Sourav Pal
Brain-wide interpolation and conditioning of gene expression in the human brain using Implicit Neural Representations
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we study the efficacy and utility of recent advances in non-local, non-linear image interpolation and extrapolation algorithms, specifically, ideas based on Implicit Neural Representations (INR), as a tool for analysis of spatial transcriptomics data. We seek to utilize the microarray gene expression data sparsely sampled in the healthy human brain, and produce fully resolved spatial maps of any given gene across the whole brain at a voxel-level resolution. To do so, we first obtained the 100 top AD risk genes, whose baseline spatial transcriptional profiles were obtained from the Allen Human Brain Atlas (AHBA). We adapted Implicit Neural Representation models so that the pipeline can produce robust voxel-resolution quantitative maps of all genes. We present a variety of experiments using interpolations obtained from Abagen as a baseline/reference.
Variational Sampling of Temporal Trajectories
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:A deterministic temporal process can be determined by its trajectory, an element in the product space of (a) initial condition $z_0 \in \mathcal{Z}$ and (b) transition function $f: (\mathcal{Z}, \mathcal{T}) \to \mathcal{Z}$ often influenced by the control of the underlying dynamical system. Existing methods often model the transition function as a differential equation or as a recurrent neural network. Despite their effectiveness in predicting future measurements, few results have successfully established a method for sampling and statistical inference of trajectories using neural networks, partially due to constraints in the parameterization. In this work, we introduce a mechanism to learn the distribution of trajectories by parameterizing the transition function $f$ explicitly as an element in a function space. Our framework allows efficient synthesis of novel trajectories, while also directly providing a convenient tool for inference, i.e., uncertainty estimation, likelihood evaluations and out of distribution detection for abnormal trajectories. These capabilities can have implications for various downstream tasks, e.g., simulation and evaluation for reinforcement learning.
Multi Resolution Analysis (MRA) for Approximate Self-Attention
Jul 21, 2022



Abstract:Transformers have emerged as a preferred model for many tasks in natural langugage processing and vision. Recent efforts on training and deploying Transformers more efficiently have identified many strategies to approximate the self-attention matrix, a key module in a Transformer architecture. Effective ideas include various prespecified sparsity patterns, low-rank basis expansions and combinations thereof. In this paper, we revisit classical Multiresolution Analysis (MRA) concepts such as Wavelets, whose potential value in this setting remains underexplored thus far. We show that simple approximations based on empirical feedback and design choices informed by modern hardware and implementation challenges, eventually yield a MRA-based approach for self-attention with an excellent performance profile across most criteria of interest. We undertake an extensive set of experiments and demonstrate that this multi-resolution scheme outperforms most efficient self-attention proposals and is favorable for both short and long sequences. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/mlpen/mra-attention}.
Deep Unlearning via Randomized Conditionally Independent Hessians
Apr 15, 2022
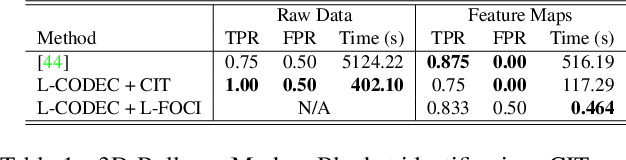


Abstract:Recent legislation has led to interest in machine unlearning, i.e., removing specific training samples from a predictive model as if they never existed in the training dataset. Unlearning may also be required due to corrupted/adversarial data or simply a user's updated privacy requirement. For models which require no training (k-NN), simply deleting the closest original sample can be effective. But this idea is inapplicable to models which learn richer representations. Recent ideas leveraging optimization-based updates scale poorly with the model dimension d, due to inverting the Hessian of the loss function. We use a variant of a new conditional independence coefficient, L-CODEC, to identify a subset of the model parameters with the most semantic overlap on an individual sample level. Our approach completely avoids the need to invert a (possibly) huge matrix. By utilizing a Markov blanket selection, we premise that L-CODEC is also suitable for deep unlearning, as well as other applications in vision. Compared to alternatives, L-CODEC makes approximate unlearning possible in settings that would otherwise be infeasible, including vision models used for face recognition, person re-identification and NLP models that may require unlearning samples identified for exclusion. Code can be found at https://github.com/vsingh-group/LCODEC-deep-unlearning/
Visual Attention for Behavioral Cloning in Autonomous Driving
Dec 05, 2018Abstract:The goal of our work is to use visual attention to enhance autonomous driving performance. We present two methods of predicting visual attention maps. The first method is a supervised learning approach in which we collect eye-gaze data for the task of driving and use this to train a model for predicting the attention map. The second method is a novel unsupervised approach where we train a model to learn to predict attention as it learns to drive a car. Finally, we present a comparative study of our results and show that the supervised approach for predicting attention when incorporated performs better than other approaches.
Saliency Prediction for Mobile User Interfaces
Nov 28, 2017



Abstract:We introduce models for saliency prediction for mobile user interfaces. A mobile interface may include elements like buttons, text, etc. in addition to natural images which enable performing a variety of tasks. Saliency in natural images is a well studied area. However, given the difference in what constitutes a mobile interface, and the usage context of these devices, we postulate that saliency prediction for mobile interface images requires a fresh approach. Mobile interface design involves operating on elements, the building blocks of the interface. We first collected eye-gaze data from mobile devices for free viewing task. Using this data, we develop a novel autoencoder based multi-scale deep learning model that provides saliency prediction at the mobile interface element level. Compared to saliency prediction approaches developed for natural images, we show that our approach performs significantly better on a range of established metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge