Katja Ludwig
MMMS: Multi-Modal Multi-Surface Interactive Segmentation
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present a method to interactively create segmentation masks on the basis of user clicks. We pay particular attention to the segmentation of multiple surfaces that are simultaneously present in the same image. Since these surfaces may be heavily entangled and adjacent, we also present a novel extended evaluation metric that accounts for the challenges of this scenario. Additionally, the presented method is able to use multi-modal inputs to facilitate the segmentation task. At the center of this method is a network architecture which takes as input an RGB image, a number of non-RGB modalities, an erroneous mask, and encoded clicks. Based on this input, the network predicts an improved segmentation mask. We design our architecture such that it adheres to two conditions: (1) The RGB backbone is only available as a black-box. (2) To reduce the response time, we want our model to integrate the interaction-specific information after the image feature extraction and the multi-modal fusion. We refer to the overall task as Multi-Modal Multi-Surface interactive segmentation (MMMS). We are able to show the effectiveness of our multi-modal fusion strategy. Using additional modalities, our system reduces the NoC@90 by up to 1.28 clicks per surface on average on DeLiVER and up to 1.19 on MFNet. On top of this, we are able to show that our RGB-only baseline achieves competitive, and in some cases even superior performance when tested in a classical, single-mask interactive segmentation scenario.
CoPa-SG: Dense Scene Graphs with Parametric and Proto-Relations
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:2D scene graphs provide a structural and explainable framework for scene understanding. However, current work still struggles with the lack of accurate scene graph data. To overcome this data bottleneck, we present CoPa-SG, a synthetic scene graph dataset with highly precise ground truth and exhaustive relation annotations between all objects. Moreover, we introduce parametric and proto-relations, two new fundamental concepts for scene graphs. The former provides a much more fine-grained representation than its traditional counterpart by enriching relations with additional parameters such as angles or distances. The latter encodes hypothetical relations in a scene graph and describes how relations would form if new objects are placed in the scene. Using CoPa-SG, we compare the performance of various scene graph generation models. We demonstrate how our new relation types can be integrated in downstream applications to enhance planning and reasoning capabilities.
Efficient 2D to Full 3D Human Pose Uplifting including Joint Rotations
Apr 14, 2025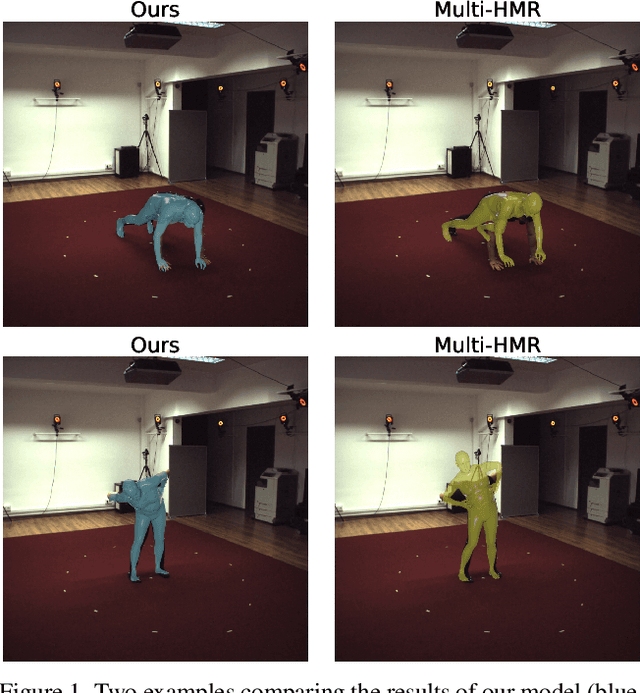
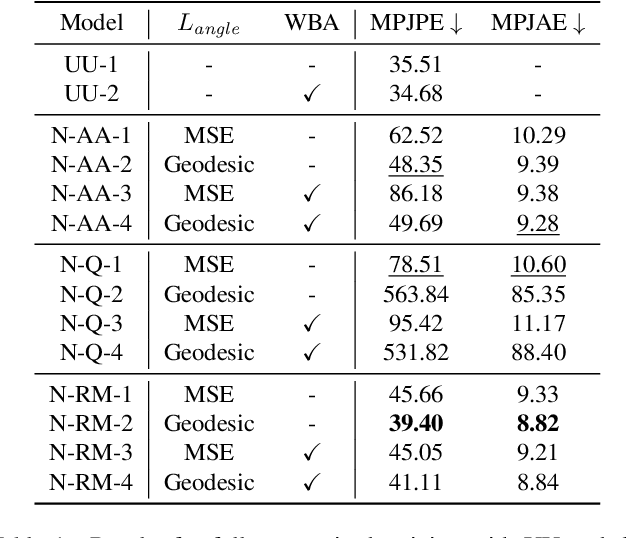
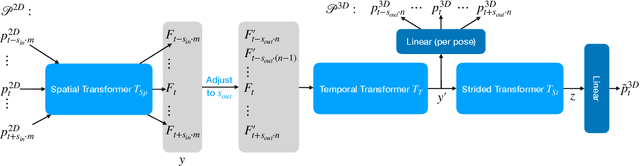
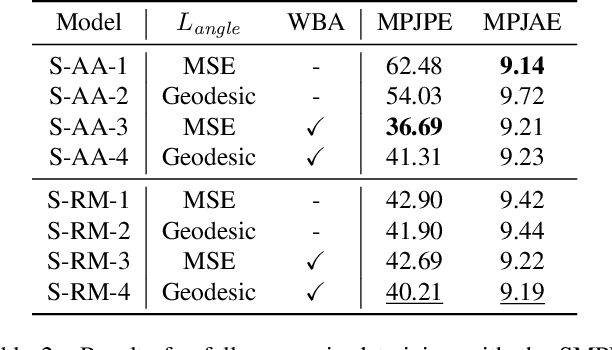
Abstract:In sports analytics, accurately capturing both the 3D locations and rotations of body joints is essential for understanding an athlete's biomechanics. While Human Mesh Recovery (HMR) models can estimate joint rotations, they often exhibit lower accuracy in joint localization compared to 3D Human Pose Estimation (HPE) models. Recent work addressed this limitation by combining a 3D HPE model with inverse kinematics (IK) to estimate both joint locations and rotations. However, IK is computationally expensive. To overcome this, we propose a novel 2D-to-3D uplifting model that directly estimates 3D human poses, including joint rotations, in a single forward pass. We investigate multiple rotation representations, loss functions, and training strategies - both with and without access to ground truth rotations. Our models achieve state-of-the-art accuracy in rotation estimation, are 150 times faster than the IK-based approach, and surpass HMR models in joint localization precision.
On the Importance of Conditioning for Privacy-Preserving Data Augmentation
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Latent diffusion models can be used as a powerful augmentation method to artificially extend datasets for enhanced training. To the human eye, these augmented images look very different to the originals. Previous work has suggested to use this data augmentation technique for data anonymization. However, we show that latent diffusion models that are conditioned on features like depth maps or edges to guide the diffusion process are not suitable as a privacy preserving method. We use a contrastive learning approach to train a model that can correctly identify people out of a pool of candidates. Moreover, we demonstrate that anonymization using conditioned diffusion models is susceptible to black box attacks. We attribute the success of the described methods to the conditioning of the latent diffusion model in the anonymization process. The diffusion model is instructed to produce similar edges for the anonymized images. Hence, a model can learn to recognize these patterns for identification.
Leveraging Anthropometric Measurements to Improve Human Mesh Estimation and Ensure Consistent Body Shapes
Sep 27, 2024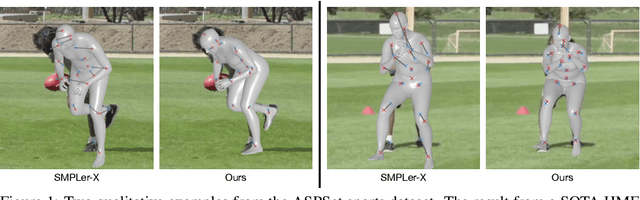
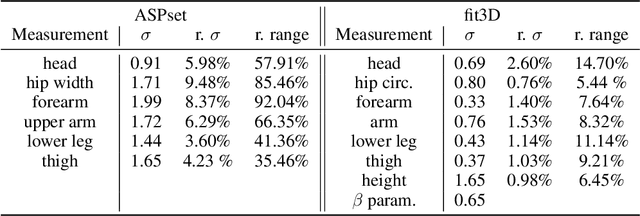
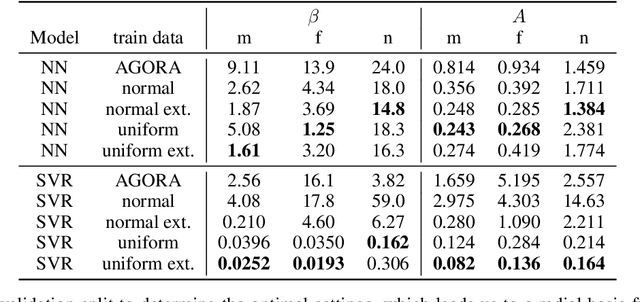
Abstract:The basic body shape of a person does not change within a single video. However, most SOTA human mesh estimation (HME) models output a slightly different body shape for each video frame, which results in inconsistent body shapes for the same person. In contrast, we leverage anthropometric measurements like tailors are already obtaining from humans for centuries. We create a model called A2B that converts such anthropometric measurements to body shape parameters of human mesh models. Moreover, we find that finetuned SOTA 3D human pose estimation (HPE) models outperform HME models regarding the precision of the estimated keypoints. We show that applying inverse kinematics (IK) to the results of such a 3D HPE model and combining the resulting body pose with the A2B body shape leads to superior and consistent human meshes for challenging datasets like ASPset or fit3D, where we can lower the MPJPE by over 30 mm compared to SOTA HME models. Further, replacing HME models estimates of the body shape parameters with A2B model results not only increases the performance of these HME models, but also leads to consistent body shapes.
A Fair Ranking and New Model for Panoptic Scene Graph Generation
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:In panoptic scene graph generation (PSGG), models retrieve interactions between objects in an image which are grounded by panoptic segmentation masks. Previous evaluations on panoptic scene graphs have been subject to an erroneous evaluation protocol where multiple masks for the same object can lead to multiple relation distributions per mask-mask pair. This can be exploited to increase the final score. We correct this flaw and provide a fair ranking over a wide range of existing PSGG models. The observed scores for existing methods increase by up to 7.4 mR@50 for all two-stage methods, while dropping by up to 19.3 mR@50 for all one-stage methods, highlighting the importance of a correct evaluation. Contrary to recent publications, we show that existing two-stage methods are competitive to one-stage methods. Building on this, we introduce the Decoupled SceneFormer (DSFormer), a novel two-stage model that outperforms all existing scene graph models by a large margin of +11 mR@50 and +10 mNgR@50 on the corrected evaluation, thus setting a new SOTA. As a core design principle, DSFormer encodes subject and object masks directly into feature space.
A Review and Efficient Implementation of Scene Graph Generation Metrics
Apr 15, 2024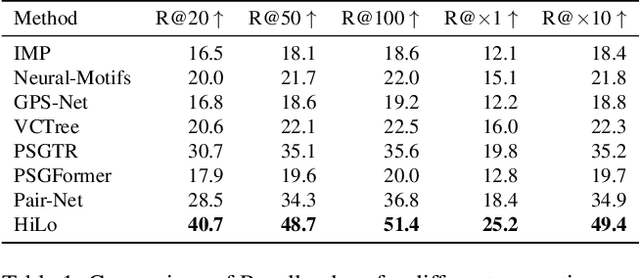
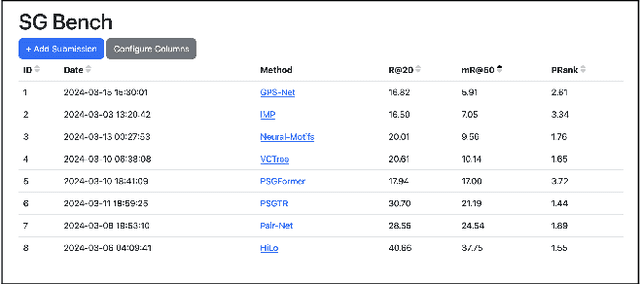
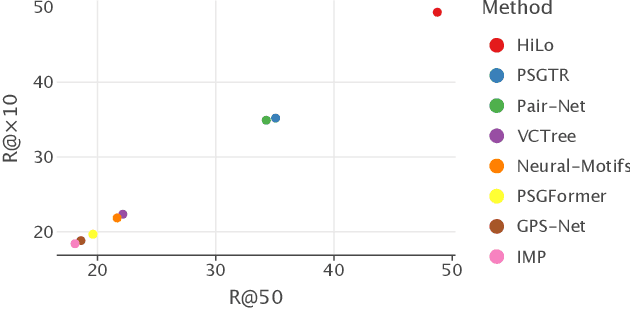
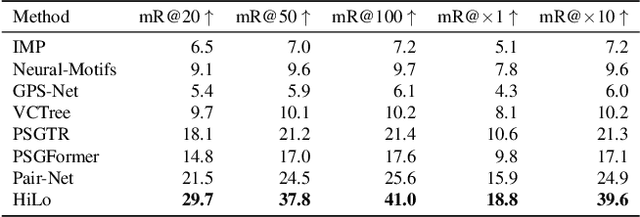
Abstract:Scene graph generation has emerged as a prominent research field in computer vision, witnessing significant advancements in the recent years. However, despite these strides, precise and thorough definitions for the metrics used to evaluate scene graph generation models are lacking. In this paper, we address this gap in the literature by providing a review and precise definition of commonly used metrics in scene graph generation. Our comprehensive examination clarifies the underlying principles of these metrics and can serve as a reference or introduction to scene graph metrics. Furthermore, to facilitate the usage of these metrics, we introduce a standalone Python package called SGBench that efficiently implements all defined metrics, ensuring their accessibility to the research community. Additionally, we present a scene graph benchmarking web service, that enables researchers to compare scene graph generation methods and increase visibility of new methods in a central place. All of our code can be found at https://lorjul.github.io/sgbench/.
Adapting the Segment Anything Model During Usage in Novel Situations
Apr 12, 2024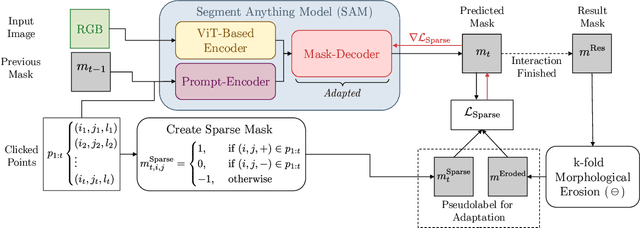
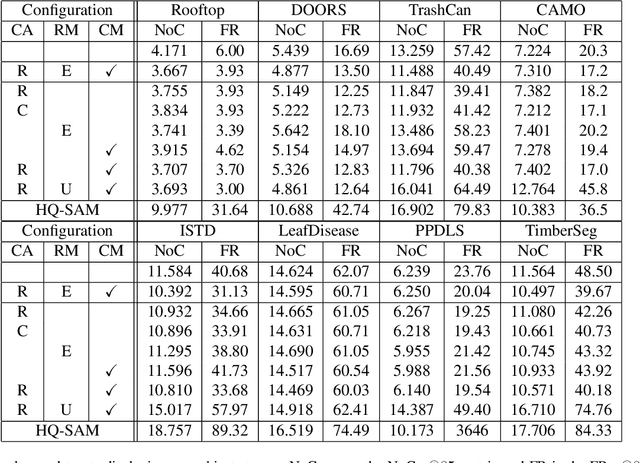
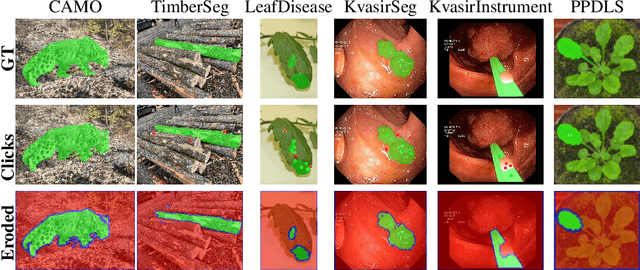
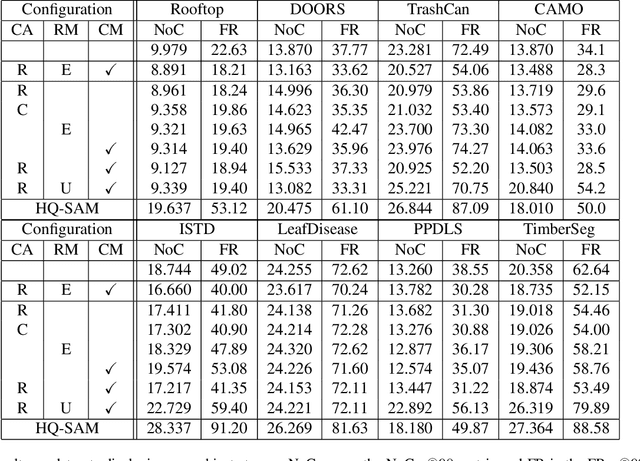
Abstract:The interactive segmentation task consists in the creation of object segmentation masks based on user interactions. The most common way to guide a model towards producing a correct segmentation consists in clicks on the object and background. The recently published Segment Anything Model (SAM) supports a generalized version of the interactive segmentation problem and has been trained on an object segmentation dataset which contains 1.1B masks. Though being trained extensively and with the explicit purpose of serving as a foundation model, we show significant limitations of SAM when being applied for interactive segmentation on novel domains or object types. On the used datasets, SAM displays a failure rate $\text{FR}_{30}@90$ of up to $72.6 \%$. Since we still want such foundation models to be immediately applicable, we present a framework that can adapt SAM during immediate usage. For this we will leverage the user interactions and masks, which are constructed during the interactive segmentation process. We use this information to generate pseudo-labels, which we use to compute a loss function and optimize a part of the SAM model. The presented method causes a relative reduction of up to $48.1 \%$ in the $\text{FR}_{20}@85$ and $46.6 \%$ in the $\text{FR}_{30}@90$ metrics.
Towards Learning Monocular 3D Object Localization From 2D Labels using the Physical Laws of Motion
Oct 26, 2023


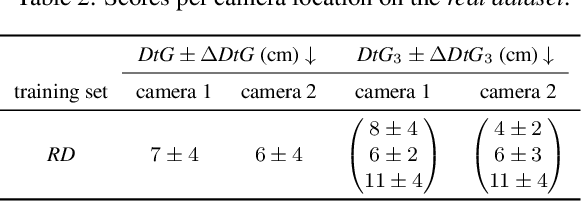
Abstract:We present a novel method for precise 3D object localization in single images from a single calibrated camera using only 2D labels. No expensive 3D labels are needed. Thus, instead of using 3D labels, our model is trained with easy-to-annotate 2D labels along with the physical knowledge of the object's motion. Given this information, the model can infer the latent third dimension, even though it has never seen this information during training. Our method is evaluated on both synthetic and real-world datasets, and we are able to achieve a mean distance error of just 6 cm in our experiments on real data. The results indicate the method's potential as a step towards learning 3D object location estimation, where collecting 3D data for training is not feasible.
The STOIC2021 COVID-19 AI challenge: applying reusable training methodologies to private data
Jun 25, 2023Abstract:Challenges drive the state-of-the-art of automated medical image analysis. The quantity of public training data that they provide can limit the performance of their solutions. Public access to the training methodology for these solutions remains absent. This study implements the Type Three (T3) challenge format, which allows for training solutions on private data and guarantees reusable training methodologies. With T3, challenge organizers train a codebase provided by the participants on sequestered training data. T3 was implemented in the STOIC2021 challenge, with the goal of predicting from a computed tomography (CT) scan whether subjects had a severe COVID-19 infection, defined as intubation or death within one month. STOIC2021 consisted of a Qualification phase, where participants developed challenge solutions using 2000 publicly available CT scans, and a Final phase, where participants submitted their training methodologies with which solutions were trained on CT scans of 9724 subjects. The organizers successfully trained six of the eight Final phase submissions. The submitted codebases for training and running inference were released publicly. The winning solution obtained an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for discerning between severe and non-severe COVID-19 of 0.815. The Final phase solutions of all finalists improved upon their Qualification phase solutions.HSUXJM-TNZF9CHSUXJM-TNZF9C
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge