Simon Jegou
KVzap: Fast, Adaptive, and Faithful KV Cache Pruning
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Growing context lengths in transformer-based language models have made the key-value (KV) cache a critical inference bottleneck. While many KV cache pruning methods have been proposed, they have not yet been adopted in major inference engines due to speed--accuracy trade-offs. We introduce KVzap, a fast, input-adaptive approximation of KVzip that works in both prefilling and decoding. On Qwen3-8B, Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct, and Qwen3-32B across long-context and reasoning tasks, KVzap achieves $2$--$4\times$ KV cache compression with negligible accuracy loss and achieves state-of-the-art performance on the KVpress leaderboard. Code and models are available at https://github.com/NVIDIA/kvpress.
Winning Amazon KDD Cup'24
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:This paper describes the winning solution of all 5 tasks for the Amazon KDD Cup 2024 Multi Task Online Shopping Challenge for LLMs. The challenge was to build a useful assistant, answering questions in the domain of online shopping. The competition contained 57 diverse tasks, covering 5 different task types (e.g. multiple choice) and across 4 different tracks (e.g. multi-lingual). Our solution is a single model per track. We fine-tune Qwen2-72B-Instruct on our own training dataset. As the competition released only 96 example questions, we developed our own training dataset by processing multiple public datasets or using Large Language Models for data augmentation and synthetic data generation. We apply wise-ft to account for distribution shifts and ensemble multiple LoRA adapters in one model. We employed Logits Processors to constrain the model output on relevant tokens for the tasks. AWQ 4-bit Quantization and vLLM are used during inference to predict the test dataset in the time constraints of 20 to 140 minutes depending on the track. Our solution achieved the first place in each individual track and is the first place overall of Amazons KDD Cup 2024.
The STOIC2021 COVID-19 AI challenge: applying reusable training methodologies to private data
Jun 25, 2023Abstract:Challenges drive the state-of-the-art of automated medical image analysis. The quantity of public training data that they provide can limit the performance of their solutions. Public access to the training methodology for these solutions remains absent. This study implements the Type Three (T3) challenge format, which allows for training solutions on private data and guarantees reusable training methodologies. With T3, challenge organizers train a codebase provided by the participants on sequestered training data. T3 was implemented in the STOIC2021 challenge, with the goal of predicting from a computed tomography (CT) scan whether subjects had a severe COVID-19 infection, defined as intubation or death within one month. STOIC2021 consisted of a Qualification phase, where participants developed challenge solutions using 2000 publicly available CT scans, and a Final phase, where participants submitted their training methodologies with which solutions were trained on CT scans of 9724 subjects. The organizers successfully trained six of the eight Final phase submissions. The submitted codebases for training and running inference were released publicly. The winning solution obtained an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for discerning between severe and non-severe COVID-19 of 0.815. The Final phase solutions of all finalists improved upon their Qualification phase solutions.HSUXJM-TNZF9CHSUXJM-TNZF9C
Self supervised learning improves dMMR/MSI detection from histology slides across multiple cancers
Sep 13, 2021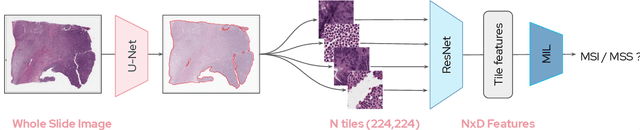

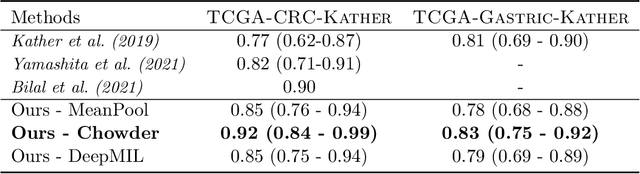
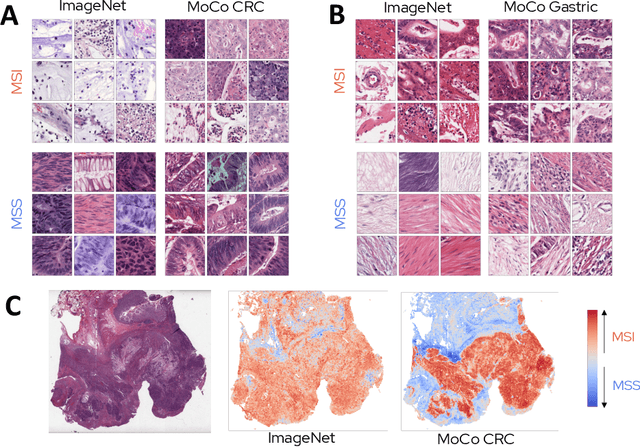
Abstract:Microsatellite instability (MSI) is a tumor phenotype whose diagnosis largely impacts patient care in colorectal cancers (CRC), and is associated with response to immunotherapy in all solid tumors. Deep learning models detecting MSI tumors directly from H&E stained slides have shown promise in improving diagnosis of MSI patients. Prior deep learning models for MSI detection have relied on neural networks pretrained on ImageNet dataset, which does not contain any medical image. In this study, we leverage recent advances in self-supervised learning by training neural networks on histology images from the TCGA dataset using MoCo V2. We show that these networks consistently outperform their counterparts pretrained using ImageNet and obtain state-of-the-art results for MSI detection with AUCs of 0.92 and 0.83 for CRC and gastric tumors, respectively. These models generalize well on an external CRC cohort (0.97 AUC on PAIP) and improve transfer from one organ to another. Finally we show that predictive image regions exhibit meaningful histological patterns, and that the use of MoCo features highlighted more relevant patterns according to an expert pathologist.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge