Sven Schmeier
DFKI GmbH
Detecting Pipeline Failures through Fine-Grained Analysis of Web Agents
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Web agents powered by large language models (LLMs) can autonomously perform complex, multistep tasks in dynamic web environments. However, current evaluations mostly focus on the overall success while overlooking intermediate errors. This limits insight into failure modes and hinders systematic improvement. This work analyzes existing benchmarks and highlights the lack of fine-grained diagnostic tools. To address this gap, we propose a modular evaluation framework that decomposes agent pipelines into interpretable stages for detailed error analysis. Using the SeeAct framework and the Mind2Web dataset as a case study, we show how this approach reveals actionable weaknesses missed by standard metrics - paving the way for more robust and generalizable web agents.
When Performance is not Enough -- A Multidisciplinary View on Clinical Decision Support
Apr 27, 2022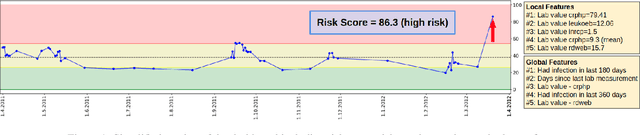
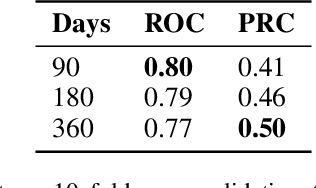
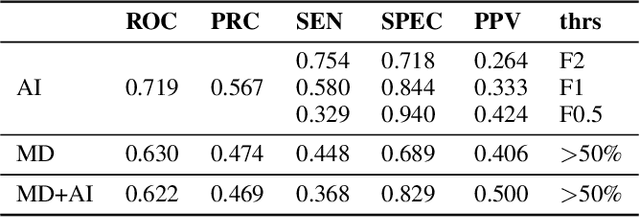
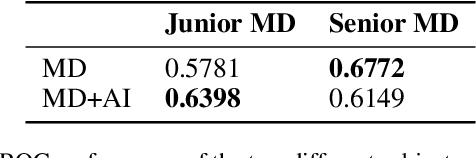
Abstract:Scientific publications about machine learning in healthcare are often about implementing novel methods and boosting the performance - at least from a computer science perspective. However, beyond such often short-lived improvements, much more needs to be taken into consideration if we want to arrive at a sustainable progress in healthcare. What does it take to actually implement such a system, make it usable for the domain expert, and possibly bring it into practical usage? Targeted at Computer Scientists, this work presents a multidisciplinary view on machine learning in medical decision support systems and covers information technology, medical, as well as ethical aspects. Along with an implemented risk prediction system in nephrology, challenges and lessons learned in a pilot project are presented.
From Witch's Shot to Music Making Bones -- Resources for Medical Laymen to Technical Language and Vice Versa
May 23, 2020



Abstract:Many people share information in social media or forums, like food they eat, sports activities they do or events which have been visited. This also applies to information about a person's health status. Information we share online unveils directly or indirectly information about our lifestyle and health situation and thus provides a valuable data resource. If we can make advantage of that data, applications can be created that enable e.g. the detection of possible risk factors of diseases or adverse drug reactions of medications. However, as most people are not medical experts, language used might be more descriptive rather than the precise medical expression as medics do. To detect and use those relevant information, laymen language has to be translated and/or linked to the corresponding medical concept. This work presents baseline data sources in order to address this challenge for German. We introduce a new data set which annotates medical laymen and technical expressions in a patient forum, along with a set of medical synonyms and definitions, and present first baseline results on the data.
SynsetRank: Degree-adjusted Random Walk for Relation Identification
Sep 15, 2016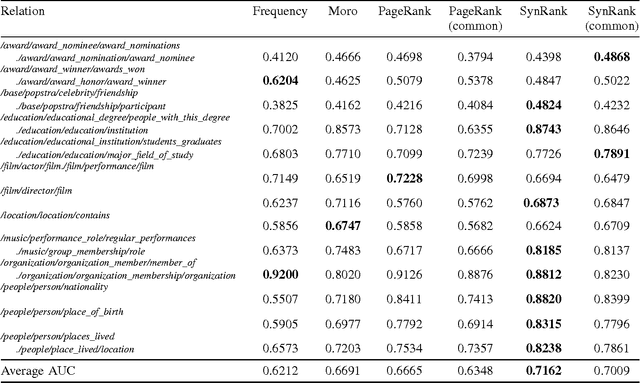

Abstract:In relation extraction, a key process is to obtain good detectors that find relevant sentences describing the target relation. To minimize the necessity of labeled data for refining detectors, previous work successfully made use of BabelNet, a semantic graph structure expressing relationships between synsets, as side information or prior knowledge. The goal of this paper is to enhance the use of graph structure in the framework of random walk with a few adjustable parameters. Actually, a straightforward application of random walk degrades the performance even after parameter optimization. With the insight from this unsuccessful trial, we propose SynsetRank, which adjusts the initial probability so that high degree nodes influence the neighbors as strong as low degree nodes. In our experiment on 13 relations in the FB15K-237 dataset, SynsetRank significantly outperforms baselines and the plain random walk approach.
Message Classification in the Call Center
Mar 14, 2000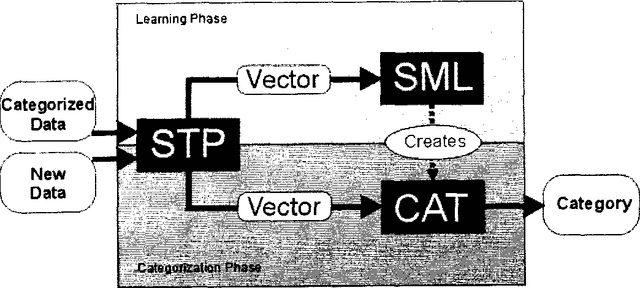
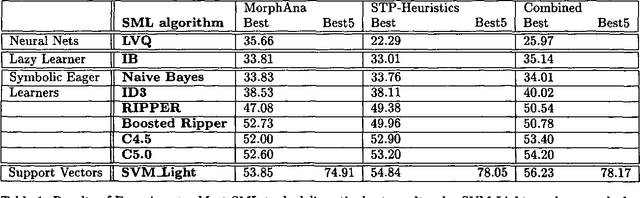
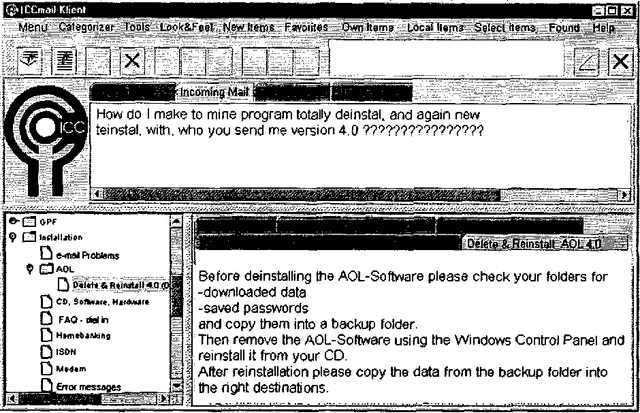
Abstract:Customer care in technical domains is increasingly based on e-mail communication, allowing for the reproduction of approved solutions. Identifying the customer's problem is often time-consuming, as the problem space changes if new products are launched. This paper describes a new approach to the classification of e-mail requests based on shallow text processing and machine learning techniques. It is implemented within an assistance system for call center agents that is used in a commercial setting.
* 8 pages with 2 figures
Natural Language Dialogue Service for Appointment Scheduling Agents
Feb 11, 1997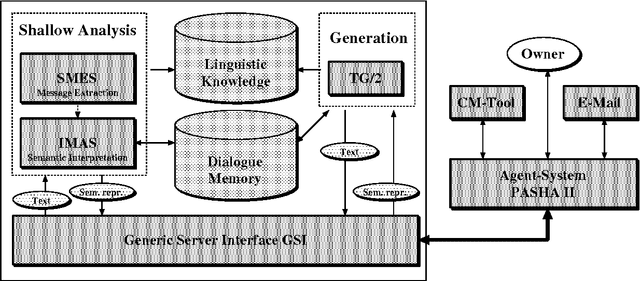
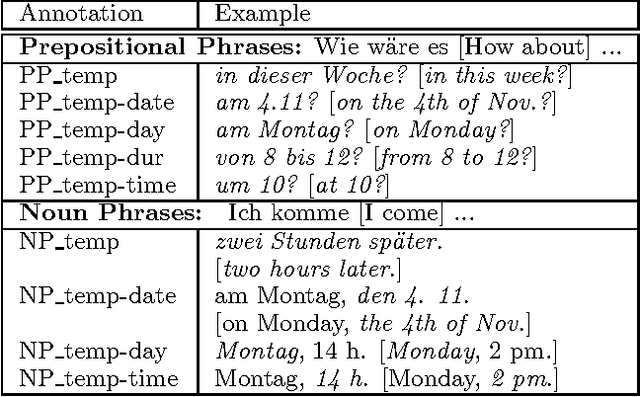
Abstract:Appointment scheduling is a problem faced daily by many individuals and organizations. Cooperating agent systems have been developed to partially automate this task. In order to extend the circle of participants as far as possible we advocate the use of natural language transmitted by e-mail. We describe COSMA, a fully implemented German language server for existing appointment scheduling agent systems. COSMA can cope with multiple dialogues in parallel, and accounts for differences in dialogue behaviour between human and machine agents. NL coverage of the sublanguage is achieved through both corpus-based grammar development and the use of message extraction techniques.
* 8 or 9 pages, LaTeX; uses aclap.sty, epsf.tex
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge