Siddhartha Rao Kamalakara
Command A: An Enterprise-Ready Large Language Model
Apr 01, 2025



Abstract:In this report we describe the development of Command A, a powerful large language model purpose-built to excel at real-world enterprise use cases. Command A is an agent-optimised and multilingual-capable model, with support for 23 languages of global business, and a novel hybrid architecture balancing efficiency with top of the range performance. It offers best-in-class Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) capabilities with grounding and tool use to automate sophisticated business processes. These abilities are achieved through a decentralised training approach, including self-refinement algorithms and model merging techniques. We also include results for Command R7B which shares capability and architectural similarities to Command A. Weights for both models have been released for research purposes. This technical report details our original training pipeline and presents an extensive evaluation of our models across a suite of enterprise-relevant tasks and public benchmarks, demonstrating excellent performance and efficiency.
Procedural Knowledge in Pretraining Drives Reasoning in Large Language Models
Nov 19, 2024



Abstract:The capabilities and limitations of Large Language Models have been sketched out in great detail in recent years, providing an intriguing yet conflicting picture. On the one hand, LLMs demonstrate a general ability to solve problems. On the other hand, they show surprising reasoning gaps when compared to humans, casting doubt on the robustness of their generalisation strategies. The sheer volume of data used in the design of LLMs has precluded us from applying the method traditionally used to measure generalisation: train-test set separation. To overcome this, we study what kind of generalisation strategies LLMs employ when performing reasoning tasks by investigating the pretraining data they rely on. For two models of different sizes (7B and 35B) and 2.5B of their pretraining tokens, we identify what documents influence the model outputs for three simple mathematical reasoning tasks and contrast this to the data that are influential for answering factual questions. We find that, while the models rely on mostly distinct sets of data for each factual question, a document often has a similar influence across different reasoning questions within the same task, indicating the presence of procedural knowledge. We further find that the answers to factual questions often show up in the most influential data. However, for reasoning questions the answers usually do not show up as highly influential, nor do the answers to the intermediate reasoning steps. When we characterise the top ranked documents for the reasoning questions qualitatively, we confirm that the influential documents often contain procedural knowledge, like demonstrating how to obtain a solution using formulae or code. Our findings indicate that the approach to reasoning the models use is unlike retrieval, and more like a generalisable strategy that synthesises procedural knowledge from documents doing a similar form of reasoning.
Exploring Low Rank Training of Deep Neural Networks
Sep 27, 2022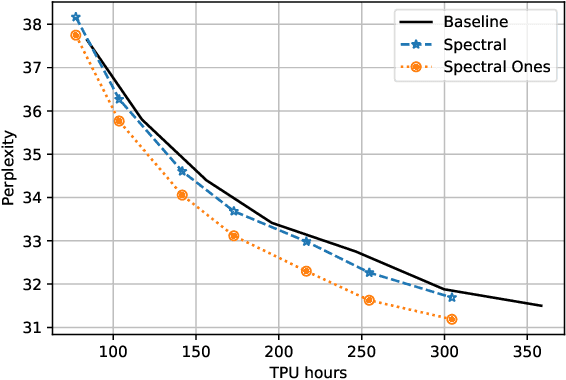
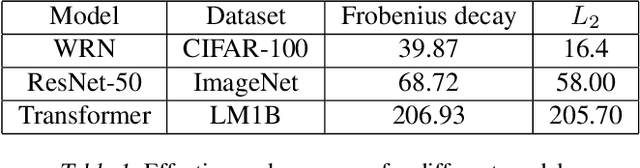
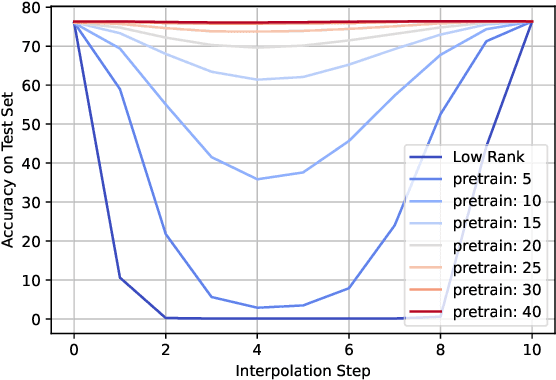
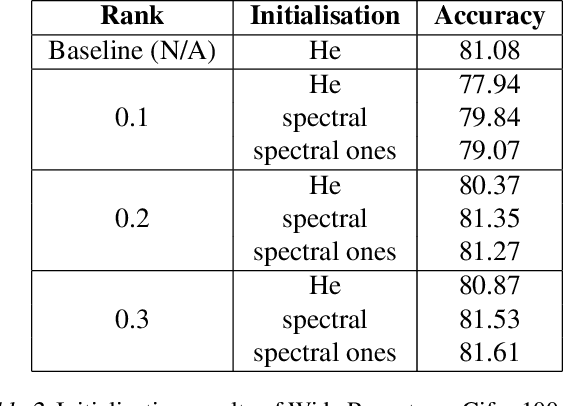
Abstract:Training deep neural networks in low rank, i.e. with factorised layers, is of particular interest to the community: it offers efficiency over unfactorised training in terms of both memory consumption and training time. Prior work has focused on low rank approximations of pre-trained networks and training in low rank space with additional objectives, offering various ad hoc explanations for chosen practice. We analyse techniques that work well in practice, and through extensive ablations on models such as GPT2 we provide evidence falsifying common beliefs in the field, hinting in the process at exciting research opportunities that still need answering.
Scalable Training of Language Models using JAX pjit and TPUv4
Apr 13, 2022



Abstract:Modern large language models require distributed training strategies due to their size. The challenges of efficiently and robustly training them are met with rapid developments on both software and hardware frontiers. In this technical report, we explore challenges and design decisions associated with developing a scalable training framework, and present a quantitative analysis of efficiency improvements coming from adopting new software and hardware solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge