Quantifying the Semantic Core of Gender Systems
Paper and Code
Oct 29, 2019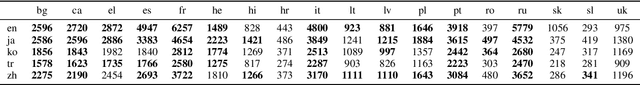
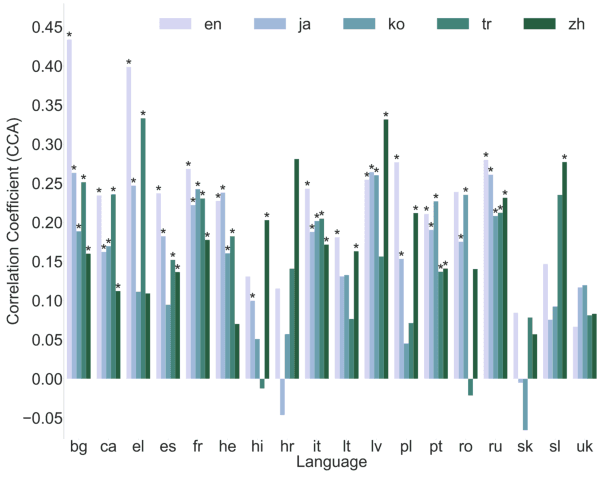
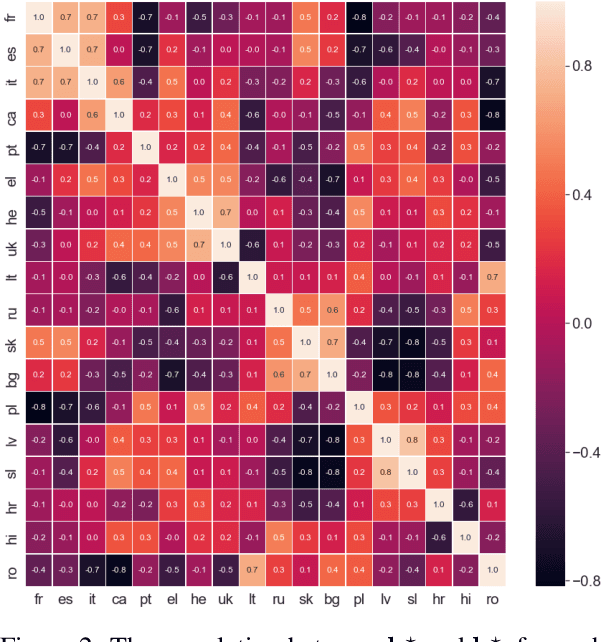
Many of the world's languages employ grammatical gender on the lexeme. For example, in Spanish, the word for 'house' (casa) is feminine, whereas the word for 'paper' (papel) is masculine. To a speaker of a genderless language, this assignment seems to exist with neither rhyme nor reason. But is the assignment of inanimate nouns to grammatical genders truly arbitrary? We present the first large-scale investigation of the arbitrariness of noun-gender assignments. To that end, we use canonical correlation analysis to correlate the grammatical gender of inanimate nouns with an externally grounded definition of their lexical semantics. We find that 18 languages exhibit a significant correlation between grammatical gender and lexical semantics.
* 6 pages, 2 figures, accepted to EMNLP 2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge