T. Hoang Ngan Le
Roughness Index and Roughness Distance for Benchmarking Medical Segmentation
Mar 23, 2021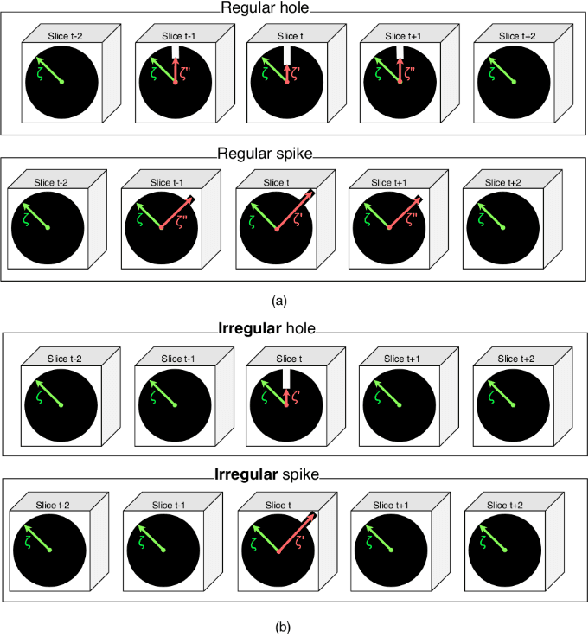
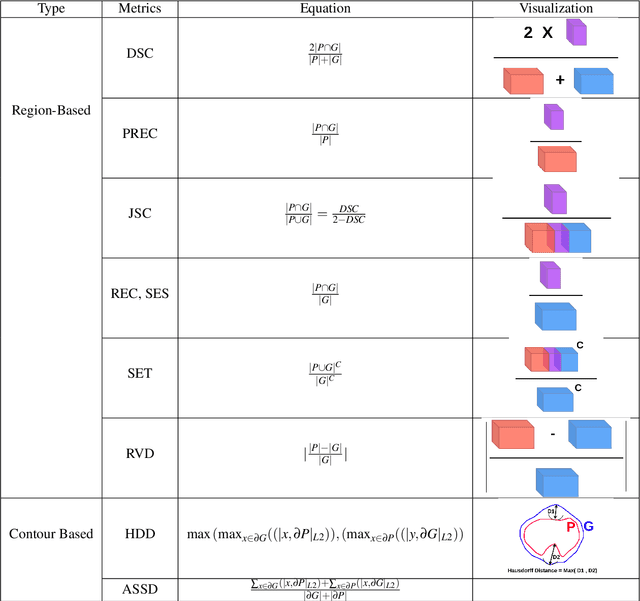
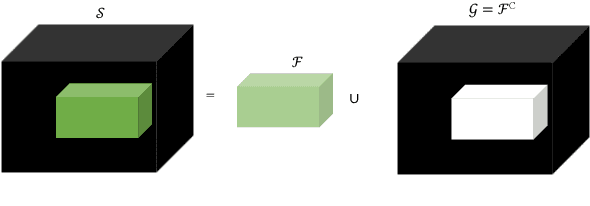
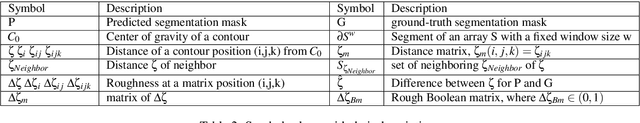
Abstract:Medical image segmentation is one of the most challenging tasks in medical image analysis and has been widely developed for many clinical applications. Most of the existing metrics have been first designed for natural images and then extended to medical images. While object surface plays an important role in medical segmentation and quantitative analysis i.e. analyze brain tumor surface, measure gray matter volume, most of the existing metrics are limited when it comes to analyzing the object surface, especially to tell about surface smoothness or roughness of a given volumetric object or to analyze the topological errors. In this paper, we first analysis both pros and cons of all existing medical image segmentation metrics, specially on volumetric data. We then propose an appropriate roughness index and roughness distance for medical image segmentation analysis and evaluation. Our proposed method addresses two kinds of segmentation errors, i.e. (i)topological errors on boundary/surface and (ii)irregularities on the boundary/surface. The contribution of this work is four-fold: (i) detect irregular spikes/holes on a surface, (ii) propose roughness index to measure surface roughness of a given object, (iii) propose a roughness distance to measure the distance of two boundaries/surfaces by utilizing the proposed roughness index and (iv) suggest an algorithm which helps to remove the irregular spikes/holes to smooth the surface. Our proposed roughness index and roughness distance are built upon the solid surface roughness parameter which has been successfully developed in the civil engineering.
Invertible Residual Network with Regularization for Effective Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 16, 2021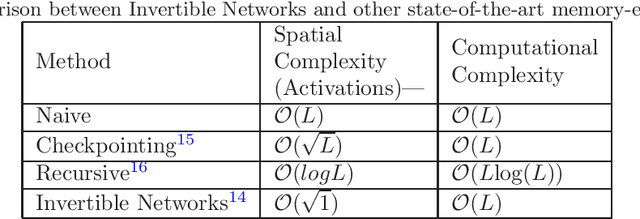
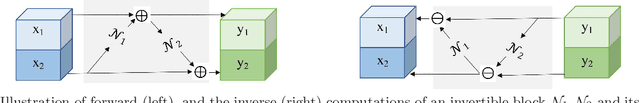
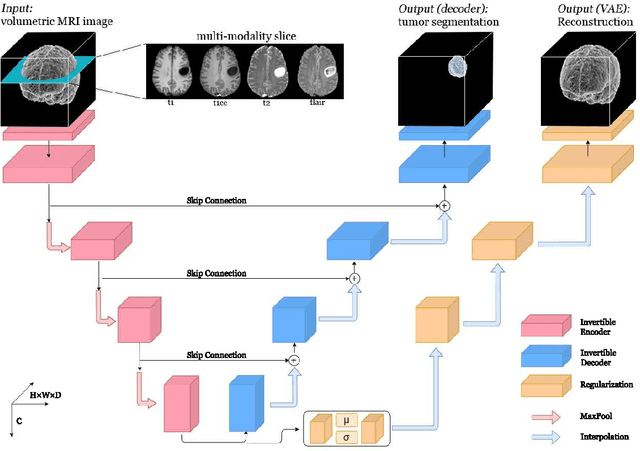
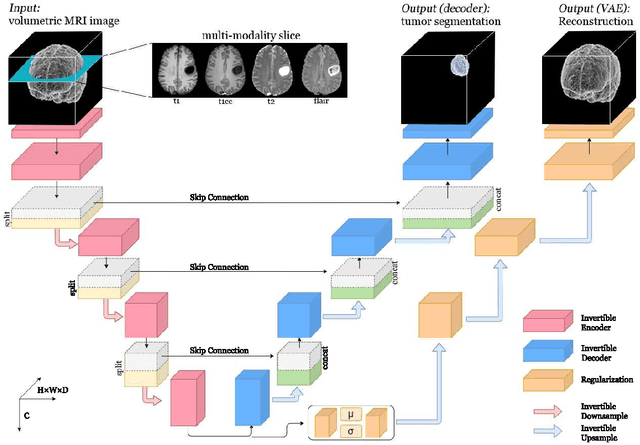
Abstract:Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) i.e. Residual Networks (ResNets) have been used successfully for many computer vision tasks, but are difficult to scale to 3D volumetric medical data. Memory is increasingly often the bottleneck when training 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Recently, invertible neural networks have been applied to significantly reduce activation memory footprint when training neural networks with backpropagation thanks to the invertible functions that allow retrieving its input from its output without storing intermediate activations in memory to perform the backpropagation. Among many successful network architectures, 3D Unet has been established as a standard architecture for volumetric medical segmentation. Thus, we choose 3D Unet as a baseline for a non-invertible network and we then extend it with the invertible residual network. In this paper, we proposed two versions of the invertible Residual Network, namely Partially Invertible Residual Network (Partially-InvRes) and Fully Invertible Residual Network (Fully-InvRes). In Partially-InvRes, the invertible residual layer is defined by a technique called additive coupling whereas in Fully-InvRes, both invertible upsampling and downsampling operations are learned based on squeezing (known as pixel shuffle). Furthermore, to avoid the overfitting problem because of less training data, a variational auto-encoder (VAE) branch is added to reconstruct the input volumetric data itself. Our results indicate that by using partially/fully invertible networks as the central workhorse in volumetric segmentation, we not only reduce memory overhead but also achieve compatible segmentation performance compared against the non-invertible 3D Unet. We have demonstrated the proposed networks on various volumetric datasets such as iSeg 2019 and BraTS 2020.
Deep Recurrent Level Set for Segmenting Brain Tumors
Oct 10, 2018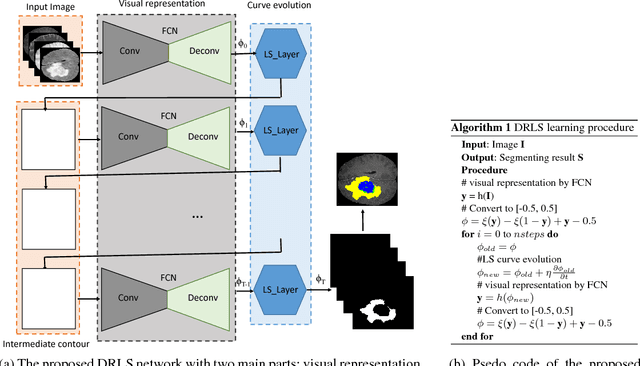
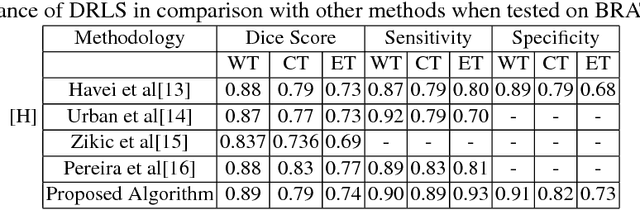
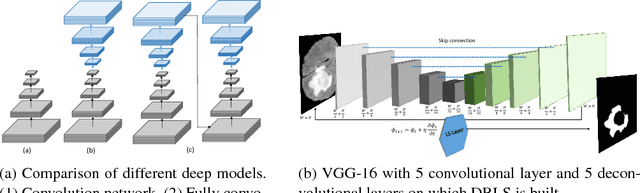
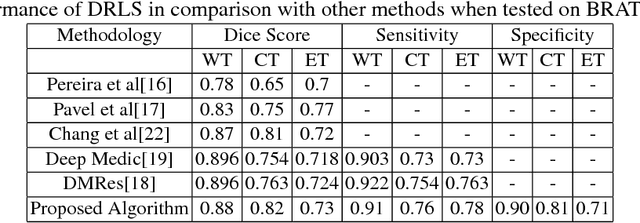
Abstract:Variational Level Set (VLS) has been a widely used method in medical segmentation. However, segmentation accuracy in the VLS method dramatically decreases when dealing with intervening factors such as lighting, shadows, colors, etc. Additionally, results are quite sensitive to initial settings and are highly dependent on the number of iterations. In order to address these limitations, the proposed method incorporates VLS into deep learning by defining a novel end-to-end trainable model called as Deep Recurrent Level Set (DRLS). The proposed DRLS consists of three layers, i.e, Convolutional layers, Deconvolutional layers with skip connections and LevelSet layers. Brain tumor segmentation is taken as an instant to illustrate the performance of the proposed DRLS. Convolutional layer learns visual representation of brain tumor at different scales. Since brain tumors occupy a small portion of the image, deconvolutional layers are designed with skip connections to obtain a high quality feature map. Level-Set Layer drives the contour towards the brain tumor. In each step, the Convolutional Layer is fed with the LevelSet map to obtain a brain tumor feature map. This in turn serves as input for the LevelSet layer in the next step. The experimental results have been obtained on BRATS2013, BRATS2015 and BRATS2017 datasets. The proposed DRLS model improves both computational time and segmentation accuracy when compared to the the classic VLS-based method. Additionally, a fully end-to-end system DRLS achieves state-of-the-art segmentation on brain tumors.
Learning from Longitudinal Face Demonstration - Where Tractable Deep Modeling Meets Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Sep 04, 2018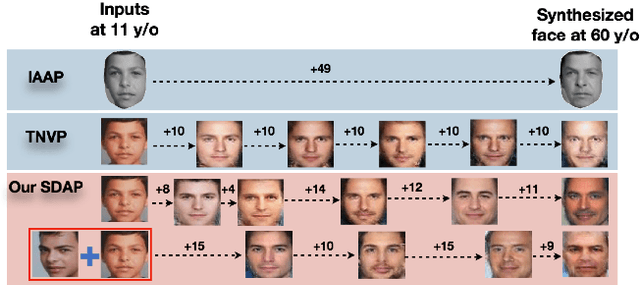
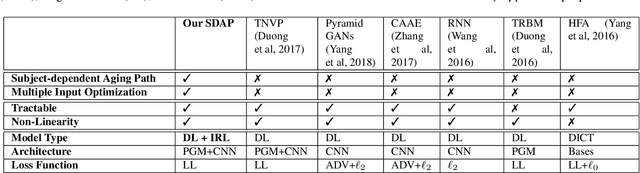
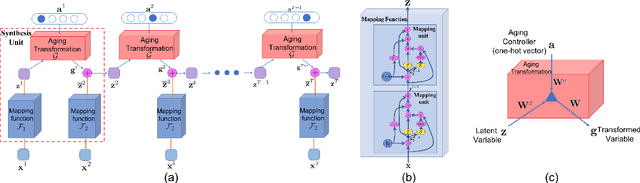
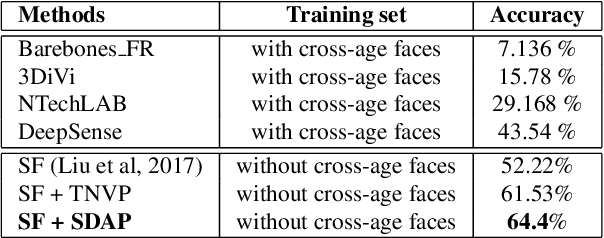
Abstract:This paper presents a novel Subject-dependent Deep Aging Path (SDAP), which inherits the merits of both Generative Probabilistic Modeling and Inverse Reinforcement Learning to model the facial structures and the longitudinal face aging process of a given subject. The proposed SDAP is optimized using tractable log-likelihood objective functions with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) based deep feature extraction. Instead of applying a fixed aging development path for all input faces and subjects, SDAP is able to provide the most appropriate aging development path for individual subject that optimizes the reward aging formulation. Unlike previous methods that can take only one image as the input, SDAP further allows multiple images as inputs, i.e. all information of a subject at either the same or different ages, to produce the optimal aging path for the given subject. Finally, SDAP allows efficiently synthesizing in-the-wild aging faces. The proposed model is experimented in both tasks of face aging synthesis and cross-age face verification. The experimental results consistently show SDAP achieves the state-of-the-art performance on numerous face aging databases, i.e. FG-NET, MORPH, AginG Faces in the Wild (AGFW), and Cross-Age Celebrity Dataset (CACD). Furthermore, we also evaluate the performance of SDAP on large-scale Megaface challenge to demonstrate the advantages of the proposed solution.
Deep Contextual Recurrent Residual Networks for Scene Labeling
Apr 12, 2017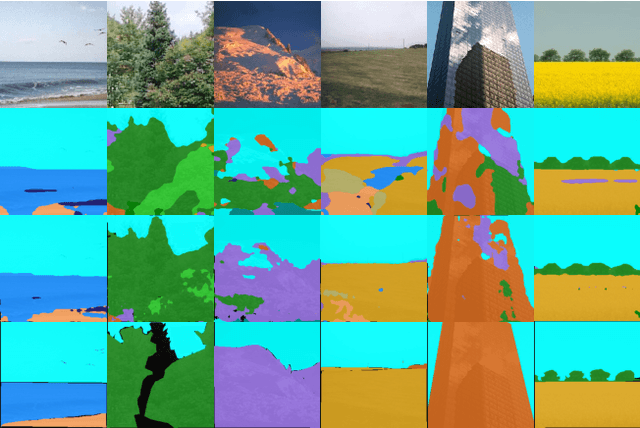
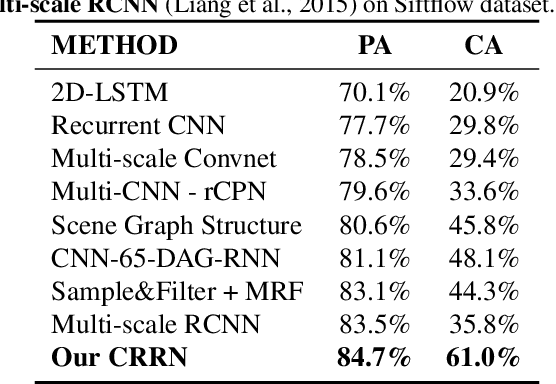
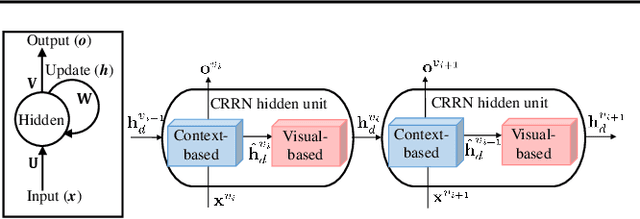
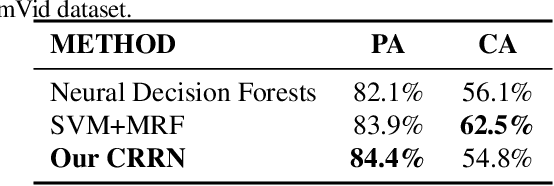
Abstract:Designed as extremely deep architectures, deep residual networks which provide a rich visual representation and offer robust convergence behaviors have recently achieved exceptional performance in numerous computer vision problems. Being directly applied to a scene labeling problem, however, they were limited to capture long-range contextual dependence, which is a critical aspect. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach, Contextual Recurrent Residual Networks (CRRN) which is able to simultaneously handle rich visual representation learning and long-range context modeling within a fully end-to-end deep network. Furthermore, our proposed end-to-end CRRN is completely trained from scratch, without using any pre-trained models in contrast to most existing methods usually fine-tuned from the state-of-the-art pre-trained models, e.g. VGG-16, ResNet, etc. The experiments are conducted on four challenging scene labeling datasets, i.e. SiftFlow, CamVid, Stanford background and SUN datasets, and compared against various state-of-the-art scene labeling methods.
Towards a Deep Learning Framework for Unconstrained Face Detection
Jan 02, 2017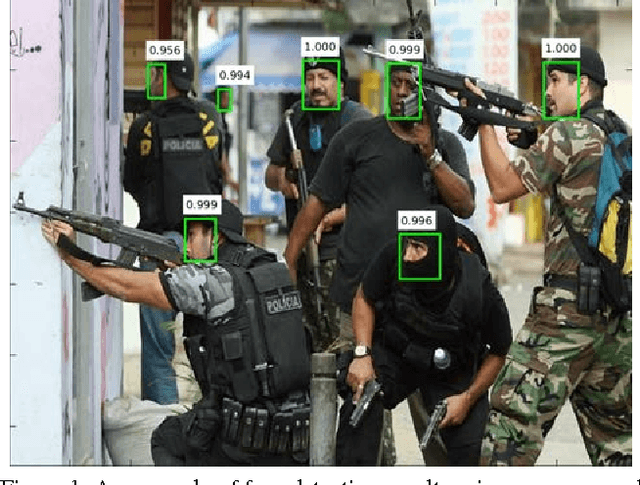
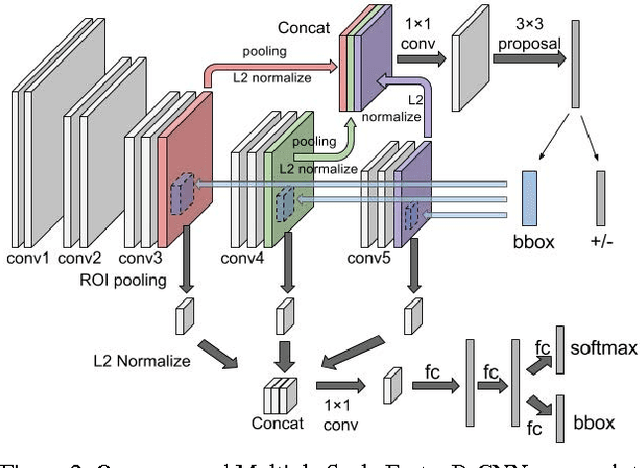
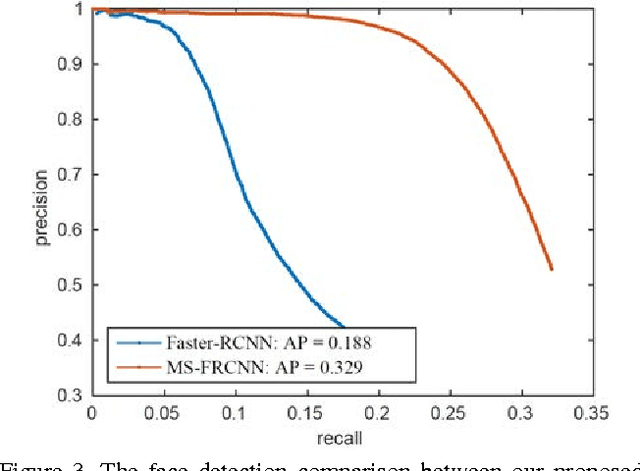
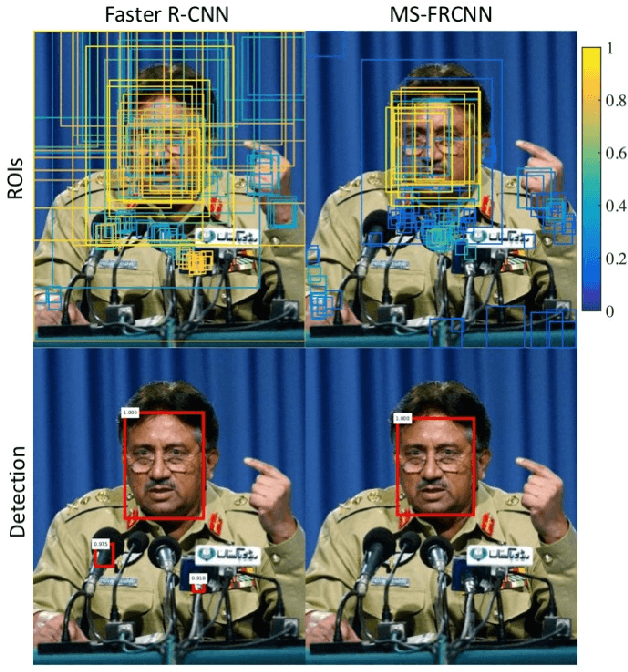
Abstract:Robust face detection is one of the most important pre-processing steps to support facial expression analysis, facial landmarking, face recognition, pose estimation, building of 3D facial models, etc. Although this topic has been intensely studied for decades, it is still challenging due to numerous variants of face images in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we present a novel approach named Multiple Scale Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (MS-FRCNN) to robustly detect human facial regions from images collected under various challenging conditions, e.g. large occlusions, extremely low resolutions, facial expressions, strong illumination variations, etc. The proposed approach is benchmarked on two challenging face detection databases, i.e. the Wider Face database and the Face Detection Dataset and Benchmark (FDDB), and compared against recent other face detection methods, e.g. Two-stage CNN, Multi-scale Cascade CNN, Faceness, Aggregate Chanel Features, HeadHunter, Multi-view Face Detection, Cascade CNN, etc. The experimental results show that our proposed approach consistently achieves highly competitive results with the state-of-the-art performance against other recent face detection methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge