Tingting Xie
Spatial-Temporal Transformer for 3D Point Cloud Sequences
Oct 19, 2021Abstract:Effective learning of spatial-temporal information within a point cloud sequence is highly important for many down-stream tasks such as 4D semantic segmentation and 3D action recognition. In this paper, we propose a novel framework named Point Spatial-Temporal Transformer (PST2) to learn spatial-temporal representations from dynamic 3D point cloud sequences. Our PST2 consists of two major modules: a Spatio-Temporal Self-Attention (STSA) module and a Resolution Embedding (RE) module. Our STSA module is introduced to capture the spatial-temporal context information across adjacent frames, while the RE module is proposed to aggregate features across neighbors to enhance the resolution of feature maps. We test the effectiveness our PST2 with two different tasks on point cloud sequences, i.e., 4D semantic segmentation and 3D action recognition. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks show that our PST2 outperforms existing methods on all datasets. The effectiveness of our STSA and RE modules have also been justified with ablation experiments.
Relationship-based Neural Baby Talk
Mar 08, 2021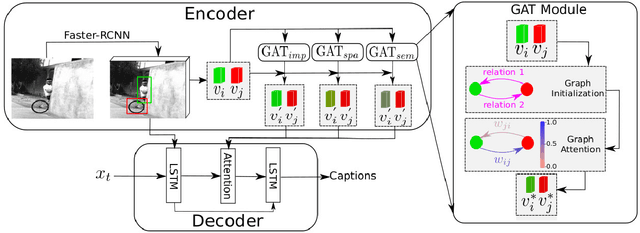
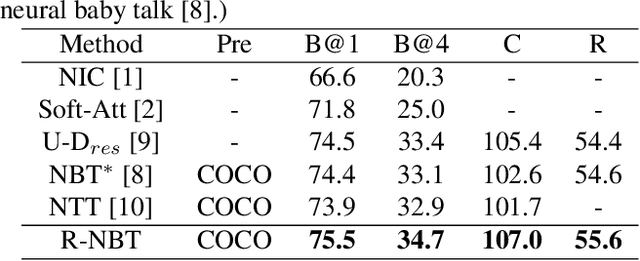
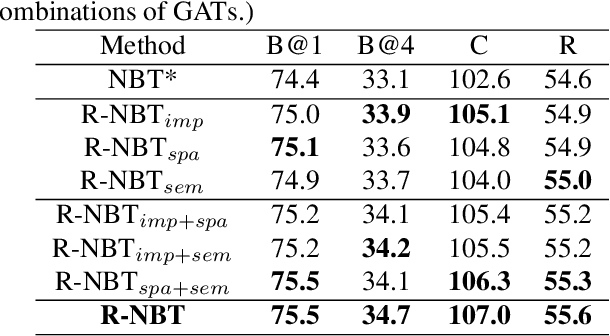

Abstract:Understanding interactions between objects in an image is an important element for generating captions. In this paper, we propose a relationship-based neural baby talk (R-NBT) model to comprehensively investigate several types of pairwise object interactions by encoding each image via three different relationship-based graph attention networks (GATs). We study three main relationships: \textit{spatial relationships} to explore geometric interactions, \textit{semantic relationships} to extract semantic interactions, and \textit{implicit relationships} to capture hidden information that could not be modelled explicitly as above. We construct three relationship graphs with the objects in an image as nodes, and the mutual relationships of pairwise objects as edges. By exploring features of neighbouring regions individually via GATs, we integrate different types of relationships into visual features of each node. Experiments on COCO dataset show that our proposed R-NBT model outperforms state-of-the-art models trained on COCO dataset in three image caption generation tasks.
Exploring Feature Representation and Training strategies in Temporal Action Localization
May 29, 2019



Abstract:Temporal action localization has recently attracted significant interest in the Computer Vision community. However, despite the great progress, it is hard to identify which aspects of the proposed methods contribute most to the increase in localization performance. To address this issue, we conduct ablative experiments on feature extraction methods, fixed-size feature representation methods and training strategies, and report how each influences the overall performance. Based on our findings, we propose a two-stage detector that outperforms the state of the art in THUMOS14, achieving a mAP@tIoU=0.5 equal to 44.2%.
hi-RF: Incremental Learning Random Forest for large-scale multi-class Data Classification
Oct 31, 2016



Abstract:In recent years, dynamically growing data and incrementally growing number of classes pose new challenges to large-scale data classification research. Most traditional methods struggle to balance the precision and computational burden when data and its number of classes increased. However, some methods are with weak precision, and the others are time-consuming. In this paper, we propose an incremental learning method, namely, heterogeneous incremental Nearest Class Mean Random Forest (hi-RF), to handle this issue. It is a heterogeneous method that either replaces trees or updates trees leaves in the random forest adaptively, to reduce the computational time in comparable performance, when data of new classes arrive. Specifically, to keep the accuracy, one proportion of trees are replaced by new NCM decision trees; to reduce the computational load, the rest trees are updated their leaves probabilities only. Most of all, out-of-bag estimation and out-of-bag boosting are proposed to balance the accuracy and the computational efficiency. Fair experiments were conducted and demonstrated its comparable precision with much less computational time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge