Simone Magistri
EFC++: Elastic Feature Consolidation with Prototype Re-balancing for Cold Start Exemplar-free Incremental Learning
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Exemplar-Free Class Incremental Learning (EFCIL) aims to learn from a sequence of tasks without having access to previous task data. In this paper, we consider the challenging Cold Start scenario in which insufficient data is available in the first task to learn a high-quality backbone. This is especially challenging for EFCIL since it requires high plasticity, resulting in feature drift which is difficult to compensate for in the exemplar-free setting. To address this problem, we propose an effective approach to consolidate feature representations by regularizing drift in directions highly relevant to previous tasks and employs prototypes to reduce task-recency bias. Our approach, which we call Elastic Feature Consolidation++ (EFC++) exploits a tractable second-order approximation of feature drift based on a proposed Empirical Feature Matrix (EFM). The EFM induces a pseudo-metric in feature space which we use to regularize feature drift in important directions and to update Gaussian prototypes. In addition, we introduce a post-training prototype re-balancing phase that updates classifiers to compensate for feature drift. Experimental results on CIFAR-100, Tiny-ImageNet, ImageNet-Subset, ImageNet-1K and DomainNet demonstrate that EFC++ is better able to learn new tasks by maintaining model plasticity and significantly outperform the state-of-the-art.
No Task Left Behind: Isotropic Model Merging with Common and Task-Specific Subspaces
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Model merging integrates the weights of multiple task-specific models into a single multi-task model. Despite recent interest in the problem, a significant performance gap between the combined and single-task models remains. In this paper, we investigate the key characteristics of task matrices -- weight update matrices applied to a pre-trained model -- that enable effective merging. We show that alignment between singular components of task-specific and merged matrices strongly correlates with performance improvement over the pre-trained model. Based on this, we propose an isotropic merging framework that flattens the singular value spectrum of task matrices, enhances alignment, and reduces the performance gap. Additionally, we incorporate both common and task-specific subspaces to further improve alignment and performance. Our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple scenarios, including various sets of tasks and model scales. This work advances the understanding of model merging dynamics, offering an effective methodology to merge models without requiring additional training. Code is available at https://github.com/danielm1405/iso-merging .
Covariances for Free: Exploiting Mean Distributions for Federated Learning with Pre-Trained Models
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Using pre-trained models has been found to reduce the effect of data heterogeneity and speed up federated learning algorithms. Recent works have investigated the use of first-order statistics and second-order statistics to aggregate local client data distributions at the server and achieve very high performance without any training. In this work we propose a training-free method based on an unbiased estimator of class covariance matrices. Our method, which only uses first-order statistics in the form of class means communicated by clients to the server, incurs only a fraction of the communication costs required by methods based on communicating second-order statistics. We show how these estimated class covariances can be used to initialize a linear classifier, thus exploiting the covariances without actually sharing them. When compared to state-of-the-art methods which also share only class means, our approach improves performance in the range of 4-26\% with exactly the same communication cost. Moreover, our method achieves performance competitive or superior to sharing second-order statistics with dramatically less communication overhead. Finally, using our method to initialize classifiers and then performing federated fine-tuning yields better and faster convergence. Code is available at https://github.com/dipamgoswami/FedCOF.
How green is continual learning, really? Analyzing the energy consumption in continual training of vision foundation models
Sep 27, 2024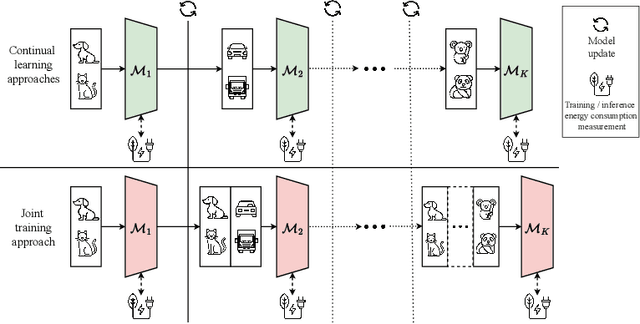
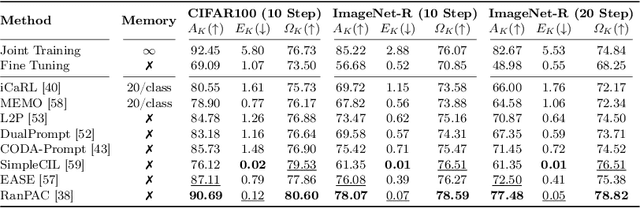
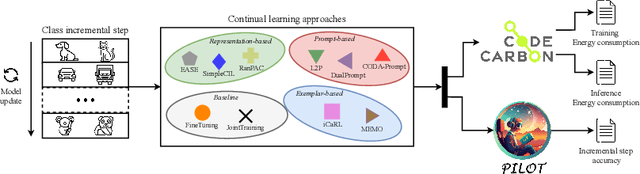
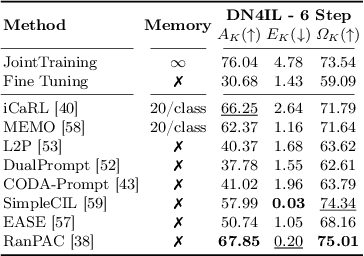
Abstract:With the ever-growing adoption of AI, its impact on the environment is no longer negligible. Despite the potential that continual learning could have towards Green AI, its environmental sustainability remains relatively uncharted. In this work we aim to gain a systematic understanding of the energy efficiency of continual learning algorithms. To that end, we conducted an extensive set of empirical experiments comparing the energy consumption of recent representation-, prompt-, and exemplar-based continual learning algorithms and two standard baseline (fine tuning and joint training) when used to continually adapt a pre-trained ViT-B/16 foundation model. We performed our experiments on three standard datasets: CIFAR-100, ImageNet-R, and DomainNet. Additionally, we propose a novel metric, the Energy NetScore, which we use measure the algorithm efficiency in terms of energy-accuracy trade-off. Through numerous evaluations varying the number and size of the incremental learning steps, our experiments demonstrate that different types of continual learning algorithms have very different impacts on energy consumption during both training and inference. Although often overlooked in the continual learning literature, we found that the energy consumed during the inference phase is crucial for evaluating the environmental sustainability of continual learning models.
An Empirical Analysis of Forgetting in Pre-trained Models with Incremental Low-Rank Updates
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Broad, open source availability of large pretrained foundation models on the internet through platforms such as HuggingFace has taken the world of practical deep learning by storm. A classical pipeline for neural network training now typically consists of finetuning these pretrained network on a small target dataset instead of training from scratch. In the case of large models this can be done even on modest hardware using a low rank training technique known as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA). While Low Rank training has already been studied in the continual learning setting, existing works often consider storing the learned adapter along with the existing model but rarely attempt to modify the weights of the pretrained model by merging the LoRA with the existing weights after finishing the training of each task. In this article we investigate this setting and study the impact of LoRA rank on the forgetting of the pretraining foundation task and on the plasticity and forgetting of subsequent ones. We observe that this rank has an important impact on forgetting of both the pretraining and downstream tasks. We also observe that vision transformers finetuned in that way exhibit a sort of ``contextual'' forgetting, a behaviour that we do not observe for residual networks and that we believe has not been observed yet in previous continual learning works.
Elastic Feature Consolidation for Cold Start Exemplar-free Incremental Learning
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Exemplar-Free Class Incremental Learning (EFCIL) aims to learn from a sequence of tasks without having access to previous task data. In this paper, we consider the challenging Cold Start scenario in which insufficient data is available in the first task to learn a high-quality backbone. This is especially challenging for EFCIL since it requires high plasticity, which results in feature drift which is difficult to compensate for in the exemplar-free setting. To address this problem, we propose a simple and effective approach that consolidates feature representations by regularizing drift in directions highly relevant to previous tasks and employs prototypes to reduce task-recency bias. Our method, called Elastic Feature Consolidation (EFC), exploits a tractable second-order approximation of feature drift based on an Empirical Feature Matrix (EFM). The EFM induces a pseudo-metric in feature space which we use to regularize feature drift in important directions and to update Gaussian prototypes used in a novel asymmetric cross entropy loss which effectively balances prototype rehearsal with data from new tasks. Experimental results on CIFAR-100, Tiny-ImageNet, ImageNet-Subset and ImageNet-1K demonstrate that Elastic Feature Consolidation is better able to learn new tasks by maintaining model plasticity and significantly outperform the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge