Shusong Xu
Patch-enhanced Mask Encoder Prompt Image Generation
May 29, 2024Abstract:Artificial Intelligence Generated Content(AIGC), known for its superior visual results, represents a promising mitigation method for high-cost advertising applications. Numerous approaches have been developed to manipulate generated content under different conditions. However, a crucial limitation lies in the accurate description of products in advertising applications. Applying previous methods directly may lead to considerable distortion and deformation of advertised products, primarily due to oversimplified content control conditions. Hence, in this work, we propose a patch-enhanced mask encoder approach to ensure accurate product descriptions while preserving diverse backgrounds. Our approach consists of three components Patch Flexible Visibility, Mask Encoder Prompt Adapter and an image Foundation Model. Patch Flexible Visibility is used for generating a more reasonable background image. Mask Encoder Prompt Adapter enables region-controlled fusion. We also conduct an analysis of the structure and operational mechanisms of the Generation Module. Experimental results show our method can achieve the highest visual results and FID scores compared with other methods.
Learned Smartphone ISP on Mobile NPUs with Deep Learning, Mobile AI 2021 Challenge: Report
May 17, 2021
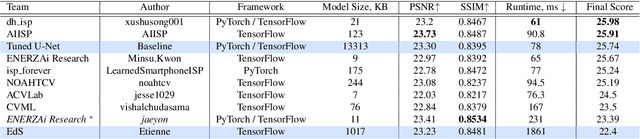
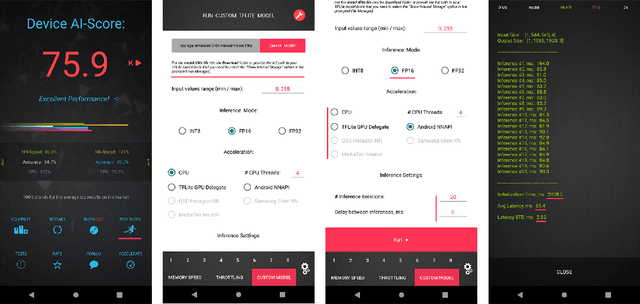
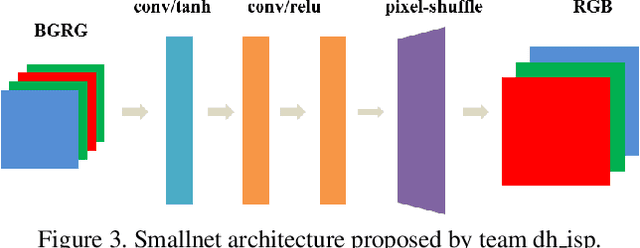
Abstract:As the quality of mobile cameras starts to play a crucial role in modern smartphones, more and more attention is now being paid to ISP algorithms used to improve various perceptual aspects of mobile photos. In this Mobile AI challenge, the target was to develop an end-to-end deep learning-based image signal processing (ISP) pipeline that can replace classical hand-crafted ISPs and achieve nearly real-time performance on smartphone NPUs. For this, the participants were provided with a novel learned ISP dataset consisting of RAW-RGB image pairs captured with the Sony IMX586 Quad Bayer mobile sensor and a professional 102-megapixel medium format camera. The runtime of all models was evaluated on the MediaTek Dimensity 1000+ platform with a dedicated AI processing unit capable of accelerating both floating-point and quantized neural networks. The proposed solutions are fully compatible with the above NPU and are capable of processing Full HD photos under 60-100 milliseconds while achieving high fidelity results. A detailed description of all models developed in this challenge is provided in this paper.
NTIRE 2020 Challenge on Real Image Denoising: Dataset, Methods and Results
May 08, 2020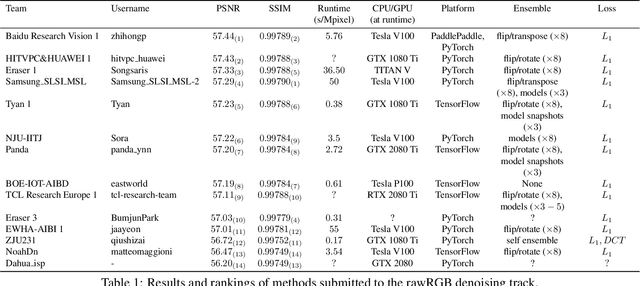
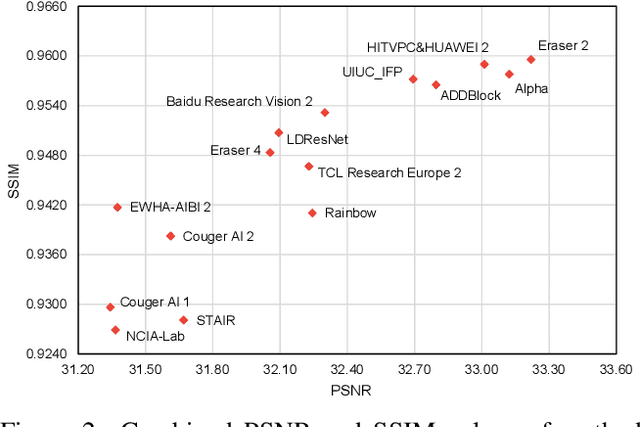
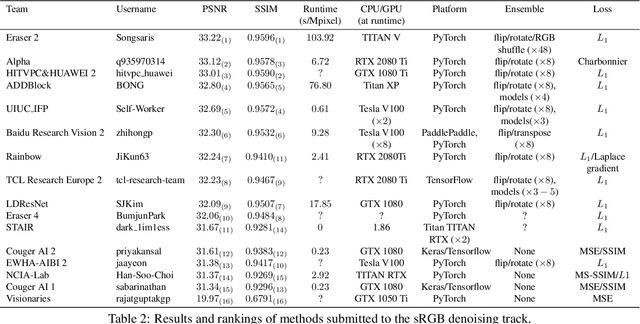
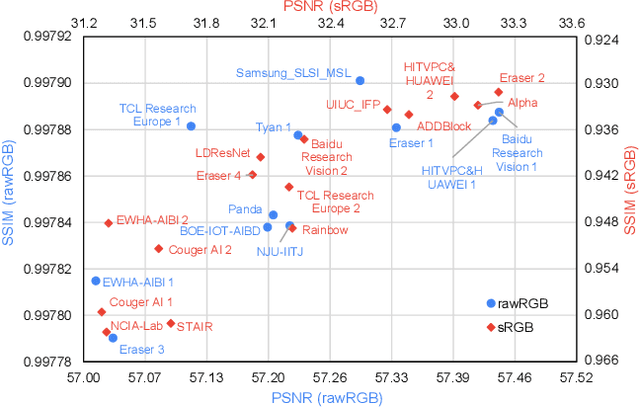
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2020 challenge on real image denoising with focus on the newly introduced dataset, the proposed methods and their results. The challenge is a new version of the previous NTIRE 2019 challenge on real image denoising that was based on the SIDD benchmark. This challenge is based on a newly collected validation and testing image datasets, and hence, named SIDD+. This challenge has two tracks for quantitatively evaluating image denoising performance in (1) the Bayer-pattern rawRGB and (2) the standard RGB (sRGB) color spaces. Each track ~250 registered participants. A total of 22 teams, proposing 24 methods, competed in the final phase of the challenge. The proposed methods by the participating teams represent the current state-of-the-art performance in image denoising targeting real noisy images. The newly collected SIDD+ datasets are publicly available at: https://bit.ly/siddplus_data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge