Invertible Residual Network with Regularization for Effective Medical Image Segmentation
Paper and Code
Mar 16, 2021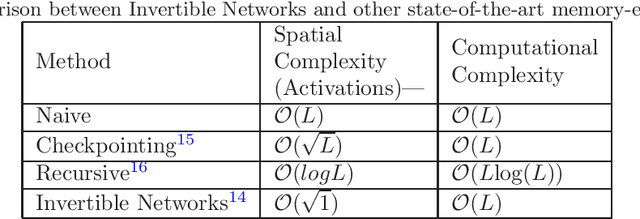
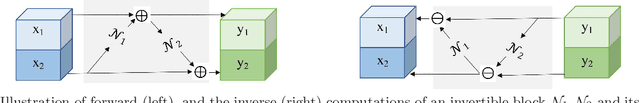
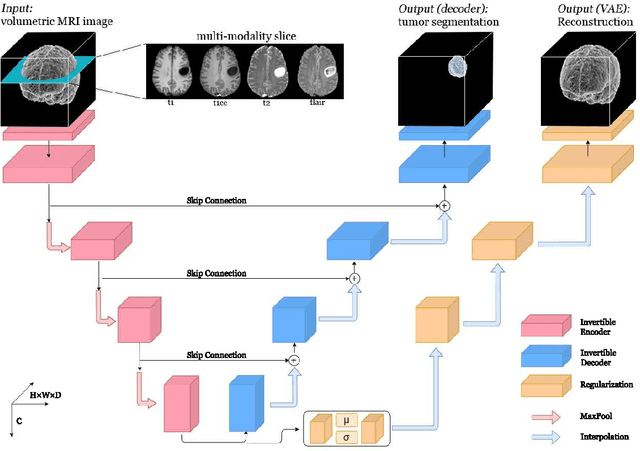
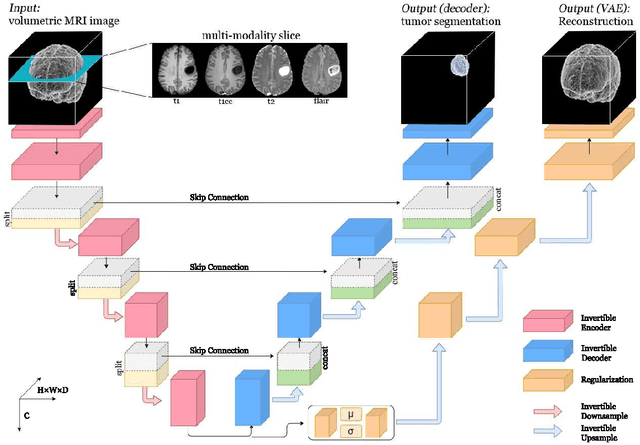
Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) i.e. Residual Networks (ResNets) have been used successfully for many computer vision tasks, but are difficult to scale to 3D volumetric medical data. Memory is increasingly often the bottleneck when training 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Recently, invertible neural networks have been applied to significantly reduce activation memory footprint when training neural networks with backpropagation thanks to the invertible functions that allow retrieving its input from its output without storing intermediate activations in memory to perform the backpropagation. Among many successful network architectures, 3D Unet has been established as a standard architecture for volumetric medical segmentation. Thus, we choose 3D Unet as a baseline for a non-invertible network and we then extend it with the invertible residual network. In this paper, we proposed two versions of the invertible Residual Network, namely Partially Invertible Residual Network (Partially-InvRes) and Fully Invertible Residual Network (Fully-InvRes). In Partially-InvRes, the invertible residual layer is defined by a technique called additive coupling whereas in Fully-InvRes, both invertible upsampling and downsampling operations are learned based on squeezing (known as pixel shuffle). Furthermore, to avoid the overfitting problem because of less training data, a variational auto-encoder (VAE) branch is added to reconstruct the input volumetric data itself. Our results indicate that by using partially/fully invertible networks as the central workhorse in volumetric segmentation, we not only reduce memory overhead but also achieve compatible segmentation performance compared against the non-invertible 3D Unet. We have demonstrated the proposed networks on various volumetric datasets such as iSeg 2019 and BraTS 2020.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge