Damián Blasi
Systematic Inequalities in Language Technology Performance across the World's Languages
Oct 13, 2021
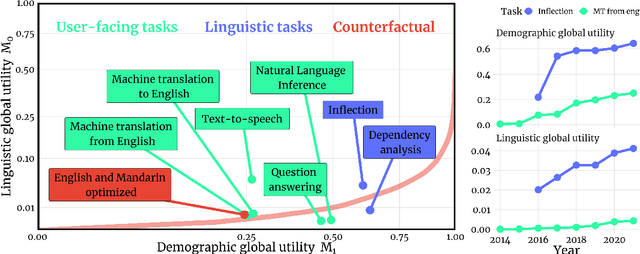
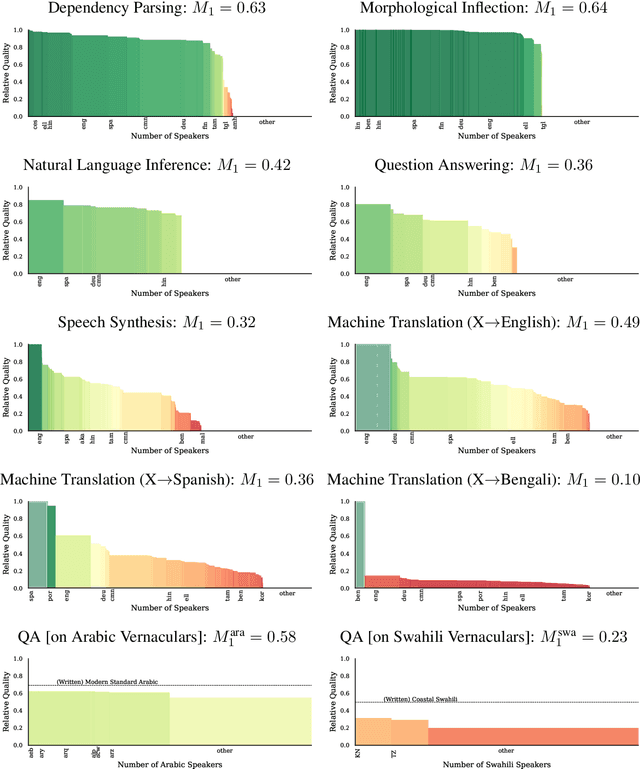
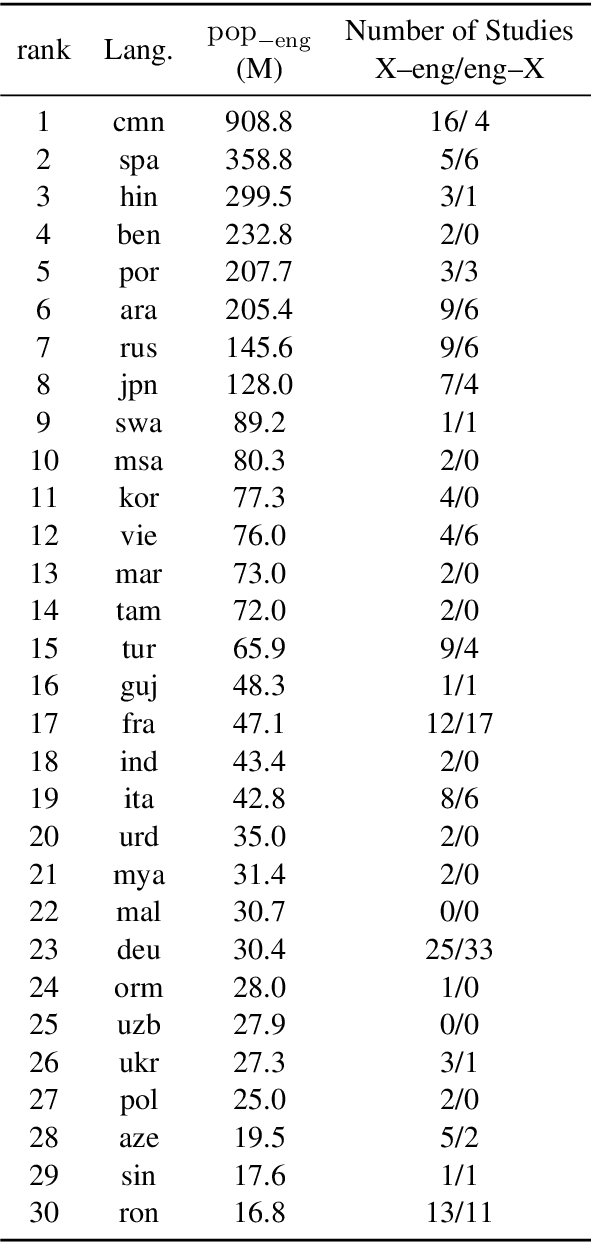
Abstract:Natural language processing (NLP) systems have become a central technology in communication, education, medicine, artificial intelligence, and many other domains of research and development. While the performance of NLP methods has grown enormously over the last decade, this progress has been restricted to a minuscule subset of the world's 6,500 languages. We introduce a framework for estimating the global utility of language technologies as revealed in a comprehensive snapshot of recent publications in NLP. Our analyses involve the field at large, but also more in-depth studies on both user-facing technologies (machine translation, language understanding, question answering, text-to-speech synthesis) as well as more linguistic NLP tasks (dependency parsing, morphological inflection). In the process, we (1) quantify disparities in the current state of NLP research, (2) explore some of its associated societal and academic factors, and (3) produce tailored recommendations for evidence-based policy making aimed at promoting more global and equitable language technologies.
A surprisal--duration trade-off across and within the world's languages
Sep 30, 2021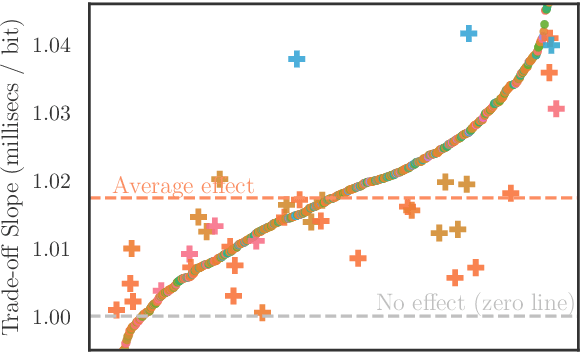
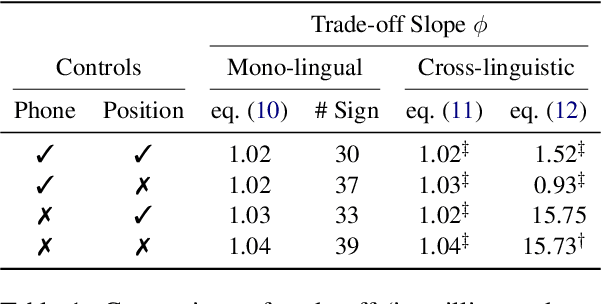
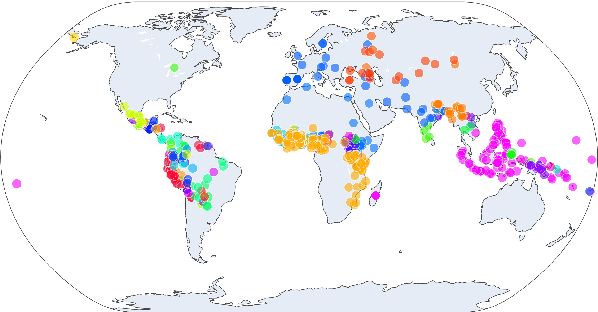
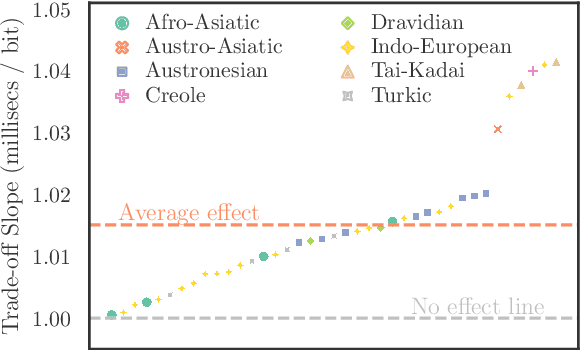
Abstract:While there exist scores of natural languages, each with its unique features and idiosyncrasies, they all share a unifying theme: enabling human communication. We may thus reasonably predict that human cognition shapes how these languages evolve and are used. Assuming that the capacity to process information is roughly constant across human populations, we expect a surprisal--duration trade-off to arise both across and within languages. We analyse this trade-off using a corpus of 600 languages and, after controlling for several potential confounds, we find strong supporting evidence in both settings. Specifically, we find that, on average, phones are produced faster in languages where they are less surprising, and vice versa. Further, we confirm that more surprising phones are longer, on average, in 319 languages out of the 600. We thus conclude that there is strong evidence of a surprisal--duration trade-off in operation, both across and within the world's languages.
How (Non-)Optimal is the Lexicon?
Apr 30, 2021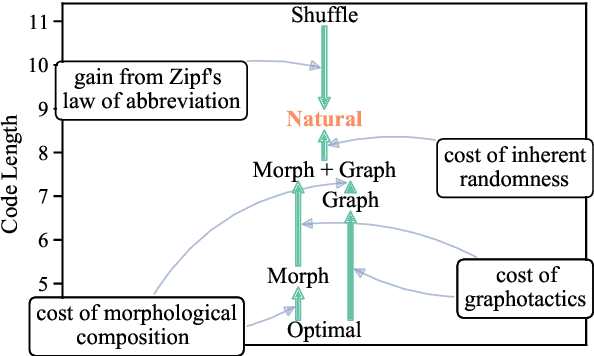
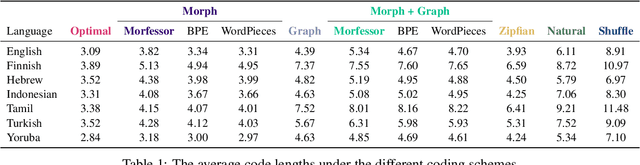
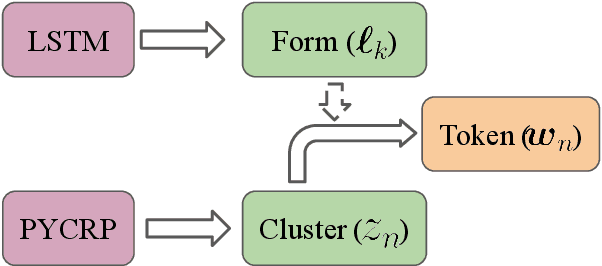
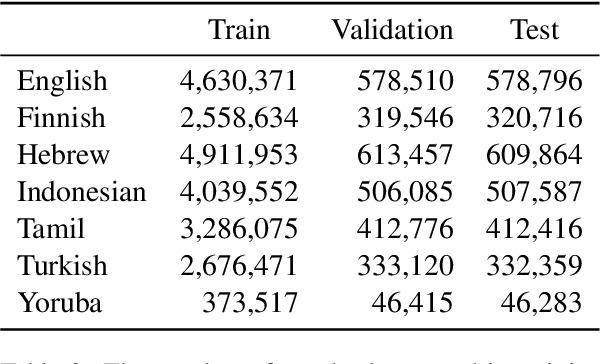
Abstract:The mapping of lexical meanings to wordforms is a major feature of natural languages. While usage pressures might assign short words to frequent meanings (Zipf's law of abbreviation), the need for a productive and open-ended vocabulary, local constraints on sequences of symbols, and various other factors all shape the lexicons of the world's languages. Despite their importance in shaping lexical structure, the relative contributions of these factors have not been fully quantified. Taking a coding-theoretic view of the lexicon and making use of a novel generative statistical model, we define upper bounds for the compressibility of the lexicon under various constraints. Examining corpora from 7 typologically diverse languages, we use those upper bounds to quantify the lexicon's optimality and to explore the relative costs of major constraints on natural codes. We find that (compositional) morphology and graphotactics can sufficiently account for most of the complexity of natural codes -- as measured by code length.
Finding Concept-specific Biases in Form--Meaning Associations
Apr 29, 2021
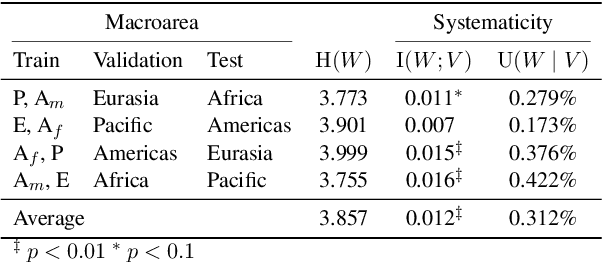
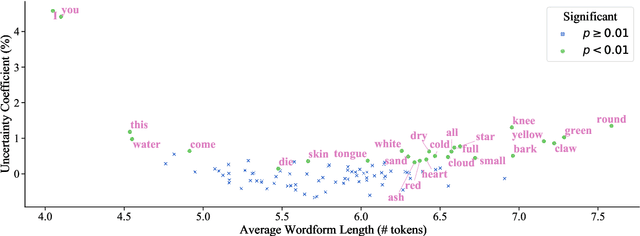
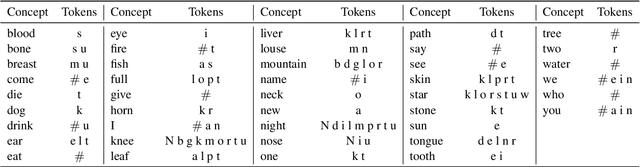
Abstract:This work presents an information-theoretic operationalisation of cross-linguistic non-arbitrariness. It is not a new idea that there are small, cross-linguistic associations between the forms and meanings of words. For instance, it has been claimed (Blasi et al., 2016) that the word for "tongue" is more likely than chance to contain the phone [l]. By controlling for the influence of language family and geographic proximity within a very large concept-aligned, cross-lingual lexicon, we extend methods previously used to detect within language non-arbitrariness (Pimentel et al., 2019) to measure cross-linguistic associations. We find that there is a significant effect of non-arbitrariness, but it is unsurprisingly small (less than 0.5% on average according to our information-theoretic estimate). We also provide a concept-level analysis which shows that a quarter of the concepts considered in our work exhibit a significant level of cross-linguistic non-arbitrariness. In sum, the paper provides new methods to detect cross-linguistic associations at scale, and confirms their effects are minor.
On the interpretation and significance of bias metrics in texts: a PMI-based approach
Apr 13, 2021
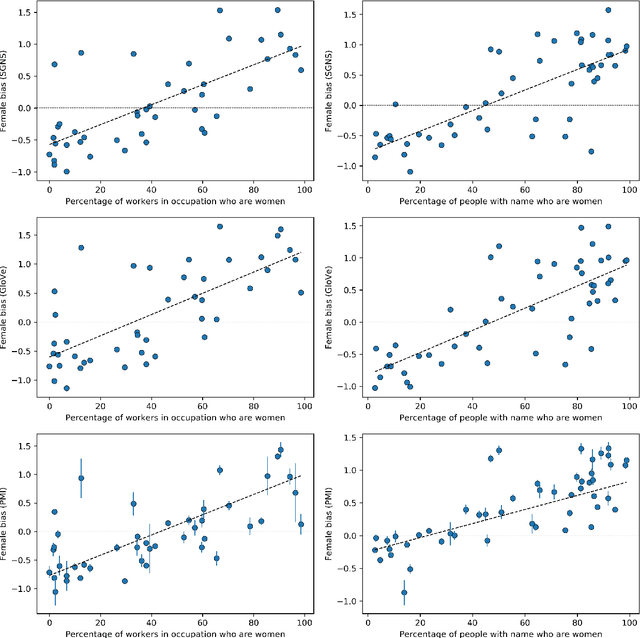

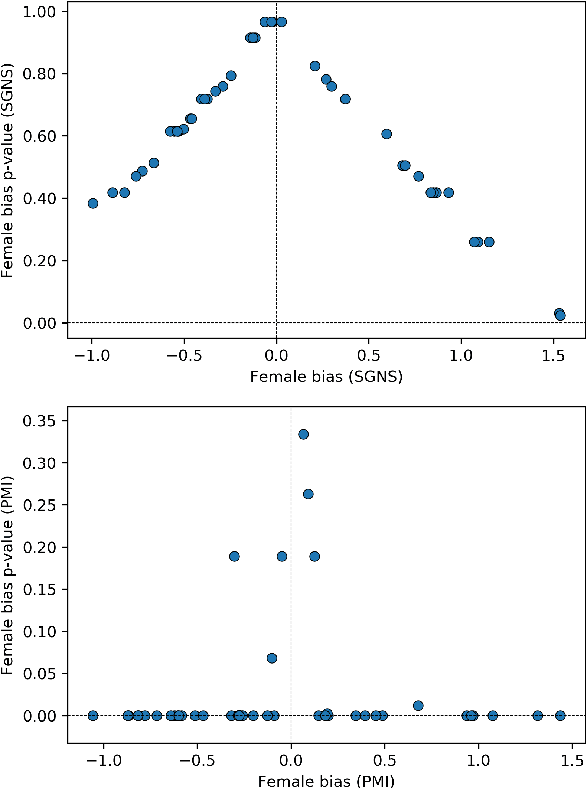
Abstract:In recent years, the use of word embeddings has become popular to measure the presence of biases in texts. Despite the fact that these measures have been shown to be effective in detecting a wide variety of biases, metrics based on word embeddings lack transparency, explainability and interpretability. In this study, we propose a PMI-based metric to quantify biases in texts. We show that this metric can be approximated by an odds ratio, which allows estimating the confidence interval and statistical significance of textual bias. We also show that this PMI-based measure can be expressed as a function of conditional probabilities, providing a simple interpretation in terms of word co-occurrences. Our approach produces a performance comparable to GloVe-based and Skip-gram-based metrics in experiments of gender-occupation and gender-name associations. We discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using methods based on first-order vs second-order co-occurrences, from the point of view of the interpretability of the metric and the sparseness of the data.
Speakers Fill Lexical Semantic Gaps with Context
Oct 05, 2020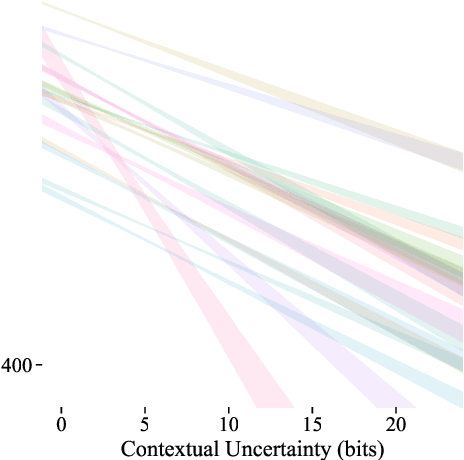
Abstract:Lexical ambiguity is widespread in language, allowing for the reuse of economical word forms and therefore making language more efficient. If ambiguous words cannot be disambiguated from context, however, this gain in efficiency might make language less clear---resulting in frequent miscommunication. For a language to be clear and efficiently encoded, we posit that the lexical ambiguity of a word type should correlate with how much information context provides about it, on average. To investigate whether this is the case, we operationalise the lexical ambiguity of a word as the entropy of meanings it can take, and provide two ways to estimate this---one which requires human annotation (using WordNet), and one which does not (using BERT), making it readily applicable to a large number of languages. We validate these measures by showing that, on six high-resource languages, there are significant Pearson correlations between our BERT-based estimate of ambiguity and the number of synonyms a word has in WordNet (e.g. $\rho = 0.40$ in English). We then test our main hypothesis---that a word's lexical ambiguity should negatively correlate with its contextual uncertainty---and find significant correlations on all 18 typologically diverse languages we analyse. This suggests that, in the presence of ambiguity, speakers compensate by making contexts more informative.
On the Relationships Between the Grammatical Genders of Inanimate Nouns and Their Co-Occurring Adjectives and Verbs
May 03, 2020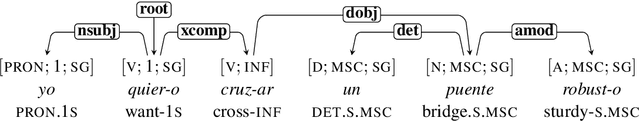
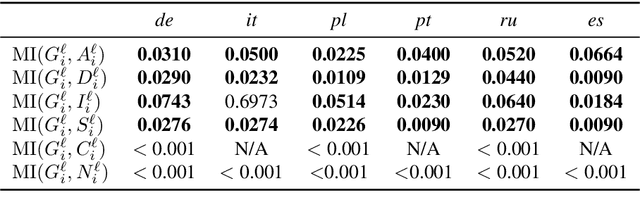
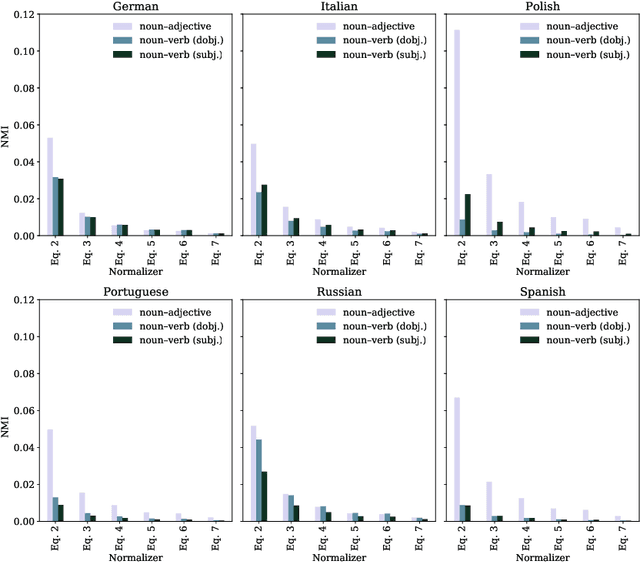
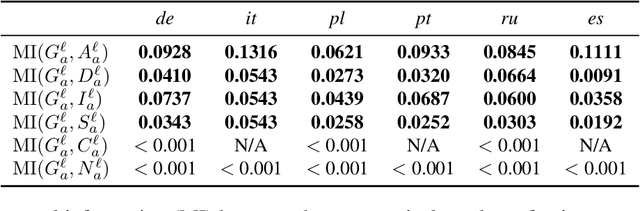
Abstract:We use large-scale corpora in six different gendered languages, along with tools from NLP and information theory, to test whether there is a relationship between the grammatical genders of inanimate nouns and the adjectives used to describe those nouns. For all six languages, we find that there is a statistically significant relationship. We also find that there are statistically significant relationships between the grammatical genders of inanimate nouns and the verbs that take those nouns as direct objects, as indirect objects, and as subjects. We defer a deeper investigation of these relationships for future work.
Quantifying the Semantic Core of Gender Systems
Oct 29, 2019
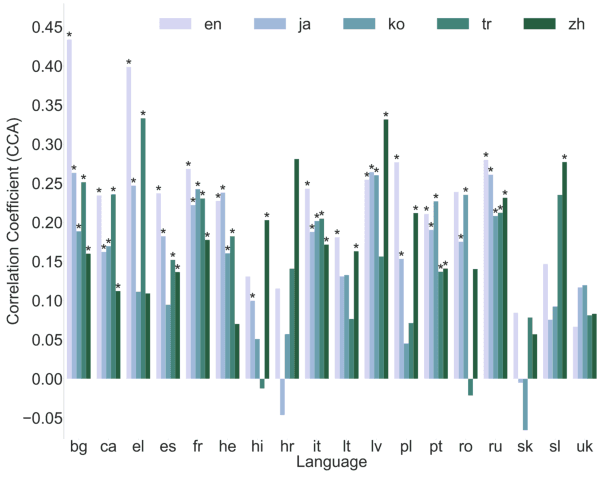
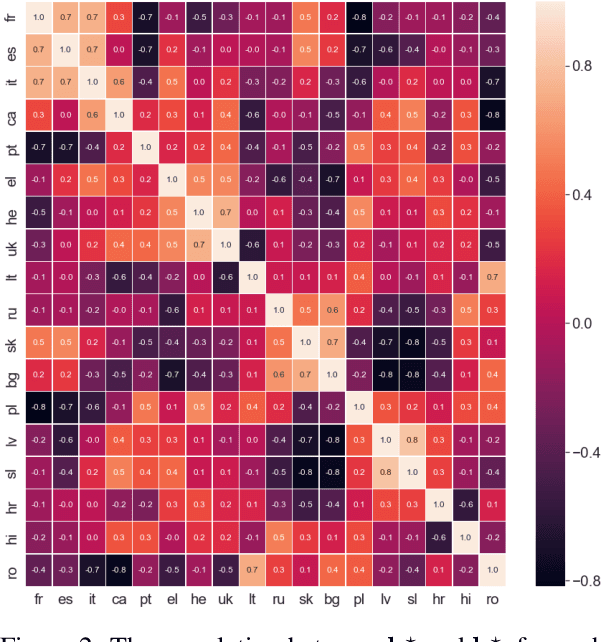
Abstract:Many of the world's languages employ grammatical gender on the lexeme. For example, in Spanish, the word for 'house' (casa) is feminine, whereas the word for 'paper' (papel) is masculine. To a speaker of a genderless language, this assignment seems to exist with neither rhyme nor reason. But is the assignment of inanimate nouns to grammatical genders truly arbitrary? We present the first large-scale investigation of the arbitrariness of noun-gender assignments. To that end, we use canonical correlation analysis to correlate the grammatical gender of inanimate nouns with an externally grounded definition of their lexical semantics. We find that 18 languages exhibit a significant correlation between grammatical gender and lexical semantics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge