state-of-the-art approaches, beginning with classical methods that rely on explicit hand-crafted priors, and then turning to deep learning methods that leverage a combination of learned and crafted priors to further push the performance envelope. We also explore the translational aspects and eventual clinical implications of these methods. We conclude by discussing future directions to address remaining challenges in MRI reconstruction. The tutorial is accompanied by a Python toolbox (https://github.com/tutorial-MRI-recon/tutorial) to demonstrate select methods discussed in the article.
Efficient Noise Calculation in Deep Learning-based MRI Reconstructions
May 04, 2025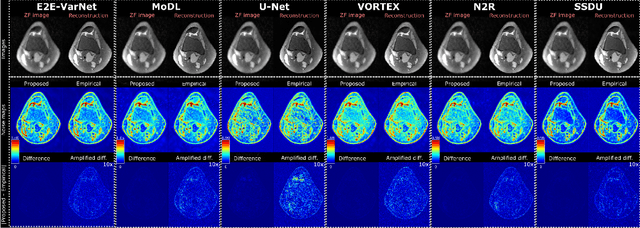
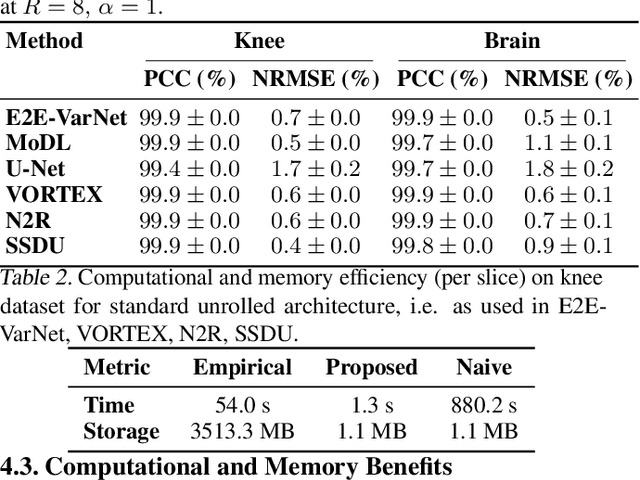
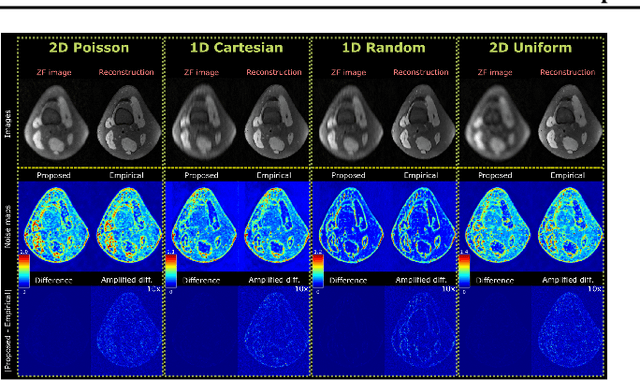
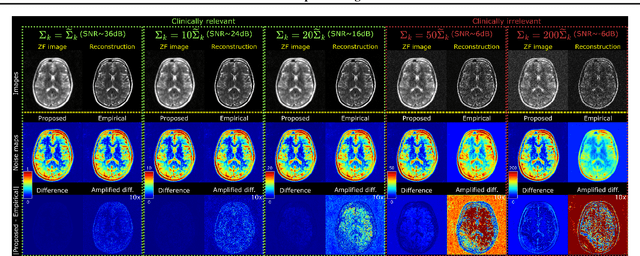
Abstract:Accelerated MRI reconstruction involves solving an ill-posed inverse problem where noise in acquired data propagates to the reconstructed images. Noise analyses are central to MRI reconstruction for providing an explicit measure of solution fidelity and for guiding the design and deployment of novel reconstruction methods. However, deep learning (DL)-based reconstruction methods have often overlooked noise propagation due to inherent analytical and computational challenges, despite its critical importance. This work proposes a theoretically grounded, memory-efficient technique to calculate voxel-wise variance for quantifying uncertainty due to acquisition noise in accelerated MRI reconstructions. Our approach approximates noise covariance using the DL network's Jacobian, which is intractable to calculate. To circumvent this, we derive an unbiased estimator for the diagonal of this covariance matrix (voxel-wise variance) and introduce a Jacobian sketching technique to efficiently implement it. We evaluate our method on knee and brain MRI datasets for both data- and physics-driven networks trained in supervised and unsupervised manners. Compared to empirical references obtained via Monte Carlo simulations, our technique achieves near-equivalent performance while reducing computational and memory demands by an order of magnitude or more. Furthermore, our method is robust across varying input noise levels, acceleration factors, and diverse undersampling schemes, highlighting its broad applicability. Our work reintroduces accurate and efficient noise analysis as a central tenet of reconstruction algorithms, holding promise to reshape how we evaluate and deploy DL-based MRI. Our code will be made publicly available upon acceptance.
Meta-Entity Driven Triplet Mining for Aligning Medical Vision-Language Models
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Diagnostic imaging relies on interpreting both images and radiology reports, but the growing data volumes place significant pressure on medical experts, yielding increased errors and workflow backlogs. Medical vision-language models (med-VLMs) have emerged as a powerful framework to efficiently process multimodal imaging data, particularly in chest X-ray (CXR) evaluations, albeit their performance hinges on how well image and text representations are aligned. Existing alignment methods, predominantly based on contrastive learning, prioritize separation between disease classes over segregation of fine-grained pathology attributes like location, size or severity, leading to suboptimal representations. Here, we propose MedTrim (Meta-entity-driven Triplet mining), a novel method that enhances image-text alignment through multimodal triplet learning synergistically guided by disease class as well as adjectival and directional pathology descriptors. Unlike common alignment methods that separate broad disease classes, MedTrim leverages structured meta-entity information to preserve subtle but clinically significant intra-class variations. For this purpose, we first introduce an ontology-based entity recognition module that extracts pathology-specific meta-entities from CXR reports, as annotations on pathology attributes are rare in public datasets. For refined sample selection in triplet mining, we then introduce a novel score function that captures an aggregate measure of inter-sample similarity based on disease classes and adjectival/directional descriptors. Lastly, we introduce a multimodal triplet alignment objective for explicit within- and cross-modal alignment between samples sharing detailed pathology characteristics. Our demonstrations indicate that MedTrim improves performance in downstream retrieval and classification tasks compared to state-of-the-art alignment methods.
Generative Autoregressive Transformers for Model-Agnostic Federated MRI Reconstruction
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Although learning-based models hold great promise for MRI reconstruction, single-site models built on limited local datasets often suffer from poor generalization. This challenge has spurred interest in collaborative model training on multi-site datasets via federated learning (FL) -- a privacy-preserving framework that aggregates model updates instead of sharing imaging data. Conventional FL builds a global model by aggregating locally trained model weights, inherently constraining all sites to a homogeneous model architecture. This rigid homogeneity requirement forces sites to forgo architectures tailored to their compute infrastructure and application-specific demands. Consequently, existing FL methods for MRI reconstruction fail to support model-heterogeneous settings, where individual sites are allowed to use distinct architectures. To overcome this fundamental limitation, here we introduce FedGAT, a novel model-agnostic FL technique based on generative autoregressive transformers. FedGAT decentralizes the training of a global generative prior that captures the distribution of multi-site MR images. For enhanced fidelity, we propose a novel site-prompted GAT prior that controllably synthesizes MR images from desired sites via autoregressive prediction across spatial scales. Each site then trains its site-specific reconstruction model -- using its preferred architecture -- on a hybrid dataset comprising the local MRI dataset and GAT-generated synthetic MRI datasets for other sites. Comprehensive experiments on multi-institutional datasets demonstrate that FedGAT supports flexible collaborations while enjoying superior within-site and across-site reconstruction performance compared to state-of-the-art FL baselines.
Physics-Driven Autoregressive State Space Models for Medical Image Reconstruction
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Medical image reconstruction from undersampled acquisitions is an ill-posed problem that involves inversion of the imaging operator linking measurement and image domains. In recent years, physics-driven (PD) models have gained prominence in learning-based reconstruction given their enhanced balance between efficiency and performance. For reconstruction, PD models cascade data-consistency modules that enforce fidelity to acquired data based on the imaging operator, with network modules that process feature maps to alleviate image artifacts due to undersampling. Success in artifact suppression inevitably depends on the ability of the network modules to tease apart artifacts from underlying tissue structures, both of which can manifest contextual relations over broad spatial scales. Convolutional modules that excel at capturing local correlations are relatively insensitive to non-local context. While transformers promise elevated sensitivity to non-local context, practical implementations often suffer from a suboptimal trade-off between local and non-local sensitivity due to intrinsic model complexity. Here, we introduce a novel physics-driven autoregressive state space model (MambaRoll) for enhanced fidelity in medical image reconstruction. In each cascade of an unrolled architecture, MambaRoll employs an autoregressive framework based on physics-driven state space modules (PSSM), where PSSMs efficiently aggregate contextual features at a given spatial scale while maintaining fidelity to acquired data, and autoregressive prediction of next-scale feature maps from earlier spatial scales enhance capture of multi-scale contextual features. Demonstrations on accelerated MRI and sparse-view CT reconstructions indicate that MambaRoll outperforms state-of-the-art PD methods based on convolutional, transformer and conventional SSM modules.
Bayesian Conditioned Diffusion Models for Inverse Problems
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have recently been shown to excel in many image reconstruction tasks that involve inverse problems based on a forward measurement operator. A common framework uses task-agnostic unconditional models that are later post-conditioned for reconstruction, an approach that typically suffers from suboptimal task performance. While task-specific conditional models have also been proposed, current methods heuristically inject measured data as a naive input channel that elicits sampling inaccuracies. Here, we address the optimal conditioning of diffusion models for solving challenging inverse problems that arise during image reconstruction. Specifically, we propose a novel Bayesian conditioning technique for diffusion models, BCDM, based on score-functions associated with the conditional distribution of desired images given measured data. We rigorously derive the theory to express and train the conditional score-function. Finally, we show state-of-the-art performance in image dealiasing, deblurring, super-resolution, and inpainting with the proposed technique.
I2I-Mamba: Multi-modal medical image synthesis via selective state space modeling
May 22, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, deep learning models comprising transformer components have pushed the performance envelope in medical image synthesis tasks. Contrary to convolutional neural networks (CNNs) that use static, local filters, transformers use self-attention mechanisms to permit adaptive, non-local filtering to sensitively capture long-range context. However, this sensitivity comes at the expense of substantial model complexity, which can compromise learning efficacy particularly on relatively modest-sized imaging datasets. Here, we propose a novel adversarial model for multi-modal medical image synthesis, I2I-Mamba, that leverages selective state space modeling (SSM) to efficiently capture long-range context while maintaining local precision. To do this, I2I-Mamba injects channel-mixed Mamba (cmMamba) blocks in the bottleneck of a convolutional backbone. In cmMamba blocks, SSM layers are used to learn context across the spatial dimension and channel-mixing layers are used to learn context across the channel dimension of feature maps. Comprehensive demonstrations are reported for imputing missing images in multi-contrast MRI and MRI-CT protocols. Our results indicate that I2I-Mamba offers superior performance against state-of-the-art CNN- and transformer-based methods in synthesizing target-modality images.
Self-Consistent Recursive Diffusion Bridge for Medical Image Translation
May 10, 2024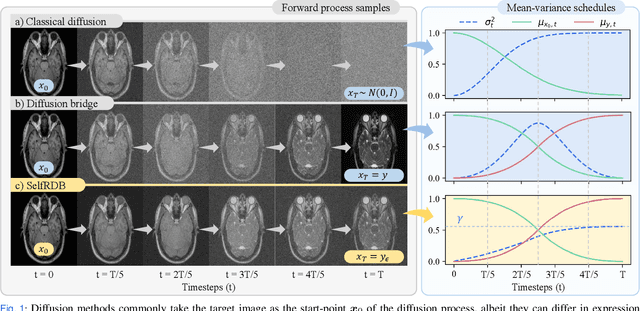
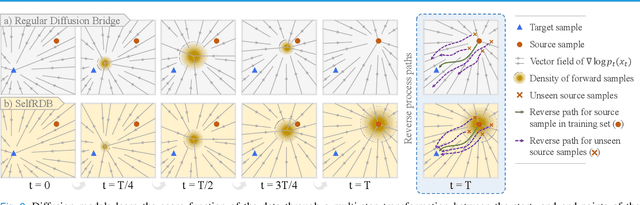
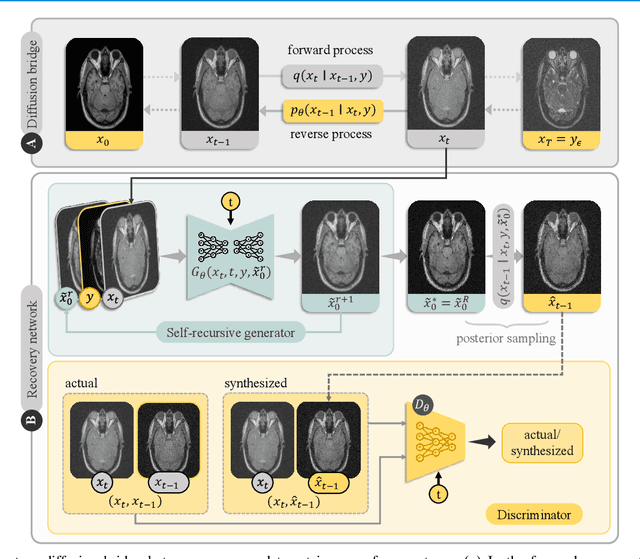
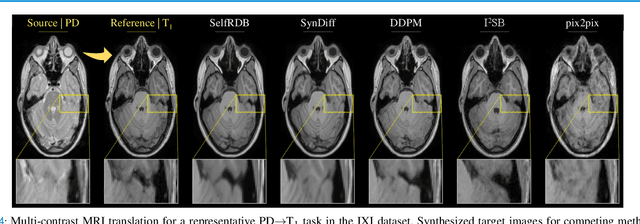
Abstract:Denoising diffusion models (DDM) have gained recent traction in medical image translation given improved training stability over adversarial models. DDMs learn a multi-step denoising transformation to progressively map random Gaussian-noise images onto target-modality images, while receiving stationary guidance from source-modality images. As this denoising transformation diverges significantly from the task-relevant source-to-target transformation, DDMs can suffer from weak source-modality guidance. Here, we propose a novel self-consistent recursive diffusion bridge (SelfRDB) for improved performance in medical image translation. Unlike DDMs, SelfRDB employs a novel forward process with start- and end-points defined based on target and source images, respectively. Intermediate image samples across the process are expressed via a normal distribution with mean taken as a convex combination of start-end points, and variance from additive noise. Unlike regular diffusion bridges that prescribe zero variance at start-end points and high variance at mid-point of the process, we propose a novel noise scheduling with monotonically increasing variance towards the end-point in order to boost generalization performance and facilitate information transfer between the two modalities. To further enhance sampling accuracy in each reverse step, we propose a novel sampling procedure where the network recursively generates a transient-estimate of the target image until convergence onto a self-consistent solution. Comprehensive analyses in multi-contrast MRI and MRI-CT translation indicate that SelfRDB offers superior performance against competing methods.
HydraViT: Adaptive Multi-Branch Transformer for Multi-Label Disease Classification from Chest X-ray Images
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Chest X-ray is an essential diagnostic tool in the identification of chest diseases given its high sensitivity to pathological abnormalities in the lungs. However, image-driven diagnosis is still challenging due to heterogeneity in size and location of pathology, as well as visual similarities and co-occurrence of separate pathology. Since disease-related regions often occupy a relatively small portion of diagnostic images, classification models based on traditional convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are adversely affected given their locality bias. While CNNs were previously augmented with attention maps or spatial masks to guide focus on potentially critical regions, learning localization guidance under heterogeneity in the spatial distribution of pathology is challenging. To improve multi-label classification performance, here we propose a novel method, HydraViT, that synergistically combines a transformer backbone with a multi-branch output module with learned weighting. The transformer backbone enhances sensitivity to long-range context in X-ray images, while using the self-attention mechanism to adaptively focus on task-critical regions. The multi-branch output module dedicates an independent branch to each disease label to attain robust learning across separate disease classes, along with an aggregated branch across labels to maintain sensitivity to co-occurrence relationships among pathology. Experiments demonstrate that, on average, HydraViT outperforms competing attention-guided methods by 1.2%, region-guided methods by 1.4%, and semantic-guided methods by 1.0% in multi-label classification performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge