Tianbo Wang
AFTER: Mitigating the Object Hallucination of LVLM via Adaptive Factual-Guided Activation Editing
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved substantial progress in cross-modal tasks. However, due to language bias, LVLMs are susceptible to object hallucination, which can be primarily divided into category, attribute, and relation hallucination, significantly impeding the trustworthy AI applications. Editing the internal activations of LVLMs has shown promising effectiveness in mitigating hallucinations with minimal cost. However, previous editing approaches neglect the effective guidance offered by factual textual semantics, thereby struggling to explicitly mitigate language bias. To address these issues, we propose Adaptive Factual-guided Visual-Textual Editing for hallucination mitigation (AFTER), which comprises Factual-Augmented Activation Steering (FAS) and Query-Adaptive Offset Optimization (QAO), to adaptively guides the original biased activations towards factual semantics. Specifically, FAS is proposed to provide factual and general guidance for activation editing, thereby explicitly modeling the precise visual-textual associations. Subsequently, QAO introduces a query-aware offset estimator to establish query-specific editing from the general steering vector, enhancing the diversity and granularity of editing. Extensive experiments on standard hallucination benchmarks across three widely adopted LVLMs validate the efficacy of the proposed AFTER, notably achieving up to a 16.3% reduction of hallucination over baseline on the AMBER benchmark. Our code and data will be released for reproducibility.
Video-rate gigapixel ptychography via space-time neural field representations
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Achieving gigapixel space-bandwidth products (SBP) at video rates represents a fundamental challenge in imaging science. Here we demonstrate video-rate ptychography that overcomes this barrier by exploiting spatiotemporal correlations through neural field representations. Our approach factorizes the space-time volume into low-rank spatial and temporal features, transforming SBP scaling from sequential measurements to efficient correlation extraction. The architecture employs dual networks for decoding real and imaginary field components, avoiding phase-wrapping discontinuities plagued in amplitude-phase representations. A gradient-domain loss on spatial derivatives ensures robust convergence. We demonstrate video-rate gigapixel imaging with centimeter-scale coverage while resolving 308-nm linewidths. Validations span from monitoring sample dynamics of crystals, bacteria, stem cells, microneedle to characterizing time-varying probes in extreme ultraviolet experiments, demonstrating versatility across wavelengths. By transforming temporal variations from a constraint into exploitable correlations, we establish that gigapixel video is tractable with single-sensor measurements, making ptychography a high-throughput sensing tool for monitoring mesoscale dynamics without lenses.
Deep-ultraviolet ptychographic pocket-scope (DART): mesoscale lensless molecular imaging with label-free spectroscopic contrast
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:The mesoscale characterization of biological specimens has traditionally required compromises between resolution, field-of-view, depth-of-field, and molecular specificity, with most approaches relying on external labels. Here we present the Deep-ultrAviolet ptychogRaphic pockeT-scope (DART), a handheld platform that transforms label-free molecular imaging through intrinsic deep-ultraviolet spectroscopic contrast. By leveraging biomolecules' natural absorption fingerprints and combining them with lensless ptychographic microscopy, DART resolves down to 308-nm linewidths across centimeter-scale areas while maintaining millimeter-scale depth-of-field. The system's virtual error-bin methodology effectively eliminates artifacts from limited temporal coherence and other optical imperfections, enabling high-fidelity molecular imaging without lenses. Through differential spectroscopic imaging at deep-ultraviolet wavelengths, DART quantitatively maps nucleic acid and protein distributions with femtogram sensitivity, providing an intrinsic basis for explainable virtual staining. We demonstrate DART's capabilities through molecular imaging of tissue sections, cytopathology specimens, blood cells, and neural populations, revealing detailed molecular contrast without external labels. The combination of high-resolution molecular mapping and broad mesoscale imaging in a portable platform opens new possibilities from rapid clinical diagnostics, tissue analysis, to biological characterization in space exploration.
Multiscale aperture synthesis imager
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Synthetic aperture imaging has enabled breakthrough observations from radar to astronomy. However, optical implementation remains challenging due to stringent wavefield synchronization requirements among multiple receivers. Here we present the multiscale aperture synthesis imager (MASI), which utilizes parallelism to break complex optical challenges into tractable sub-problems. MASI employs a distributed array of coded sensors that operate independently yet coherently to surpass the diffraction limit of single receiver. It combines the propagated wavefields from individual sensors through a computational phase synchronization scheme, eliminating the need for overlapping measurement regions to establish phase coherence. Light diffraction in MASI naturally expands the imaging field, generating phase-contrast visualizations that are substantially larger than sensor dimensions. Without using lenses, MASI resolves sub-micron features at ultralong working distances and reconstructs 3D shapes over centimeter-scale fields. MASI transforms the intractable optical synchronization problem into a computational one, enabling practical deployment of scalable synthetic aperture systems at optical wavelengths.
Ptychographic non-line-of-sight imaging for depth-resolved visualization of hidden objects
May 17, 2024



Abstract:Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) imaging enables the visualization of objects hidden from direct view, with applications in surveillance, remote sensing, and light detection and ranging. Here, we introduce a NLOS imaging technique termed ptychographic NLOS (pNLOS), which leverages coded ptychography for depth-resolved imaging of obscured objects. Our approach involves scanning a laser spot on a wall to illuminate the hidden objects in an obscured region. The reflected wavefields from these objects then travel back to the wall, get modulated by the wall's complex-valued profile, and the resulting diffraction patterns are captured by a camera. By modulating the object wavefields, the wall surface serves the role of the coded layer as in coded ptychography. As we scan the laser spot to different positions, the reflected object wavefields on the wall translate accordingly, with the shifts varying for objects at different depths. This translational diversity enables the acquisition of a set of modulated diffraction patterns referred to as a ptychogram. By processing the ptychogram, we recover both the objects at different depths and the modulation profile of the wall surface. Experimental results demonstrate high-resolution, high-fidelity imaging of hidden objects, showcasing the potential of pNLOS for depth-aware vision beyond the direct line of sight.
PPBFL: A Privacy Protected Blockchain-based Federated Learning Model
Jan 08, 2024Abstract:With the rapid development of machine learning and a growing concern for data privacy, federated learning has become a focal point of attention. However, attacks on model parameters and a lack of incentive mechanisms hinder the effectiveness of federated learning. Therefore, we propose A Privacy Protected Blockchain-based Federated Learning Model (PPBFL) to enhance the security of federated learning and encourage active participation of nodes in model training. Blockchain technology ensures the integrity of model parameters stored in the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), providing protection against tampering. Within the blockchain, we introduce a Proof of Training Work (PoTW) consensus algorithm tailored for federated learning, aiming to incentive training nodes. This algorithm rewards nodes with greater computational power, promoting increased participation and effort in the federated learning process. A novel adaptive differential privacy algorithm is simultaneously applied to local and global models. This safeguards the privacy of local data at training clients, preventing malicious nodes from launching inference attacks. Additionally, it enhances the security of the global model, preventing potential security degradation resulting from the combination of numerous local models. The possibility of security degradation is derived from the composition theorem. By introducing reverse noise in the global model, a zero-bias estimate of differential privacy noise between local and global models is achieved. Furthermore, we propose a new mix transactions mechanism utilizing ring signature technology to better protect the identity privacy of local training clients. Security analysis and experimental results demonstrate that PPBFL, compared to baseline methods, not only exhibits superior model performance but also achieves higher security.
FBChain: A Blockchain-based Federated Learning Model with Efficiency and Secure Communication
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:Privacy and security in the parameter transmission process of federated learning are currently among the most prominent concerns. However, there are two thorny problems caused by unprotected communication methods: "parameter-leakage" and "inefficient-communication". This article proposes Blockchain-based Federated Learning (FBChain) model for federated learning parameter communication to overcome the above two problems. First, we utilize the immutability of blockchain to store the global model and hash value of local model parameters in case of tampering during the communication process, protect data privacy by encrypting parameters, and verify data consistency by comparing the hash values of local parameters, thus addressing the "parameter-leakage" problem. Second, the Proof of Weighted Link Speed (PoWLS) consensus algorithm comprehensively selects nodes with the higher weighted link speed to aggregate global model and package blocks, thereby solving the "inefficient-communication" problem. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed FBChain model and its ability to improve model communication efficiency in federated learning.
BRFL: A Blockchain-based Byzantine-Robust Federated Learning Model
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:With the increasing importance of machine learning, the privacy and security of training data have become critical. Federated learning, which stores data in distributed nodes and shares only model parameters, has gained significant attention for addressing this concern. However, a challenge arises in federated learning due to the Byzantine Attack Problem, where malicious local models can compromise the global model's performance during aggregation. This article proposes the Blockchain-based Byzantine-Robust Federated Learning (BRLF) model that combines federated learning with blockchain technology. This integration enables traceability of malicious models and provides incentives for locally trained clients. Our approach involves selecting the aggregation node based on Pearson's correlation coefficient, and we perform spectral clustering and calculate the average gradient within each cluster, validating its accuracy using local dataset of the aggregation nodes. Experimental results on public datasets demonstrate the superior byzantine robustness of our secure aggregation algorithm compared to other baseline byzantine robust aggregation methods, and proved our proposed model effectiveness in addressing the resource consumption problem.
High-throughput lensless whole slide imaging via continuous height-varying modulation of tilted sensor
Sep 28, 2021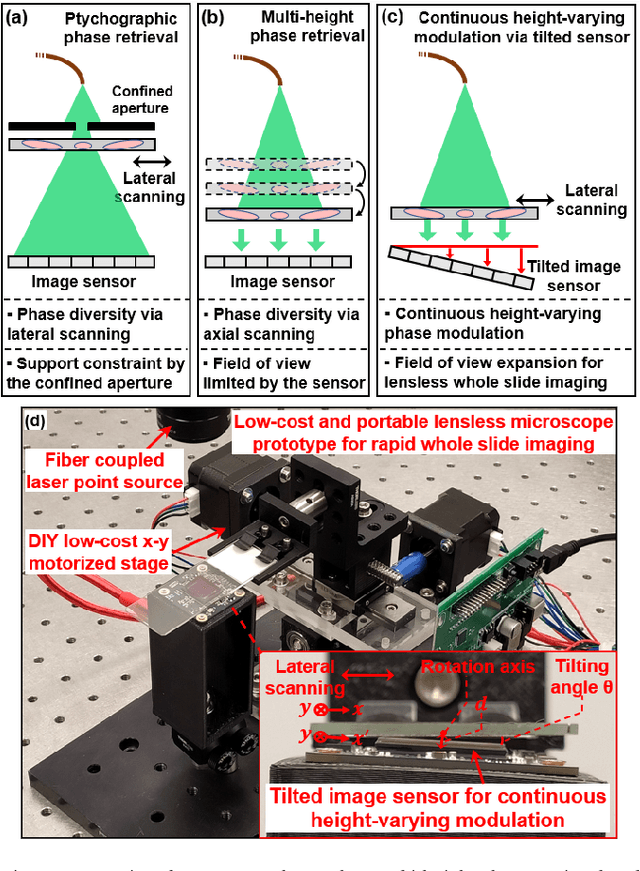
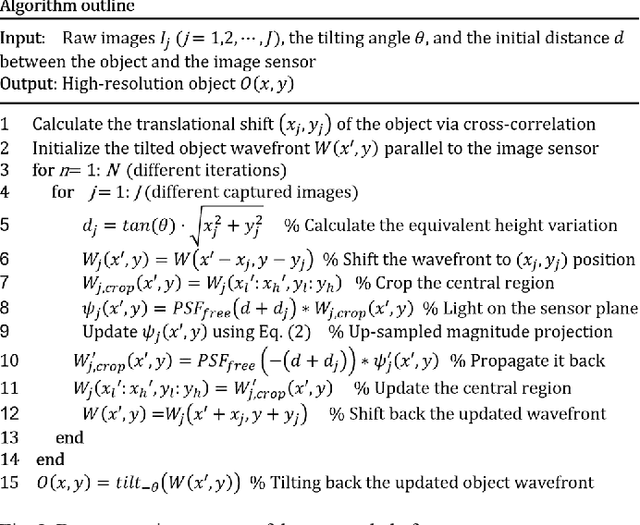

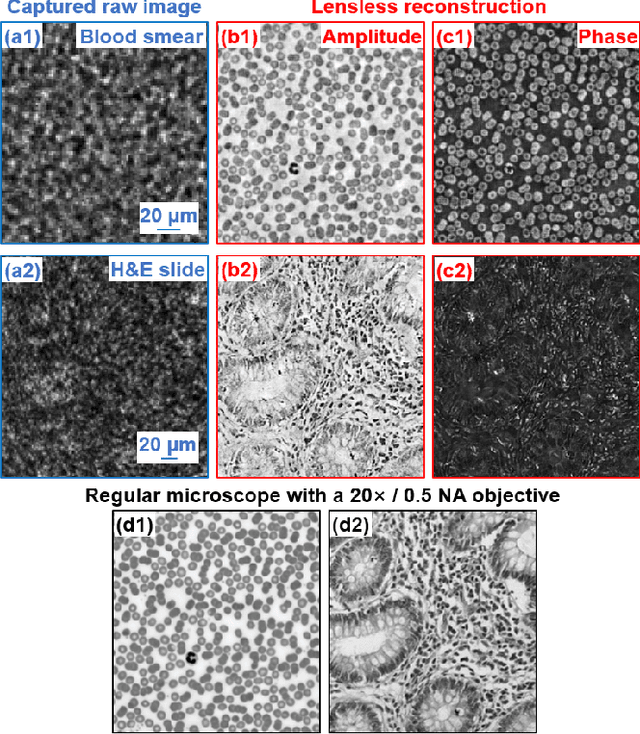
Abstract:We report a new lensless microscopy configuration by integrating the concepts of transverse translational ptychography and defocus multi-height phase retrieval. In this approach, we place a tilted image sensor under the specimen for linearly-increasing phase modulation along one lateral direction. Similar to the operation of ptychography, we laterally translate the specimen and acquire the diffraction images for reconstruction. Since the axial distance between the specimen and the sensor varies at different lateral positions, laterally translating the specimen effectively introduces defocus multi-height measurements while eliminating axial scanning. Lateral translation further introduces sub-pixel shift for pixel super-resolution imaging and naturally expands the field of view for rapid whole slide imaging. We show that the equivalent height variation can be precisely estimated from the lateral shift of the specimen, thereby addressing the challenge of precise axial positioning in conventional multi-height phase retrieval. Using a sensor with a 1.67-micron pixel size, our low-cost and field-portable prototype can resolve 690-nm linewidth on the resolution target. We show that a whole slide image of a blood smear with a 120-mm^2 field of view can be acquired in 18 seconds. We also demonstrate accurate automatic white blood cell counting from the recovered image. The reported approach may provide a turnkey solution for addressing point-of-care- and telemedicine-related challenges.
Bypassing the resolution limit of diffractive zone plate optics via rotational Fourier ptychography
Feb 07, 2021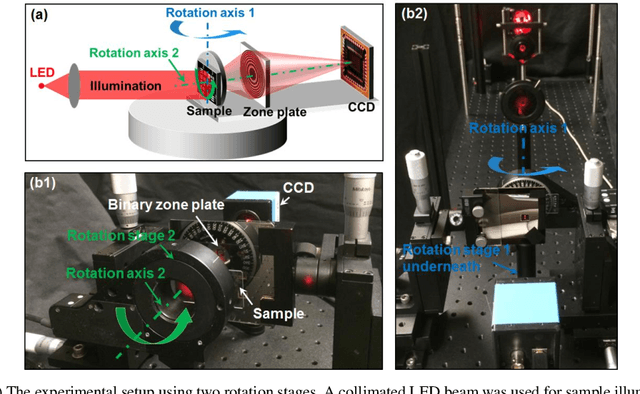
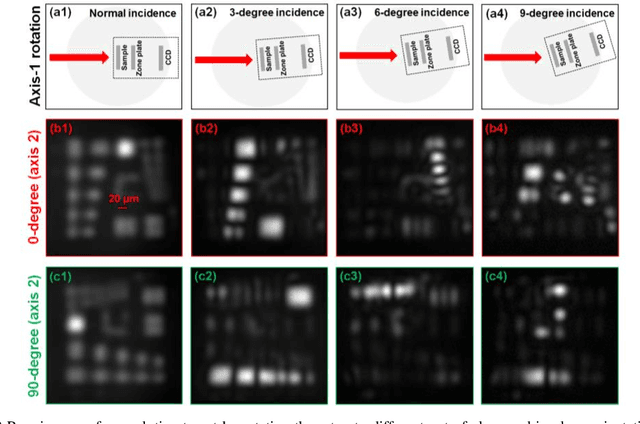

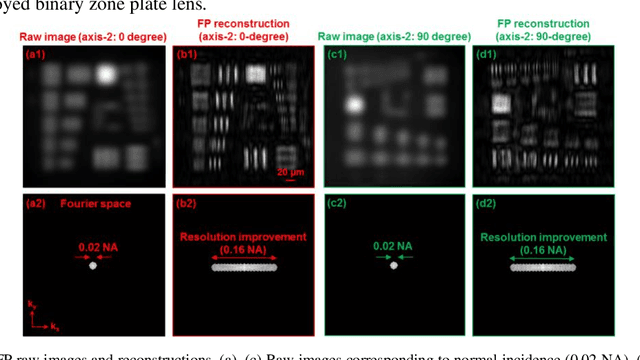
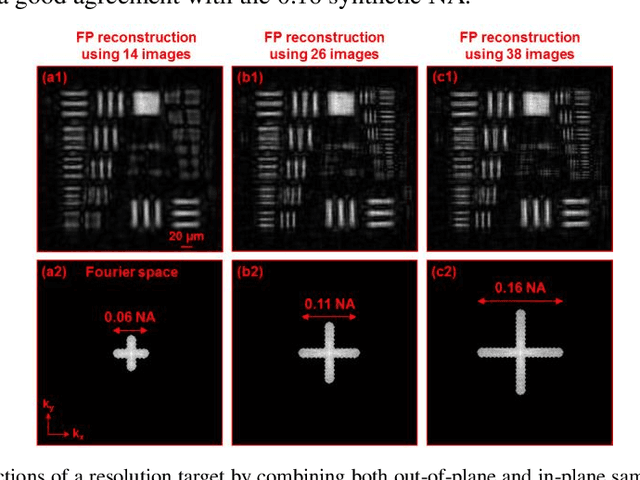
Abstract:Diffractive zone plate optics uses a thin micro-structure pattern to alter the propagation direction of the incoming light wave. It has found important applications in extreme-wavelength imaging where conventional refractive lenses do not exist. The resolution limit of zone plate optics is determined by the smallest width of the outermost zone. In order to improve the achievable resolution, significant efforts have been devoted to the fabrication of very small zone width with ultrahigh placement accuracy. Here, we report the use of a diffractometer setup for bypassing the resolution limit of zone plate optics. In our prototype, we mounted the sample on two rotation stages and used a low-resolution binary zone plate to relay the sample plane to the detector. We then performed both in-plane and out-of-plane sample rotations and captured the corresponding raw images. The captured images were processed using a Fourier ptychographic procedure for resolution improvement. The final achievable resolution of the reported setup is not determined by the smallest width structures of the employed binary zone plate; instead, it is determined by the maximum angle of the out-of-plane rotation. In our experiment, we demonstrated 8-fold resolution improvement using both a resolution target and a titanium dioxide sample. The reported approach may be able to bypass the fabrication challenge of diffractive elements and open up new avenues for microscopy with extreme wavelengths.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge