Taylor Webb
Position: We Need An Algorithmic Understanding of Generative AI
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:What algorithms do LLMs actually learn and use to solve problems? Studies addressing this question are sparse, as research priorities are focused on improving performance through scale, leaving a theoretical and empirical gap in understanding emergent algorithms. This position paper proposes AlgEval: a framework for systematic research into the algorithms that LLMs learn and use. AlgEval aims to uncover algorithmic primitives, reflected in latent representations, attention, and inference-time compute, and their algorithmic composition to solve task-specific problems. We highlight potential methodological paths and a case study toward this goal, focusing on emergent search algorithms. Our case study illustrates both the formation of top-down hypotheses about candidate algorithms, and bottom-up tests of these hypotheses via circuit-level analysis of attention patterns and hidden states. The rigorous, systematic evaluation of how LLMs actually solve tasks provides an alternative to resource-intensive scaling, reorienting the field toward a principled understanding of underlying computations. Such algorithmic explanations offer a pathway to human-understandable interpretability, enabling comprehension of the model's internal reasoning performance measures. This can in turn lead to more sample-efficient methods for training and improving performance, as well as novel architectures for end-to-end and multi-agent systems.
Few-Shot Learning of Visual Compositional Concepts through Probabilistic Schema Induction
May 14, 2025Abstract:The ability to learn new visual concepts from limited examples is a hallmark of human cognition. While traditional category learning models represent each example as an unstructured feature vector, compositional concept learning is thought to depend on (1) structured representations of examples (e.g., directed graphs consisting of objects and their relations) and (2) the identification of shared relational structure across examples through analogical mapping. Here, we introduce Probabilistic Schema Induction (PSI), a prototype model that employs deep learning to perform analogical mapping over structured representations of only a handful of examples, forming a compositional concept called a schema. In doing so, PSI relies on a novel conception of similarity that weighs object-level similarity and relational similarity, as well as a mechanism for amplifying relations relevant to classification, analogous to selective attention parameters in traditional models. We show that PSI produces human-like learning performance and outperforms two controls: a prototype model that uses unstructured feature vectors extracted from a deep learning model, and a variant of PSI with weaker structured representations. Notably, we find that PSI's human-like performance is driven by an adaptive strategy that increases relational similarity over object-level similarity and upweights the contribution of relations that distinguish classes. These findings suggest that structured representations and analogical mapping are critical to modeling rapid human-like learning of compositional visual concepts, and demonstrate how deep learning can be leveraged to create psychological models.
Emergent Symbolic Mechanisms Support Abstract Reasoning in Large Language Models
Feb 27, 2025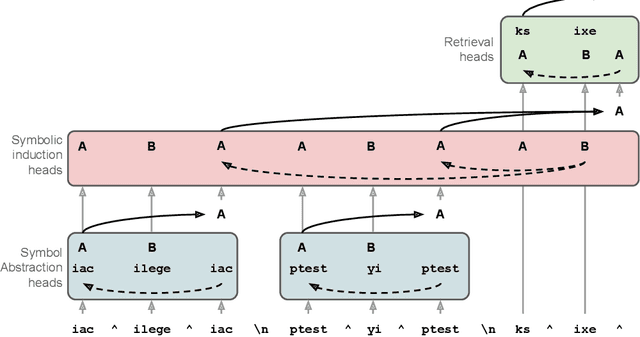
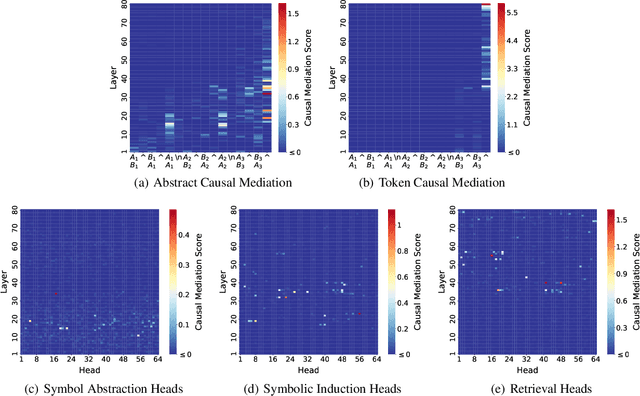
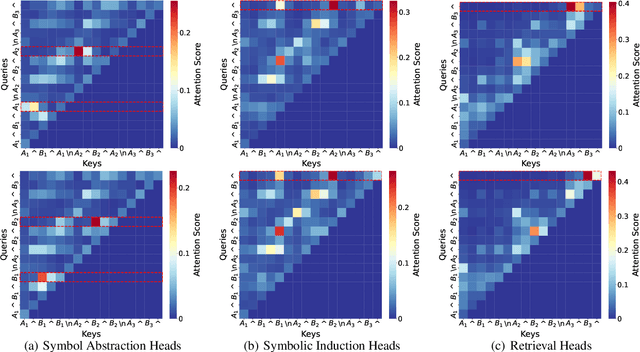
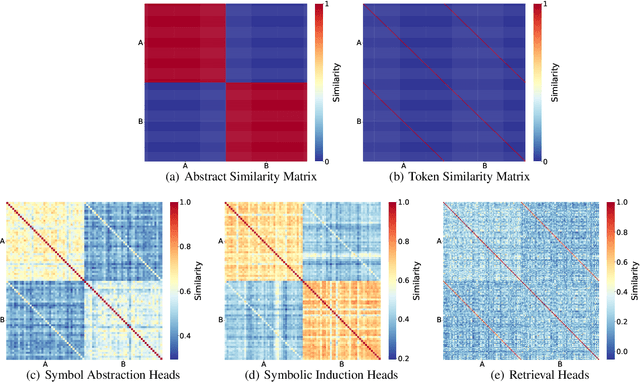
Abstract:Many recent studies have found evidence for emergent reasoning capabilities in large language models, but debate persists concerning the robustness of these capabilities, and the extent to which they depend on structured reasoning mechanisms. To shed light on these issues, we perform a comprehensive study of the internal mechanisms that support abstract rule induction in an open-source language model (Llama3-70B). We identify an emergent symbolic architecture that implements abstract reasoning via a series of three computations. In early layers, symbol abstraction heads convert input tokens to abstract variables based on the relations between those tokens. In intermediate layers, symbolic induction heads perform sequence induction over these abstract variables. Finally, in later layers, retrieval heads predict the next token by retrieving the value associated with the predicted abstract variable. These results point toward a resolution of the longstanding debate between symbolic and neural network approaches, suggesting that emergent reasoning in neural networks depends on the emergence of symbolic mechanisms.
Evidence from counterfactual tasks supports emergent analogical reasoning in large language models
Apr 29, 2024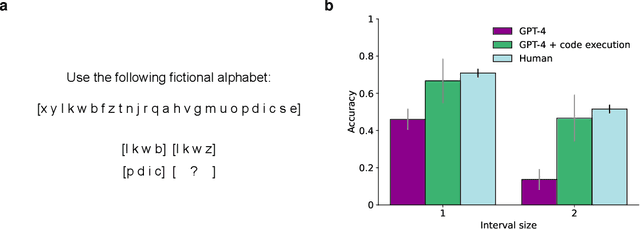
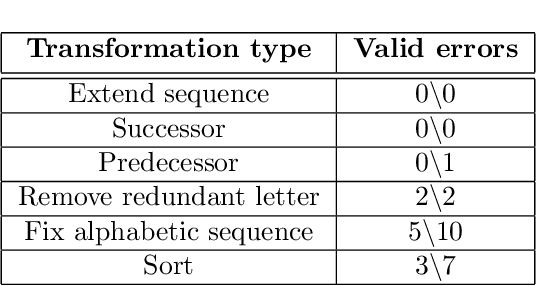
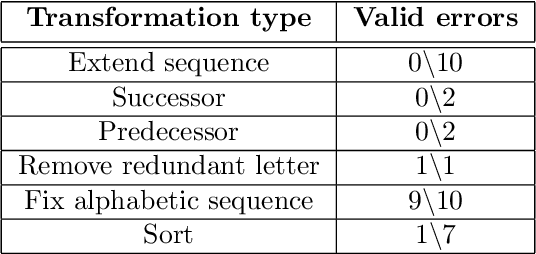
Abstract:We recently reported evidence that large language models are capable of solving a wide range of text-based analogy problems in a zero-shot manner, indicating the presence of an emergent capacity for analogical reasoning. Two recent commentaries have challenged these results, citing evidence from so-called `counterfactual' tasks in which the standard sequence of the alphabet is arbitrarily permuted so as to decrease similarity with materials that may have been present in the language model's training data. Here, we reply to these critiques, clarifying some misunderstandings about the test materials used in our original work, and presenting evidence that language models are also capable of generalizing to these new counterfactual task variants.
A Prefrontal Cortex-inspired Architecture for Planning in Large Language Models
Sep 30, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive performance on a wide variety of tasks, but they often struggle with tasks that require multi-step reasoning or goal-directed planning. To address this, we take inspiration from the human brain, in which planning is accomplished via the recurrent interaction of specialized modules in the prefrontal cortex (PFC). These modules perform functions such as conflict monitoring, state prediction, state evaluation, task decomposition, and task coordination. We find that LLMs are sometimes capable of carrying out these functions in isolation, but struggle to autonomously coordinate them in the service of a goal. Therefore, we propose a black box architecture with multiple LLM-based (GPT-4) modules. The architecture improves planning through the interaction of specialized PFC-inspired modules that break down a larger problem into multiple brief automated calls to the LLM. We evaluate the combined architecture on two challenging planning tasks -- graph traversal and Tower of Hanoi -- finding that it yields significant improvements over standard LLM methods (e.g., zero-shot prompting or in-context learning). These results demonstrate the benefit of utilizing knowledge from cognitive neuroscience to improve planning in LLMs.
Determinantal Point Process Attention Over Grid Codes Supports Out of Distribution Generalization
May 28, 2023



Abstract:Deep neural networks have made tremendous gains in emulating human-like intelligence, and have been used increasingly as ways of understanding how the brain may solve the complex computational problems on which this relies. However, these still fall short of, and therefore fail to provide insight into how the brain supports strong forms of generalization of which humans are capable. One such case is out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization -- successful performance on test examples that lie outside the distribution of the training set. Here, we identify properties of processing in the brain that may contribute to this ability. We describe a two-part algorithm that draws on specific features of neural computation to achieve OOD generalization, and provide a proof of concept by evaluating performance on two challenging cognitive tasks. First we draw on the fact that the mammalian brain represents metric spaces using grid-like representations (e.g., in entorhinal cortex): abstract representations of relational structure, organized in recurring motifs that cover the representational space. Second, we propose an attentional mechanism that operates over these grid representations using determinantal point process (DPP-A) -- a transformation that ensures maximum sparseness in the coverage of that space. We show that a loss function that combines standard task-optimized error with DPP-A can exploit the recurring motifs in grid codes, and can be integrated with common architectures to achieve strong OOD generalization performance on analogy and arithmetic tasks. This provides both an interpretation of how grid codes in the mammalian brain may contribute to generalization performance, and at the same time a potential means for improving such capabilities in artificial neural networks.
Abstractors: Transformer Modules for Symbolic Message Passing and Relational Reasoning
Apr 01, 2023



Abstract:A framework is proposed that casts relational learning in terms of transformers, implementing binding between sensory states and abstract states with relational cross attention mechanisms.
Learning to reason over visual objects
Mar 03, 2023



Abstract:A core component of human intelligence is the ability to identify abstract patterns inherent in complex, high-dimensional perceptual data, as exemplified by visual reasoning tasks such as Raven's Progressive Matrices (RPM). Motivated by the goal of designing AI systems with this capacity, recent work has focused on evaluating whether neural networks can learn to solve RPM-like problems. Previous work has generally found that strong performance on these problems requires the incorporation of inductive biases that are specific to the RPM problem format, raising the question of whether such models might be more broadly useful. Here, we investigated the extent to which a general-purpose mechanism for processing visual scenes in terms of objects might help promote abstract visual reasoning. We found that a simple model, consisting only of an object-centric encoder and a transformer reasoning module, achieved state-of-the-art results on both of two challenging RPM-like benchmarks (PGM and I-RAVEN), as well as a novel benchmark with greater visual complexity (CLEVR-Matrices). These results suggest that an inductive bias for object-centric processing may be a key component of abstract visual reasoning, obviating the need for problem-specific inductive biases.
Emergent Analogical Reasoning in Large Language Models
Dec 19, 2022Abstract:The recent advent of large language models - large neural networks trained on a simple predictive objective over a massive corpus of natural language - has reinvigorated debate over whether human cognitive capacities might emerge in such generic models given sufficient training data. Of particular interest is the ability of these models to reason about novel problems zero-shot, without any direct training on those problems. In human cognition, this capacity is closely tied to an ability to reason by analogy. Here, we performed a direct comparison between human reasoners and a large language model (GPT-3) on a range of analogical tasks, including a novel text-based matrix reasoning task closely modeled on Raven's Progressive Matrices. We found that GPT-3 displayed a surprisingly strong capacity for abstract pattern induction, matching or even surpassing human capabilities in most settings. Our results indicate that large language models such as GPT-3 have acquired an emergent ability to find zero-shot solutions to a broad range of analogy problems.
Modelling the development of counting with memory-augmented neural networks
May 21, 2021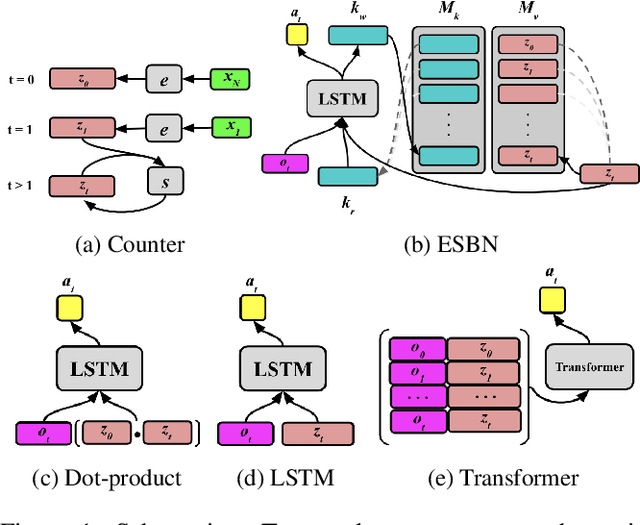
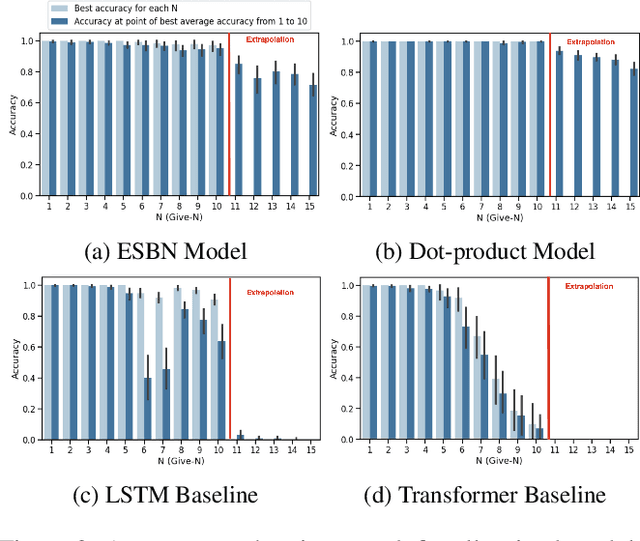
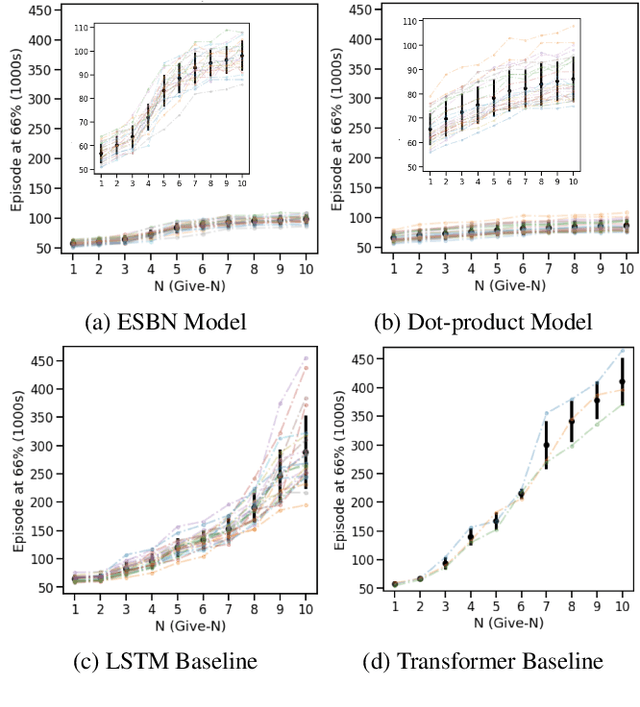
Abstract:Learning to count is an important example of the broader human capacity for systematic generalization, and the development of counting is often characterized by an inflection point when children rapidly acquire proficiency with the procedures that support this ability. We aimed to model this process by training a reinforcement learning agent to select N items from a binary vector when instructed (known as the give-$N$ task). We found that a memory-augmented modular network architecture based on the recently proposed Emergent Symbol Binding Network (ESBN) exhibited an inflection during learning that resembled human development. This model was also capable of systematic extrapolation outside the range of its training set - for example, trained only to select between 1 and 10 items, it could succeed at selecting 11 to 15 items as long as it could make use of an arbitrary count sequence of at least that length. The close parallels to child development and the capacity for extrapolation suggest that our model could shed light on the emergence of systematicity in humans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge