Simone Teufel
IMS-CL, University of Stuttgart
Can Language Models Rival Mathematics Students? Evaluating Mathematical Reasoning through Textual Manipulation and Human Experiments
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:In this paper we look at the ability of recent large language models (LLMs) at solving mathematical problems in combinatorics. We compare models LLaMA-2, LLaMA-3.1, GPT-4, and Mixtral against each other and against human pupils and undergraduates with prior experience in mathematical olympiads. To facilitate these comparisons we introduce the Combi-Puzzles dataset, which contains 125 problem variants based on 25 combinatorial reasoning problems. Each problem is presented in one of five distinct forms, created by systematically manipulating the problem statements through adversarial additions, numeric parameter changes, and linguistic obfuscation. Our variations preserve the mathematical core and are designed to measure the generalisability of LLM problem-solving abilities, while also increasing confidence that problems are submitted to LLMs in forms that have not been seen as training instances. We found that a model based on GPT-4 outperformed all other models in producing correct responses, and performed significantly better in the mathematical variation of the problems than humans. We also found that modifications to problem statements significantly impact the LLM's performance, while human performance remains unaffected.
Misalignment of Semantic Relation Knowledge between WordNet and Human Intuition
Dec 03, 2024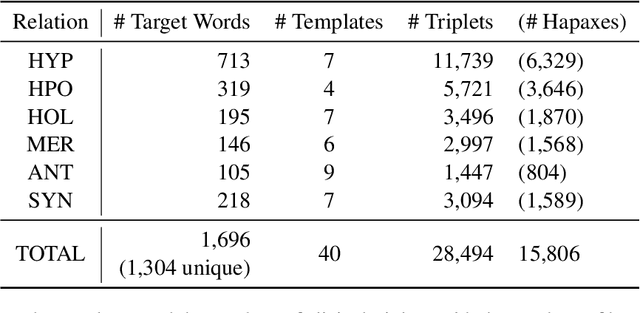
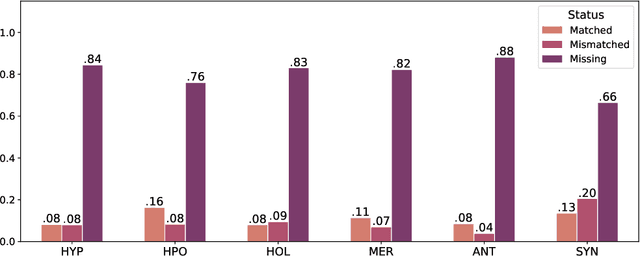
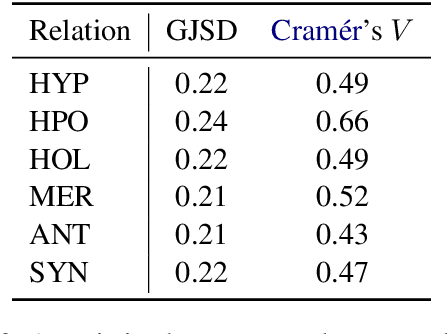
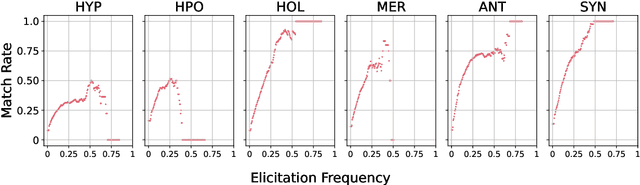
Abstract:WordNet provides a carefully constructed repository of semantic relations, created by specialists. But there is another source of information on semantic relations, the intuition of language users. We present the first systematic study of the degree to which these two sources are aligned. Investigating the cases of misalignment could make proper use of WordNet and facilitate its improvement. Our analysis which uses templates to elicit responses from human participants, reveals a general misalignment of semantic relation knowledge between WordNet and human intuition. Further analyses find a systematic pattern of mismatch among synonymy and taxonomic relations~(hypernymy and hyponymy), together with the fact that WordNet path length does not serve as a reliable indicator of human intuition regarding hypernymy or hyponymy relations.
A Comprehensive Evaluation of Semantic Relation Knowledge of Pretrained Language Models and Humans
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Recently, much work has concerned itself with the enigma of what exactly PLMs (pretrained language models) learn about different aspects of language, and how they learn it. One stream of this type of research investigates the knowledge that PLMs have about semantic relations. However, many aspects of semantic relations were left unexplored. Only one relation was considered, namely hypernymy. Furthermore, previous work did not measure humans' performance on the same task as that solved by the PLMs. This means that at this point in time, there is only an incomplete view of models' semantic relation knowledge. To address this gap, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation framework covering five relations beyond hypernymy, namely hyponymy, holonymy, meronymy, antonymy, and synonymy. We use six metrics (two newly introduced here) for recently untreated aspects of semantic relation knowledge, namely soundness, completeness, symmetry, asymmetry, prototypicality, and distinguishability and fairly compare humans and models on the same task. Our extensive experiments involve 16 PLMs, eight masked and eight causal language models. Up to now only masked language models had been tested although causal and masked language models treat context differently. Our results reveal a significant knowledge gap between humans and models for almost all semantic relations. Antonymy is the outlier relation where all models perform reasonably well. In general, masked language models perform significantly better than causal language models. Nonetheless, both masked and causal language models are likely to confuse non-antonymy relations with antonymy.
ChainNet: Structured Metaphor and Metonymy in WordNet
Mar 29, 2024



Abstract:The senses of a word exhibit rich internal structure. In a typical lexicon, this structure is overlooked: a word's senses are encoded as a list without inter-sense relations. We present ChainNet, a lexical resource which for the first time explicitly identifies these structures. ChainNet expresses how senses in the Open English Wordnet are derived from one another: every nominal sense of a word is either connected to another sense by metaphor or metonymy, or is disconnected in the case of homonymy. Because WordNet senses are linked to resources which capture information about their meaning, ChainNet represents the first dataset of grounded metaphor and metonymy.
Semantic Map-based Generation of Navigation Instructions
Mar 28, 2024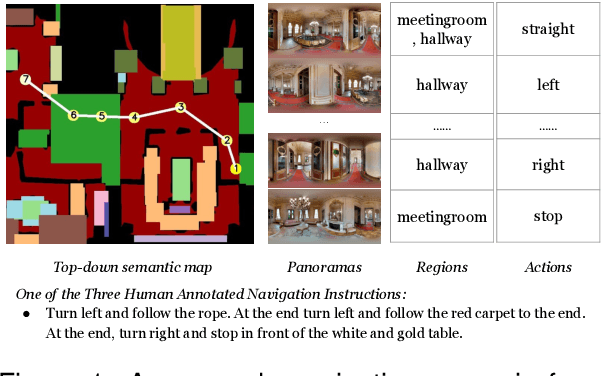
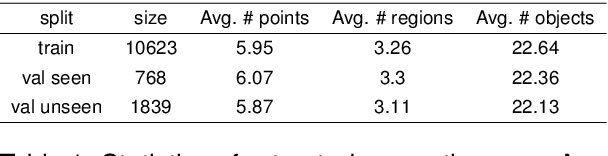
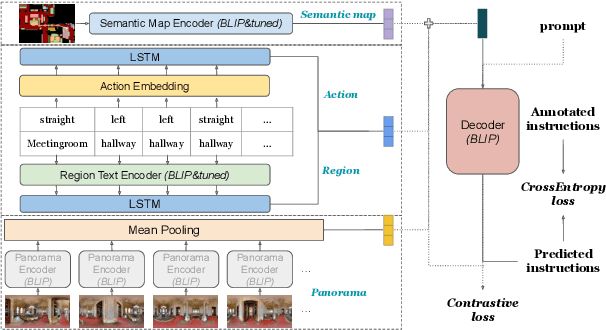
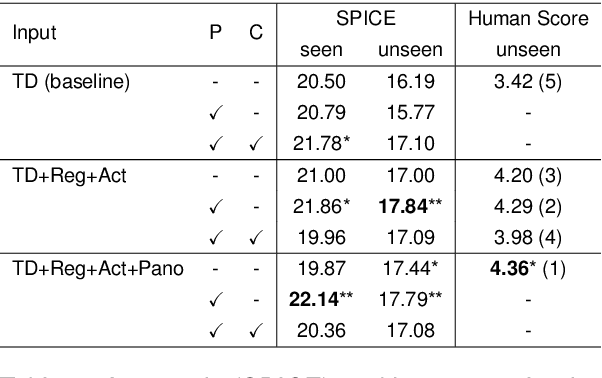
Abstract:We are interested in the generation of navigation instructions, either in their own right or as training material for robotic navigation task. In this paper, we propose a new approach to navigation instruction generation by framing the problem as an image captioning task using semantic maps as visual input. Conventional approaches employ a sequence of panorama images to generate navigation instructions. Semantic maps abstract away from visual details and fuse the information in multiple panorama images into a single top-down representation, thereby reducing computational complexity to process the input. We present a benchmark dataset for instruction generation using semantic maps, propose an initial model and ask human subjects to manually assess the quality of generated instructions. Our initial investigations show promise in using semantic maps for instruction generation instead of a sequence of panorama images, but there is vast scope for improvement. We release the code for data preparation and model training at https://github.com/chengzu-li/VLGen.
The Ethics of Automating Legal Actors
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:The introduction of large public legal datasets has brought about a renaissance in legal NLP. Many of these datasets are comprised of legal judgements - the product of judges deciding cases. This fact, together with the way machine learning works, means that several legal NLP models are models of judges. While some have argued for the automation of judges, in this position piece, we argue that automating the role of the judge raises difficult ethical challenges, in particular for common law legal systems. Our argument follows from the social role of the judge in actively shaping the law, rather than merely applying it. Since current NLP models come nowhere close to having the facilities necessary for this task, they should not be used to automate judges. Furthermore, even in the case the models could achieve human-level capabilities, there would still be remaining ethical concerns inherent in the automation of the legal process.
Metaphorical Polysemy Detection: Conventional Metaphor meets Word Sense Disambiguation
Dec 16, 2022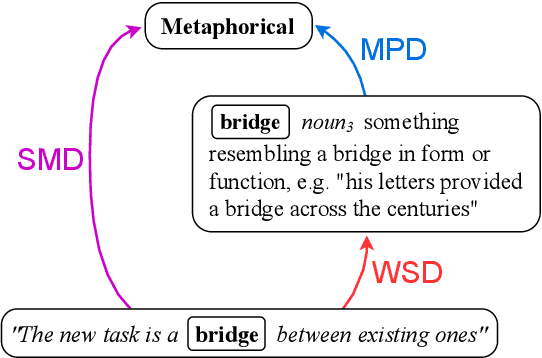


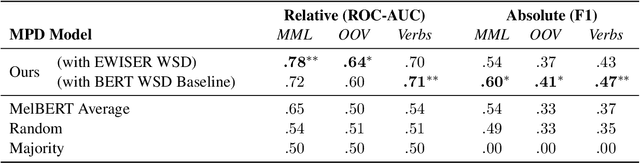
Abstract:Linguists distinguish between novel and conventional metaphor, a distinction which the metaphor detection task in NLP does not take into account. Instead, metaphoricity is formulated as a property of a token in a sentence, regardless of metaphor type. In this paper, we investigate the limitations of treating conventional metaphors in this way, and advocate for an alternative which we name 'metaphorical polysemy detection' (MPD). In MPD, only conventional metaphoricity is treated, and it is formulated as a property of word senses in a lexicon. We develop the first MPD model, which learns to identify conventional metaphors in the English WordNet. To train it, we present a novel training procedure that combines metaphor detection with word sense disambiguation (WSD). For evaluation, we manually annotate metaphor in two subsets of WordNet. Our model significantly outperforms a strong baseline based on a state-of-the-art metaphor detection model, attaining an ROC-AUC score of .78 (compared to .65) on one of the sets. Additionally, when paired with a WSD model, our approach outperforms a state-of-the-art metaphor detection model at identifying conventional metaphors in text (.659 F1 compared to .626).
Homonymy Information for English WordNet
Dec 16, 2022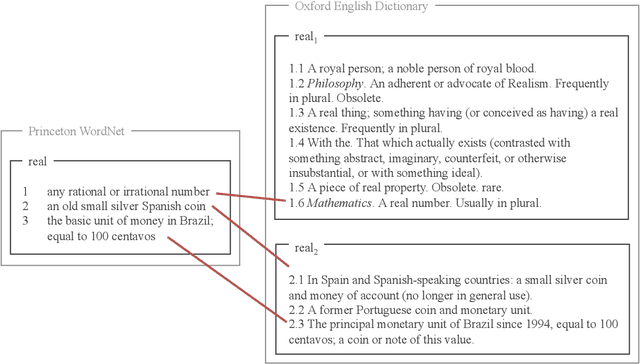

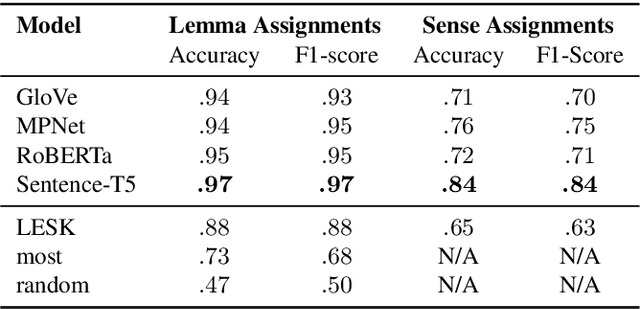
Abstract:A widely acknowledged shortcoming of WordNet is that it lacks a distinction between word meanings which are systematically related (polysemy), and those which are coincidental (homonymy). Several previous works have attempted to fill this gap, by inferring this information using computational methods. We revisit this task, and exploit recent advances in language modelling to synthesise homonymy annotation for Princeton WordNet. Previous approaches treat the problem using clustering methods; by contrast, our method works by linking WordNet to the Oxford English Dictionary, which contains the information we need. To perform this alignment, we pair definitions based on their proximity in an embedding space produced by a Transformer model. Despite the simplicity of this approach, our best model attains an F1 of .97 on an evaluation set that we annotate. The outcome of our work is a high-quality homonymy annotation layer for Princeton WordNet, which we release.
On the Role of Negative Precedent in Legal Outcome Prediction
Aug 17, 2022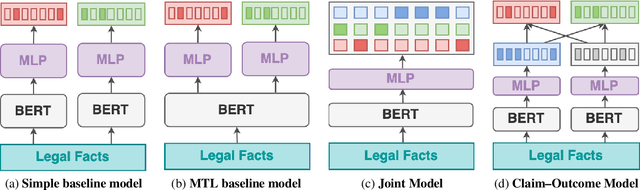
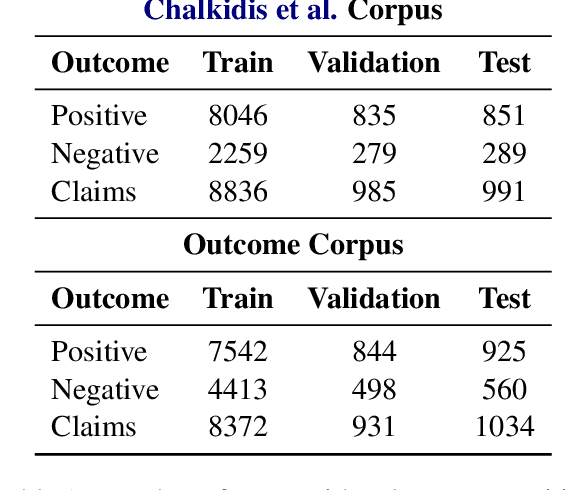
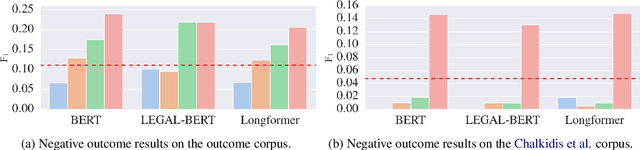
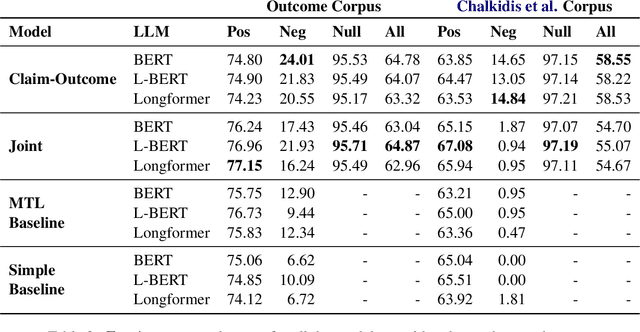
Abstract:Every legal case sets a precedent by developing the law in one of the following two ways. It either expands its scope, in which case it sets positive precedent, or it narrows it down, in which case it sets negative precedent. While legal outcome prediction, which is nothing other than the prediction of positive precedents, is an increasingly popular task in AI, we are the first to investigate negative precedent prediction by focusing on negative outcomes. We discover an asymmetry in existing models' ability to predict positive and negative outcomes. Where state-of-the-art outcome prediction models predicts positive outcomes at 75.06 F1, they predicts negative outcomes at only 10.09 F1, worse than a random baseline. To address this performance gap, we develop two new models inspired by the dynamics of a court process. Our first model significantly improves positive outcome prediction score to 77.15 F1 and our second model more than doubles the negative outcome prediction performance to 24.01 F1. Despite this improvement, shifting focus to negative outcomes reveals that there is still plenty of room to grow when it comes to modelling law.
A surprisal--duration trade-off across and within the world's languages
Sep 30, 2021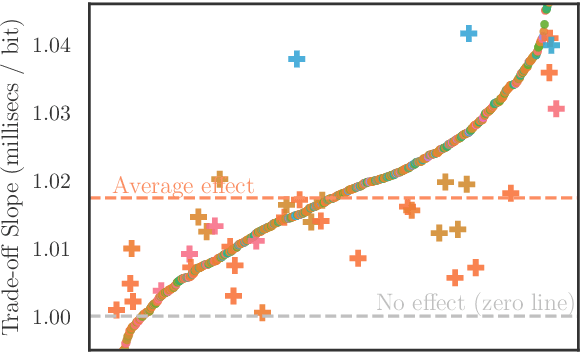
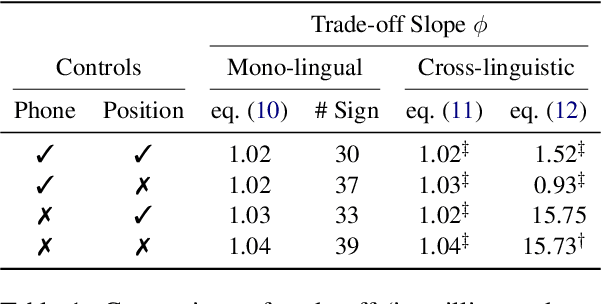
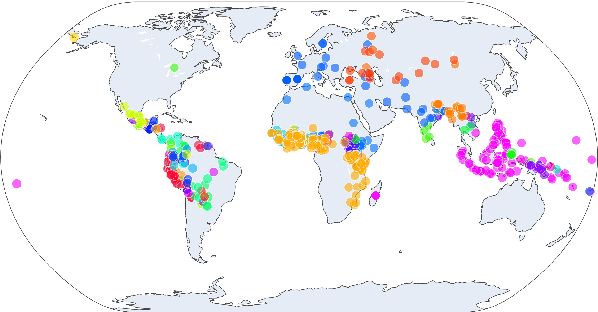
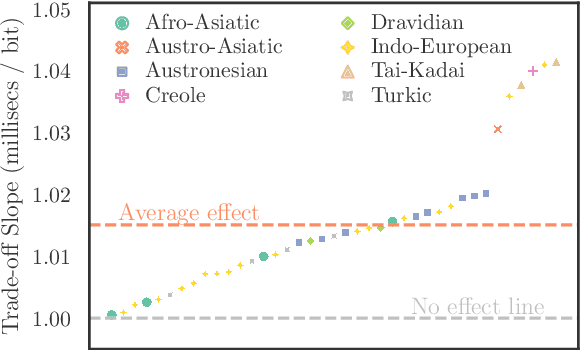
Abstract:While there exist scores of natural languages, each with its unique features and idiosyncrasies, they all share a unifying theme: enabling human communication. We may thus reasonably predict that human cognition shapes how these languages evolve and are used. Assuming that the capacity to process information is roughly constant across human populations, we expect a surprisal--duration trade-off to arise both across and within languages. We analyse this trade-off using a corpus of 600 languages and, after controlling for several potential confounds, we find strong supporting evidence in both settings. Specifically, we find that, on average, phones are produced faster in languages where they are less surprising, and vice versa. Further, we confirm that more surprising phones are longer, on average, in 319 languages out of the 600. We thus conclude that there is strong evidence of a surprisal--duration trade-off in operation, both across and within the world's languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge