Shishir Muralidhara
Domain-Incremental Semantic Segmentation for Autonomous Driving under Adverse Driving Conditions
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:Semantic segmentation for autonomous driving is an even more challenging task when faced with adverse driving conditions. Standard models trained on data recorded under ideal conditions show a deteriorated performance in unfavorable weather or illumination conditions. Fine-tuning on the new task or condition would lead to overwriting the previously learned information resulting in catastrophic forgetting. Adapting to the new conditions through traditional domain adaption methods improves the performance on the target domain at the expense of the source domain. Addressing these issues, we propose an architecture-based domain-incremental learning approach called Progressive Semantic Segmentation (PSS). PSS is a task-agnostic, dynamically growing collection of domain-specific segmentation models. The task of inferring the domain and subsequently selecting the appropriate module for segmentation is carried out using a collection of convolutional autoencoders. We extensively evaluate our proposed approach using several datasets at varying levels of granularity in the categorization of adverse driving conditions. Furthermore, we demonstrate the generalization of the proposed approach to similar and unseen domains.
Modality-Incremental Learning with Disjoint Relevance Mapping Networks for Image-based Semantic Segmentation
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:In autonomous driving, environment perception has significantly advanced with the utilization of deep learning techniques for diverse sensors such as cameras, depth sensors, or infrared sensors. The diversity in the sensor stack increases the safety and contributes to robustness against adverse weather and lighting conditions. However, the variance in data acquired from different sensors poses challenges. In the context of continual learning (CL), incremental learning is especially challenging for considerably large domain shifts, e.g. different sensor modalities. This amplifies the problem of catastrophic forgetting. To address this issue, we formulate the concept of modality-incremental learning and examine its necessity, by contrasting it with existing incremental learning paradigms. We propose the use of a modified Relevance Mapping Network (RMN) to incrementally learn new modalities while preserving performance on previously learned modalities, in which relevance maps are disjoint. Experimental results demonstrate that the prevention of shared connections in this approach helps alleviate the problem of forgetting within the constraints of a strict continual learning framework.
CLEO: Continual Learning of Evolving Ontologies
Jul 11, 2024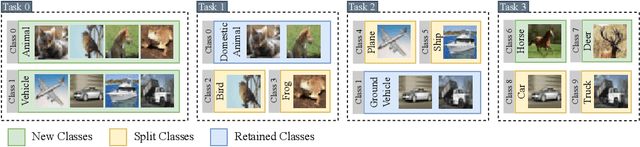
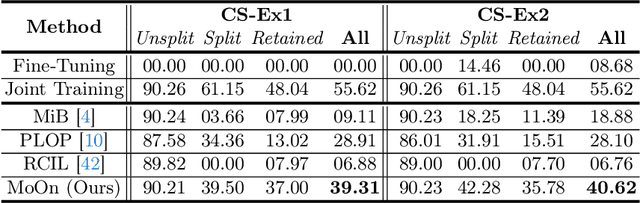

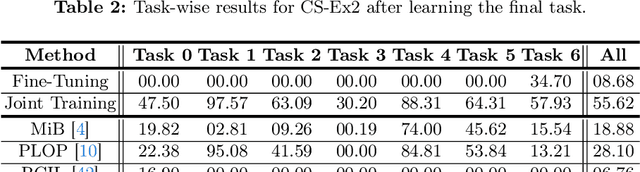
Abstract:Continual learning (CL) addresses the problem of catastrophic forgetting in neural networks, which occurs when a trained model tends to overwrite previously learned information, when presented with a new task. CL aims to instill the lifelong learning characteristic of humans in intelligent systems, making them capable of learning continuously while retaining what was already learned. Current CL problems involve either learning new domains (domain-incremental) or new and previously unseen classes (class-incremental). However, general learning processes are not just limited to learning information, but also refinement of existing information. In this paper, we define CLEO - Continual Learning of Evolving Ontologies, as a new incremental learning setting under CL to tackle evolving classes. CLEO is motivated by the need for intelligent systems to adapt to real-world ontologies that change over time, such as those in autonomous driving. We use Cityscapes, PASCAL VOC, and Mapillary Vistas to define the task settings and demonstrate the applicability of CLEO. We highlight the shortcomings of existing CIL methods in adapting to CLEO and propose a baseline solution, called Modelling Ontologies (MoOn). CLEO is a promising new approach to CL that addresses the challenge of evolving ontologies in real-world applications. MoOn surpasses previous CL approaches in the context of CLEO.
JPPF: Multi-task Fusion for Consistent Panoptic-Part Segmentation
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:Part-aware panoptic segmentation is a problem of computer vision that aims to provide a semantic understanding of the scene at multiple levels of granularity. More precisely, semantic areas, object instances, and semantic parts are predicted simultaneously. In this paper, we present our Joint Panoptic Part Fusion (JPPF) that combines the three individual segmentations effectively to obtain a panoptic-part segmentation. Two aspects are of utmost importance for this: First, a unified model for the three problems is desired that allows for mutually improved and consistent representation learning. Second, balancing the combination so that it gives equal importance to all individual results during fusion. Our proposed JPPF is parameter-free and dynamically balances its input. The method is evaluated and compared on the Cityscapes Panoptic Parts (CPP) and Pascal Panoptic Parts (PPP) datasets in terms of PartPQ and Part-Whole Quality (PWQ). In extensive experiments, we verify the importance of our fair fusion, highlight its most significant impact for areas that can be further segmented into parts, and demonstrate the generalization capabilities of our design without fine-tuning on 5 additional datasets.
1st Workshop on Maritime Computer Vision 2023: Challenge Results
Nov 28, 2022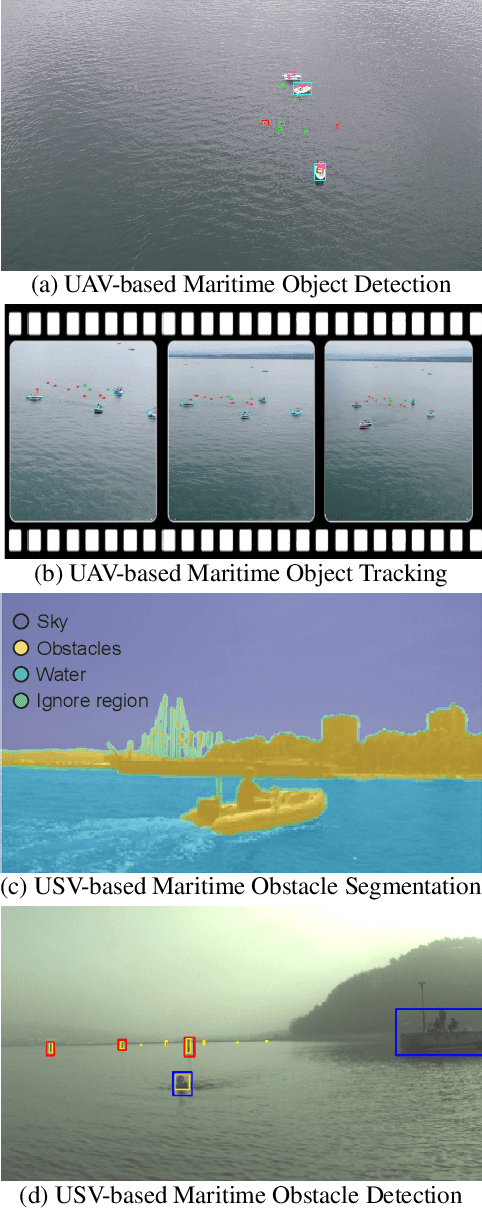

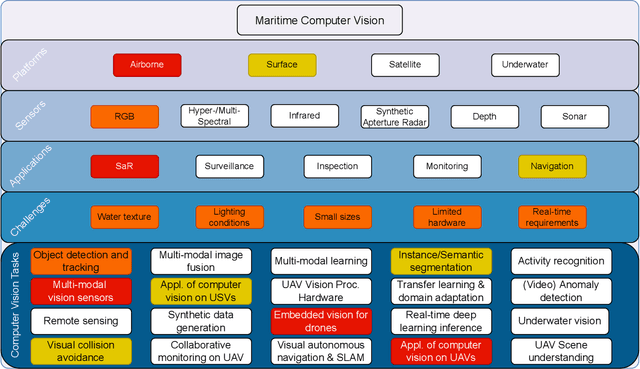
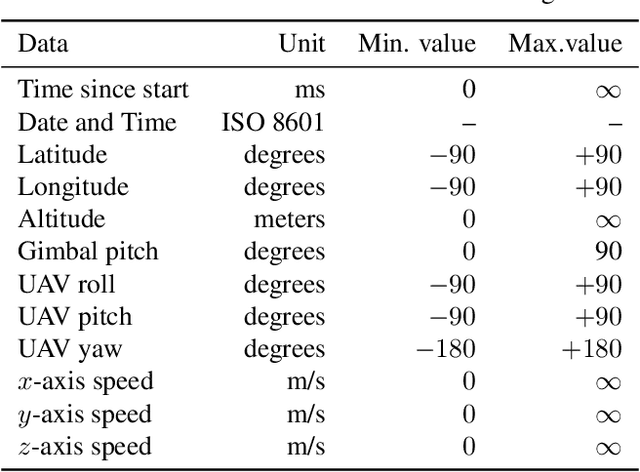
Abstract:The 1$^{\text{st}}$ Workshop on Maritime Computer Vision (MaCVi) 2023 focused on maritime computer vision for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) and Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV), and organized several subchallenges in this domain: (i) UAV-based Maritime Object Detection, (ii) UAV-based Maritime Object Tracking, (iii) USV-based Maritime Obstacle Segmentation and (iv) USV-based Maritime Obstacle Detection. The subchallenges were based on the SeaDronesSee and MODS benchmarks. This report summarizes the main findings of the individual subchallenges and introduces a new benchmark, called SeaDronesSee Object Detection v2, which extends the previous benchmark by including more classes and footage. We provide statistical and qualitative analyses, and assess trends in the best-performing methodologies of over 130 submissions. The methods are summarized in the appendix. The datasets, evaluation code and the leaderboard are publicly available at https://seadronessee.cs.uni-tuebingen.de/macvi.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge