Sujuan Hou
Multimodal Inverse Attention Network with Intrinsic Discriminant Feature Exploitation for Fake News Detection
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal fake news detection has garnered significant attention due to its profound implications for social security. While existing approaches have contributed to understanding cross-modal consistency, they often fail to leverage modal-specific representations and explicit discrepant features. To address these limitations, we propose a Multimodal Inverse Attention Network (MIAN), a novel framework that explores intrinsic discriminative features based on news content to advance fake news detection. Specifically, MIAN introduces a hierarchical learning module that captures diverse intra-modal relationships through local-to-global and local-to-local interactions, thereby generating enhanced unimodal representations to improve the identification of fake news at the intra-modal level. Additionally, a cross-modal interaction module employs a co-attention mechanism to establish and model dependencies between the refined unimodal representations, facilitating seamless semantic integration across modalities. To explicitly extract inconsistency features, we propose an inverse attention mechanism that effectively highlights the conflicting patterns and semantic deviations introduced by fake news in both intra- and inter-modality. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that MIAN significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, underscoring its pivotal contribution to advancing social security through enhanced multimodal fake news detection.
Molecular Odor Prediction Based on Multi-Feature Graph Attention Networks
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Olfactory perception plays a critical role in both human and organismal interactions, yet understanding of its underlying mechanisms and influencing factors remain insufficient. Molecular structures influence odor perception through intricate biochemical interactions, and accurately quantifying structure-odor relationships presents significant challenges. The Quantitative Structure-Odor Relationship (QSOR) task, which involves predicting the associations between molecular structures and their corresponding odors, seeks to address these challenges. To this end, we propose a method for QSOR, utilizing Graph Attention Networks to model molecular structures and capture both local and global features. Unlike conventional QSOR approaches reliant on predefined descriptors, our method leverages diverse molecular feature extraction techniques to automatically learn comprehensive representations. This integration enhances the model's capacity to handle complex molecular information, improves prediction accuracy. Our approach demonstrates clear advantages in QSOR prediction tasks, offering valuable insights into the application of deep learning in cheminformatics.
Molecular Odor Prediction with Harmonic Modulated Feature Mapping and Chemically-Informed Loss
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Molecular odor prediction has great potential across diverse fields such as chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and environmental science, enabling the rapid design of new materials and enhancing environmental monitoring. However, current methods face two main challenges: First, existing models struggle with non-smooth objective functions and the complexity of mixed feature dimensions; Second, datasets suffer from severe label imbalance, which hampers model training, particularly in learning minority class labels. To address these issues, we introduce a novel feature mapping method and a molecular ensemble optimization loss function. By incorporating feature importance learning and frequency modulation, our model adaptively adjusts the contribution of each feature, efficiently capturing the intricate relationship between molecular structures and odor descriptors. Our feature mapping preserves feature independence while enhancing the model's efficiency in utilizing molecular features through frequency modulation. Furthermore, the proposed loss function dynamically adjusts label weights, improves structural consistency, and strengthens label correlations, effectively addressing data imbalance and label co-occurrence challenges. Experimental results show that our method significantly can improves the accuracy of molecular odor prediction across various deep learning models, demonstrating its promising potential in molecular structure representation and chemoinformatics.
Deep Learning for Logo Detection: A Survey
Oct 10, 2022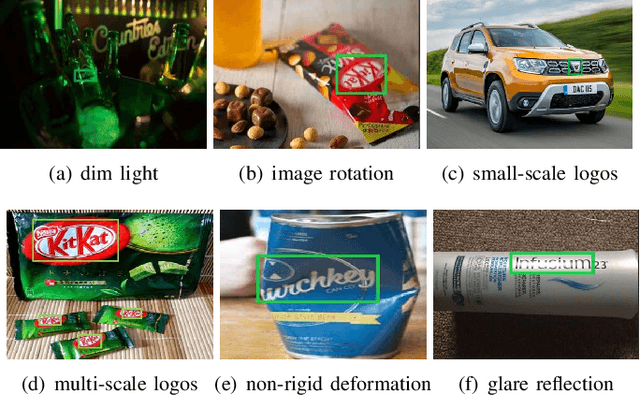
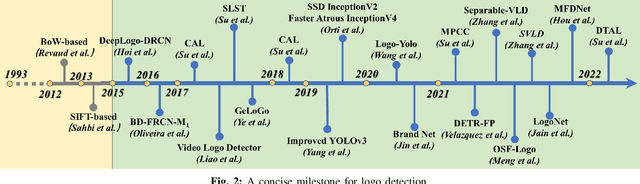

Abstract:When logos are increasingly created, logo detection has gradually become a research hotspot across many domains and tasks. Recent advances in this area are dominated by deep learning-based solutions, where many datasets, learning strategies, network architectures, etc. have been employed. This paper reviews the advance in applying deep learning techniques to logo detection. Firstly, we discuss a comprehensive account of public datasets designed to facilitate performance evaluation of logo detection algorithms, which tend to be more diverse, more challenging, and more reflective of real life. Next, we perform an in-depth analysis of the existing logo detection strategies and the strengths and weaknesses of each learning strategy. Subsequently, we summarize the applications of logo detection in various fields, from intelligent transportation and brand monitoring to copyright and trademark compliance. Finally, we analyze the potential challenges and present the future directions for the development of logo detection to complete this survey.
Discriminative Semantic Feature Pyramid Network with Guided Anchoring for Logo Detection
Aug 31, 2021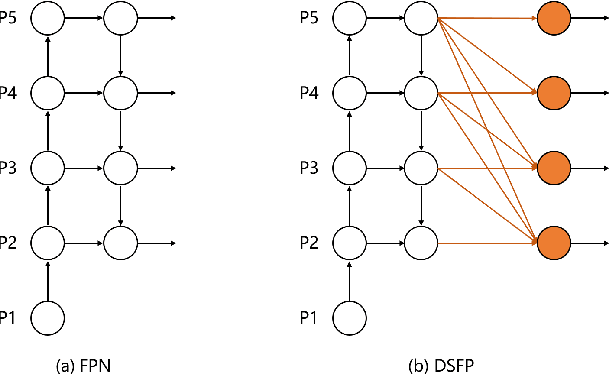
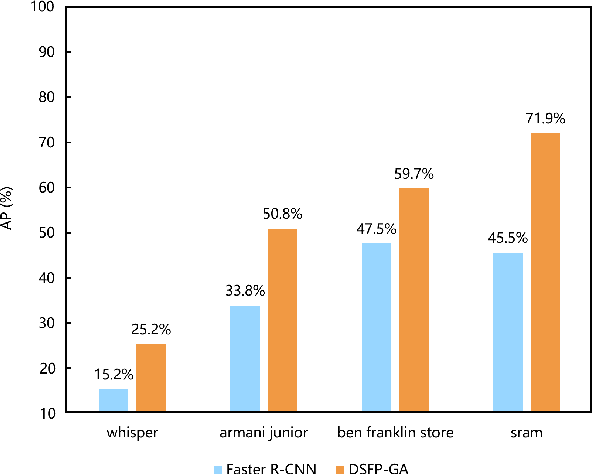
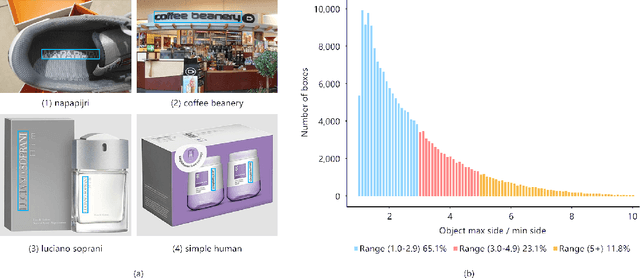
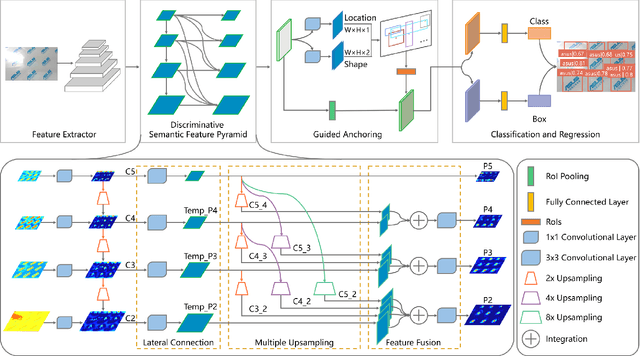
Abstract:Recently, logo detection has received more and more attention for its wide applications in the multimedia field, such as intellectual property protection, product brand management, and logo duration monitoring. Unlike general object detection, logo detection is a challenging task, especially for small logo objects and large aspect ratio logo objects in the real-world scenario. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, named Discriminative Semantic Feature Pyramid Network with Guided Anchoring (DSFP-GA), which can address these challenges via aggregating the semantic information and generating different aspect ratio anchor boxes. More specifically, our approach mainly consists of Discriminative Semantic Feature Pyramid (DSFP) and Guided Anchoring (GA). Considering that low-level feature maps that are used to detect small logo objects lack semantic information, we propose the DSFP, which can enrich more discriminative semantic features of low-level feature maps and can achieve better performance on small logo objects. Furthermore, preset anchor boxes are less efficient for detecting large aspect ratio logo objects. We therefore integrate the GA into our method to generate large aspect ratio anchor boxes to mitigate this issue. Extensive experimental results on four benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed DSFP-GA. Moreover, we further conduct visual analysis and ablation studies to illustrate the advantage of our method in detecting small and large aspect logo objects. The code and models can be found at https://github.com/Zhangbaisong/DSFP-GA.
FoodLogoDet-1500: A Dataset for Large-Scale Food Logo Detection via Multi-Scale Feature Decoupling Network
Aug 10, 2021
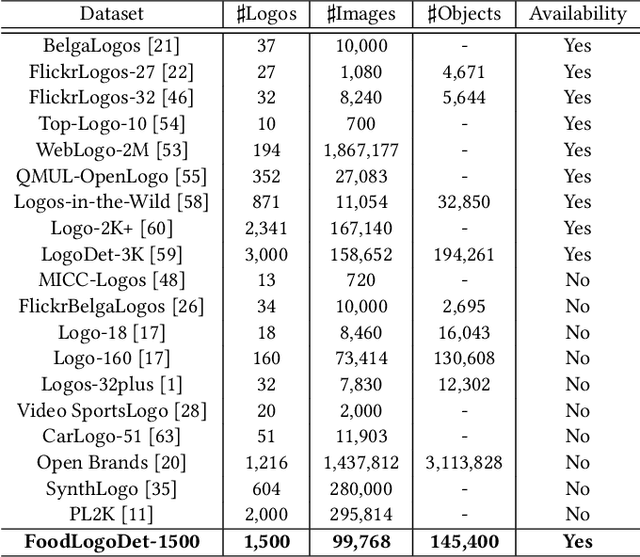

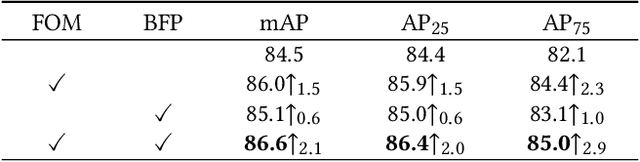
Abstract:Food logo detection plays an important role in the multimedia for its wide real-world applications, such as food recommendation of the self-service shop and infringement detection on e-commerce platforms. A large-scale food logo dataset is urgently needed for developing advanced food logo detection algorithms. However, there are no available food logo datasets with food brand information. To support efforts towards food logo detection, we introduce the dataset FoodLogoDet-1500, a new large-scale publicly available food logo dataset, which has 1,500 categories, about 100,000 images and about 150,000 manually annotated food logo objects. We describe the collection and annotation process of FoodLogoDet-1500, analyze its scale and diversity, and compare it with other logo datasets. To the best of our knowledge, FoodLogoDet-1500 is the first largest publicly available high-quality dataset for food logo detection. The challenge of food logo detection lies in the large-scale categories and similarities between food logo categories. For that, we propose a novel food logo detection method Multi-scale Feature Decoupling Network (MFDNet), which decouples classification and regression into two branches and focuses on the classification branch to solve the problem of distinguishing multiple food logo categories. Specifically, we introduce the feature offset module, which utilizes the deformation-learning for optimal classification offset and can effectively obtain the most representative features of classification in detection. In addition, we adopt a balanced feature pyramid in MFDNet, which pays attention to global information, balances the multi-scale feature maps, and enhances feature extraction capability. Comprehensive experiments on FoodLogoDet-1500 and other two benchmark logo datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The FoodLogoDet-1500 can be found at this https URL.
LogoDet-3K: A Large-Scale Image Dataset for Logo Detection
Aug 12, 2020



Abstract:Logo detection has been gaining considerable attention because of its wide range of applications in the multimedia field, such as copyright infringement detection, brand visibility monitoring, and product brand management on social media. In this paper, we introduce LogoDet-3K, the largest logo detection dataset with full annotation, which has 3,000 logo categories, about 200,000 manually annotated logo objects and 158,652 images. LogoDet-3K creates a more challenging benchmark for logo detection, for its higher comprehensive coverage and wider variety in both logo categories and annotated objects compared with existing datasets. We describe the collection and annotation process of our dataset, analyze its scale and diversity in comparison to other datasets for logo detection. We further propose a strong baseline method Logo-Yolo, which incorporates Focal loss and CIoU loss into the state-of-the-art YOLOv3 framework for large-scale logo detection. Logo-Yolo can solve the problems of multi-scale objects, logo sample imbalance and inconsistent bounding-box regression. It obtains about 4% improvement on the average performance compared with YOLOv3, and greater improvements compared with reported several deep detection models on LogoDet-3K. The evaluations on other three existing datasets further verify the effectiveness of our method, and demonstrate better generalization ability of LogoDet-3K on logo detection and retrieval tasks. The LogoDet-3K dataset is used to promote large-scale logo-related research and it can be found at https://github.com/Wangjing1551/LogoDet-3K-Dataset.
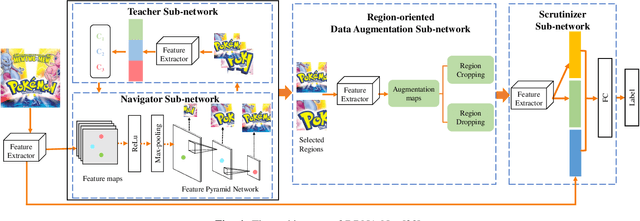
Logo-2K+: A Large-Scale Logo Dataset for Scalable Logo Classification
Nov 11, 2019



Abstract:Logo classification has gained increasing attention for its various applications, such as copyright infringement detection, product recommendation and contextual advertising. Compared with other types of object images, the real-world logo images have larger variety in logo appearance and more complexity in their background. Therefore, recognizing the logo from images is challenging. To support efforts towards scalable logo classification task, we have curated a dataset, Logo-2K+, a new large-scale publicly available real-world logo dataset with 2,341 categories and 167,140 images. Compared with existing popular logo datasets, such as FlickrLogos-32 and LOGO-Net, Logo-2K+ has more comprehensive coverage of logo categories and larger quantity of logo images. Moreover, we propose a Discriminative Region Navigation and Augmentation Network (DRNA-Net), which is capable of discovering more informative logo regions and augmenting these image regions for logo classification. DRNA-Net consists of four sub-networks: the navigator sub-network first selected informative logo-relevant regions guided by the teacher sub-network, which can evaluate its confidence belonging to the ground-truth logo class. The data augmentation sub-network then augments the selected regions via both region cropping and region dropping. Finally, the scrutinizer sub-network fuses features from augmented regions and the whole image for logo classification. Comprehensive experiments on Logo-2K+ and other three existing benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of proposed method. Logo-2K+ and the proposed strong baseline DRNA-Net are expected to further the development of scalable logo image recognition, and the Logo-2K+ dataset can be found at https://github.com/msn199959/Logo-2k-plus-Dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge