Tariq Mahmood Khan
LVS-Net: A Lightweight Vessels Segmentation Network for Retinal Image Analysis
Dec 08, 2024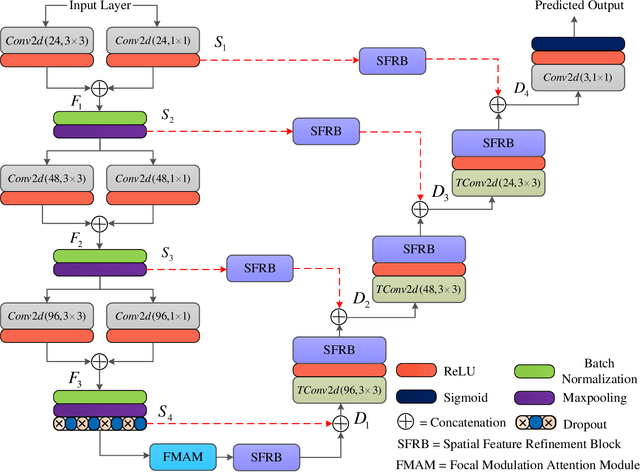
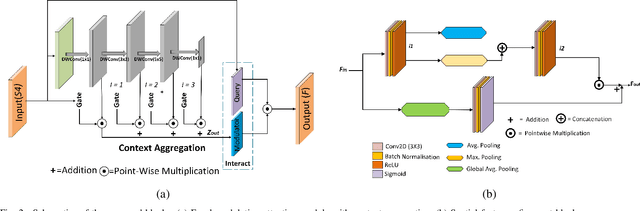
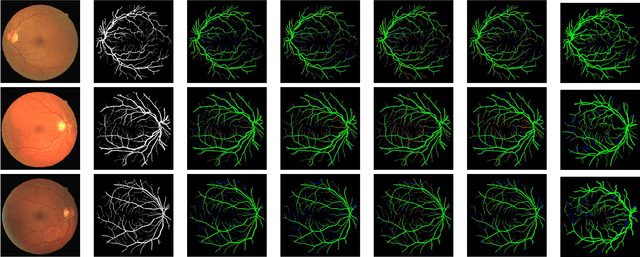

Abstract:The analysis of retinal images for the diagnosis of various diseases is one of the emerging areas of research. Recently, the research direction has been inclined towards investigating several changes in retinal blood vessels in subjects with many neurological disorders, including dementia. This research focuses on detecting diseases early by improving the performance of models for segmentation of retinal vessels with fewer parameters, which reduces computational costs and supports faster processing. This paper presents a novel lightweight encoder-decoder model that segments retinal vessels to improve the efficiency of disease detection. It incorporates multi-scale convolutional blocks in the encoder to accurately identify vessels of various sizes and thicknesses. The bottleneck of the model integrates the Focal Modulation Attention and Spatial Feature Refinement Blocks to refine and enhance essential features for efficient segmentation. The decoder upsamples features and integrates them with the corresponding feature in the encoder using skip connections and the spatial feature refinement block at every upsampling stage to enhance feature representation at various scales. The estimated computation complexity of our proposed model is around 29.60 GFLOP with 0.71 million parameters and 2.74 MB of memory size, and it is evaluated using public datasets, that is, DRIVE, CHASE\_DB, and STARE. It outperforms existing models with dice scores of 86.44\%, 84.22\%, and 87.88\%, respectively.
Latent fingerprint enhancement for accurate minutiae detection
Sep 18, 2024Abstract:Identification of suspects based on partial and smudged fingerprints, commonly referred to as fingermarks or latent fingerprints, presents a significant challenge in the field of fingerprint recognition. Although fixed-length embeddings have shown effectiveness in recognising rolled and slap fingerprints, the methods for matching latent fingerprints have primarily centred around local minutiae-based embeddings, failing to fully exploit global representations for matching purposes. Consequently, enhancing latent fingerprints becomes critical to ensuring robust identification for forensic investigations. Current approaches often prioritise restoring ridge patterns, overlooking the fine-macroeconomic details crucial for accurate fingerprint recognition. To address this, we propose a novel approach that uses generative adversary networks (GANs) to redefine Latent Fingerprint Enhancement (LFE) through a structured approach to fingerprint generation. By directly optimising the minutiae information during the generation process, the model produces enhanced latent fingerprints that exhibit exceptional fidelity to ground-truth instances. This leads to a significant improvement in identification performance. Our framework integrates minutiae locations and orientation fields, ensuring the preservation of both local and structural fingerprint features. Extensive evaluations conducted on two publicly available datasets demonstrate our method's dominance over existing state-of-the-art techniques, highlighting its potential to significantly enhance latent fingerprint recognition accuracy in forensic applications.
MESAHA-Net: Multi-Encoders based Self-Adaptive Hard Attention Network with Maximum Intensity Projections for Lung Nodule Segmentation in CT Scan
Apr 04, 2023Abstract:Accurate lung nodule segmentation is crucial for early-stage lung cancer diagnosis, as it can substantially enhance patient survival rates. Computed tomography (CT) images are widely employed for early diagnosis in lung nodule analysis. However, the heterogeneity of lung nodules, size diversity, and the complexity of the surrounding environment pose challenges for developing robust nodule segmentation methods. In this study, we propose an efficient end-to-end framework, the multi-encoder-based self-adaptive hard attention network (MESAHA-Net), for precise lung nodule segmentation in CT scans. MESAHA-Net comprises three encoding paths, an attention block, and a decoder block, facilitating the integration of three types of inputs: CT slice patches, forward and backward maximum intensity projection (MIP) images, and region of interest (ROI) masks encompassing the nodule. By employing a novel adaptive hard attention mechanism, MESAHA-Net iteratively performs slice-by-slice 2D segmentation of lung nodules, focusing on the nodule region in each slice to generate 3D volumetric segmentation of lung nodules. The proposed framework has been comprehensively evaluated on the LIDC-IDRI dataset, the largest publicly available dataset for lung nodule segmentation. The results demonstrate that our approach is highly robust for various lung nodule types, outperforming previous state-of-the-art techniques in terms of segmentation accuracy and computational complexity, rendering it suitable for real-time clinical implementation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge