Ta Duc Huy
EMAG: Self-Rectifying Diffusion Sampling with Exponential Moving Average Guidance
Dec 19, 2025
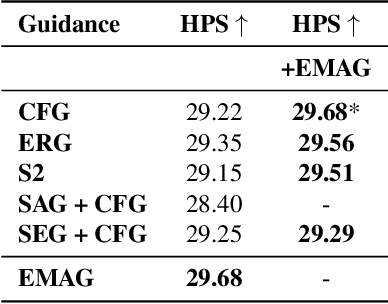
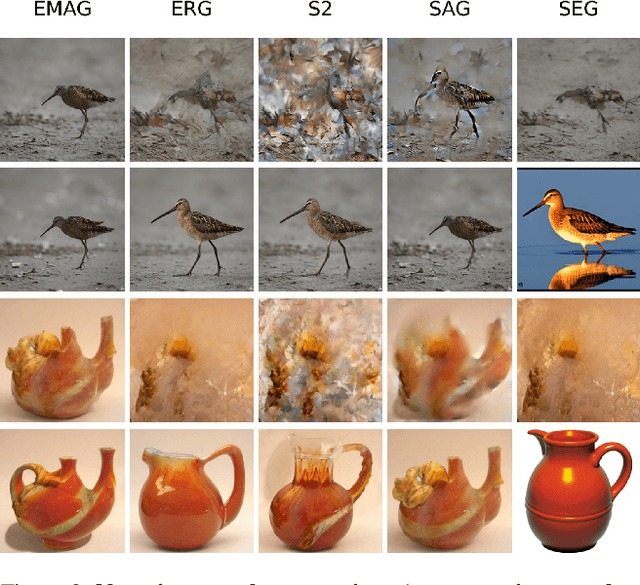
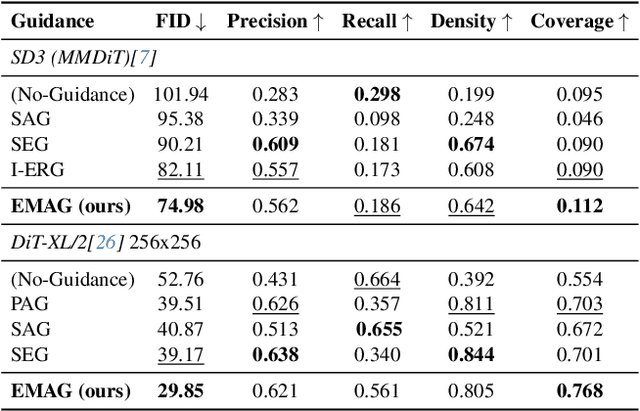
Abstract:In diffusion and flow-matching generative models, guidance techniques are widely used to improve sample quality and consistency. Classifier-free guidance (CFG) is the de facto choice in modern systems and achieves this by contrasting conditional and unconditional samples. Recent work explores contrasting negative samples at inference using a weaker model, via strong/weak model pairs, attention-based masking, stochastic block dropping, or perturbations to the self-attention energy landscape. While these strategies refine the generation quality, they still lack reliable control over the granularity or difficulty of the negative samples, and target-layer selection is often fixed. We propose Exponential Moving Average Guidance (EMAG), a training-free mechanism that modifies attention at inference time in diffusion transformers, with a statistics-based, adaptive layer-selection rule. Unlike prior methods, EMAG produces harder, semantically faithful negatives (fine-grained degradations), surfacing difficult failure modes, enabling the denoiser to refine subtle artifacts, boosting the quality and human preference score (HPS) by +0.46 over CFG. We further demonstrate that EMAG naturally composes with advanced guidance techniques, such as APG and CADS, further improving HPS.
Seeing the Trees for the Forest: Rethinking Weakly-Supervised Medical Visual Grounding
May 21, 2025Abstract:Visual grounding (VG) is the capability to identify the specific regions in an image associated with a particular text description. In medical imaging, VG enhances interpretability by highlighting relevant pathological features corresponding to textual descriptions, improving model transparency and trustworthiness for wider adoption of deep learning models in clinical practice. Current models struggle to associate textual descriptions with disease regions due to inefficient attention mechanisms and a lack of fine-grained token representations. In this paper, we empirically demonstrate two key observations. First, current VLMs assign high norms to background tokens, diverting the model's attention from regions of disease. Second, the global tokens used for cross-modal learning are not representative of local disease tokens. This hampers identifying correlations between the text and disease tokens. To address this, we introduce simple, yet effective Disease-Aware Prompting (DAP) process, which uses the explainability map of a VLM to identify the appropriate image features. This simple strategy amplifies disease-relevant regions while suppressing background interference. Without any additional pixel-level annotations, DAP improves visual grounding accuracy by 20.74% compared to state-of-the-art methods across three major chest X-ray datasets.
Interactive Medical Image Analysis with Concept-based Similarity Reasoning
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:The ability to interpret and intervene model decisions is important for the adoption of computer-aided diagnosis methods in clinical workflows. Recent concept-based methods link the model predictions with interpretable concepts and modify their activation scores to interact with the model. However, these concepts are at the image level, which hinders the model from pinpointing the exact patches the concepts are activated. Alternatively, prototype-based methods learn representations from training image patches and compare these with test image patches, using the similarity scores for final class prediction. However, interpreting the underlying concepts of these patches can be challenging and often necessitates post-hoc guesswork. To address this issue, this paper introduces the novel Concept-based Similarity Reasoning network (CSR), which offers (i) patch-level prototype with intrinsic concept interpretation, and (ii) spatial interactivity. First, the proposed CSR provides localized explanation by grounding prototypes of each concept on image regions. Second, our model introduces novel spatial-level interaction, allowing doctors to engage directly with specific image areas, making it an intuitive and transparent tool for medical imaging. CSR improves upon prior state-of-the-art interpretable methods by up to 4.5\% across three biomedical datasets. Our code is released at https://github.com/tadeephuy/InteractCSR.
* Accepted CVPR2025
ProjectedEx: Enhancing Generation in Explainable AI for Prostate Cancer
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Prostate cancer, a growing global health concern, necessitates precise diagnostic tools, with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offering high-resolution soft tissue imaging that significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy. Recent advancements in explainable AI and representation learning have significantly improved prostate cancer diagnosis by enabling automated and precise lesion classification. However, existing explainable AI methods, particularly those based on frameworks like generative adversarial networks (GANs), are predominantly developed for natural image generation, and their application to medical imaging often leads to suboptimal performance due to the unique characteristics and complexity of medical image. To address these challenges, our paper introduces three key contributions. First, we propose ProjectedEx, a generative framework that provides interpretable, multi-attribute explanations, effectively linking medical image features to classifier decisions. Second, we enhance the encoder module by incorporating feature pyramids, which enables multiscale feedback to refine the latent space and improves the quality of generated explanations. Additionally, we conduct comprehensive experiments on both the generator and classifier, demonstrating the clinical relevance and effectiveness of ProjectedEx in enhancing interpretability and supporting the adoption of AI in medical settings. Code will be released at https://github.com/Richardqiyi/ProjectedEx
ViMQ: A Vietnamese Medical Question Dataset for Healthcare Dialogue System Development
Apr 27, 2023Abstract:Existing medical text datasets usually take the form of ques- tion and answer pairs that support the task of natural language gener- ation, but lacking the composite annotations of the medical terms. In this study, we publish a Vietnamese dataset of medical questions from patients with sentence-level and entity-level annotations for the Intent Classification and Named Entity Recognition tasks. The tag sets for two tasks are in medical domain and can facilitate the development of task- oriented healthcare chatbots with better comprehension of queries from patients. We train baseline models for the two tasks and propose a simple self-supervised training strategy with span-noise modelling that substan- tially improves the performance. Dataset and code will be published at https://github.com/tadeephuy/ViMQ
* accepted at ICONIP 2021
Vietnamese Capitalization and Punctuation Recovery Models
Jul 04, 2022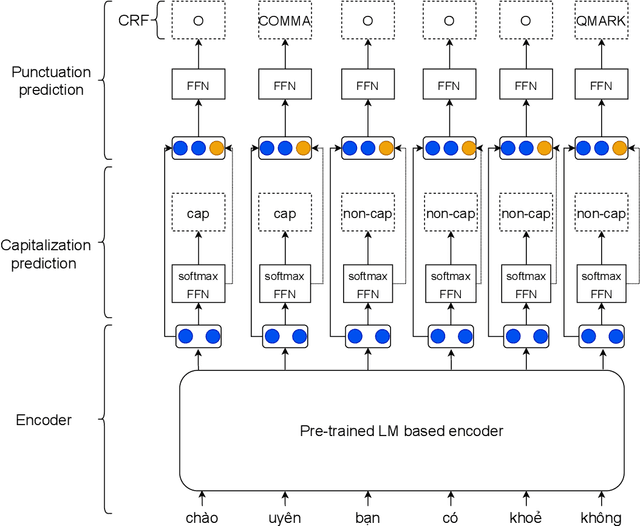
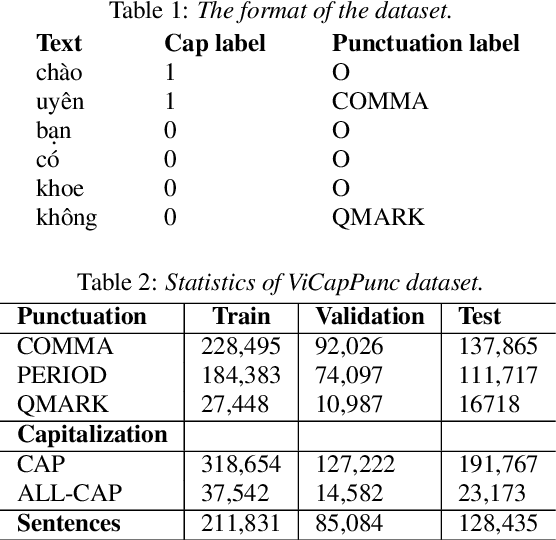
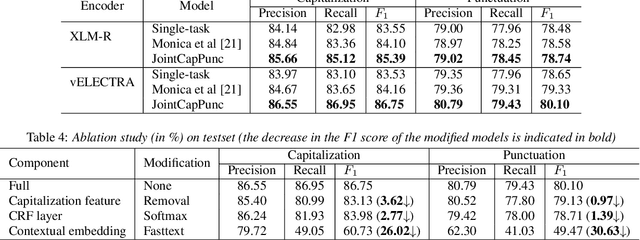
Abstract:Despite the rise of recent performant methods in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), such methods do not ensure proper casing and punctuation for their outputs. This problem has a significant impact on the comprehension of both Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms and human to process. Capitalization and punctuation restoration is imperative in pre-processing pipelines for raw textual inputs. For low resource languages like Vietnamese, public datasets for this task are scarce. In this paper, we contribute a public dataset for capitalization and punctuation recovery for Vietnamese; and propose a joint model for both tasks named JointCapPunc. Experimental results on the Vietnamese dataset show the effectiveness of our joint model compare to single model and previous joint learning model. We publicly release our dataset and the implementation of our model at https://github.com/anhtunguyen98/JointCapPunc
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge