Shaunak Mishra
Salient Object-Aware Background Generation using Text-Guided Diffusion Models
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Generating background scenes for salient objects plays a crucial role across various domains including creative design and e-commerce, as it enhances the presentation and context of subjects by integrating them into tailored environments. Background generation can be framed as a task of text-conditioned outpainting, where the goal is to extend image content beyond a salient object's boundaries on a blank background. Although popular diffusion models for text-guided inpainting can also be used for outpainting by mask inversion, they are trained to fill in missing parts of an image rather than to place an object into a scene. Consequently, when used for background creation, inpainting models frequently extend the salient object's boundaries and thereby change the object's identity, which is a phenomenon we call "object expansion." This paper introduces a model for adapting inpainting diffusion models to the salient object outpainting task using Stable Diffusion and ControlNet architectures. We present a series of qualitative and quantitative results across models and datasets, including a newly proposed metric to measure object expansion that does not require any human labeling. Compared to Stable Diffusion 2.0 Inpainting, our proposed approach reduces object expansion by 3.6x on average with no degradation in standard visual metrics across multiple datasets.
Staging E-Commerce Products for Online Advertising using Retrieval Assisted Image Generation
Jul 28, 2023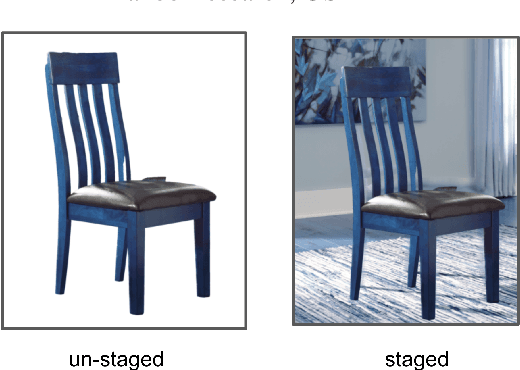

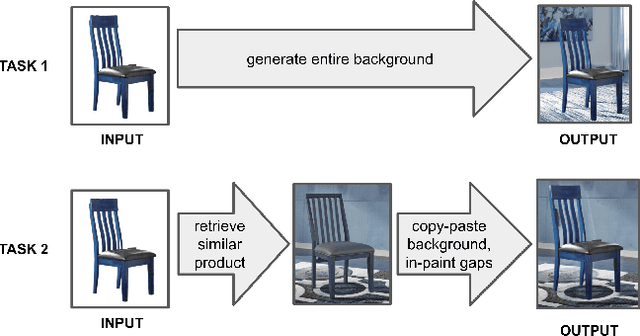

Abstract:Online ads showing e-commerce products typically rely on the product images in a catalog sent to the advertising platform by an e-commerce platform. In the broader ads industry such ads are called dynamic product ads (DPA). It is common for DPA catalogs to be in the scale of millions (corresponding to the scale of products which can be bought from the e-commerce platform). However, not all product images in the catalog may be appealing when directly re-purposed as an ad image, and this may lead to lower click-through rates (CTRs). In particular, products just placed against a solid background may not be as enticing and realistic as a product staged in a natural environment. To address such shortcomings of DPA images at scale, we propose a generative adversarial network (GAN) based approach to generate staged backgrounds for un-staged product images. Generating the entire staged background is a challenging task susceptible to hallucinations. To get around this, we introduce a simpler approach called copy-paste staging using retrieval assisted GANs. In copy paste staging, we first retrieve (from the catalog) staged products similar to the un-staged input product, and then copy-paste the background of the retrieved product in the input image. A GAN based in-painting model is used to fill the holes left after this copy-paste operation. We show the efficacy of our copy-paste staging method via offline metrics, and human evaluation. In addition, we show how our staging approach can enable animations of moving products leading to a video ad from a product image.
TSI: an Ad Text Strength Indicator using Text-to-CTR and Semantic-Ad-Similarity
Aug 18, 2021
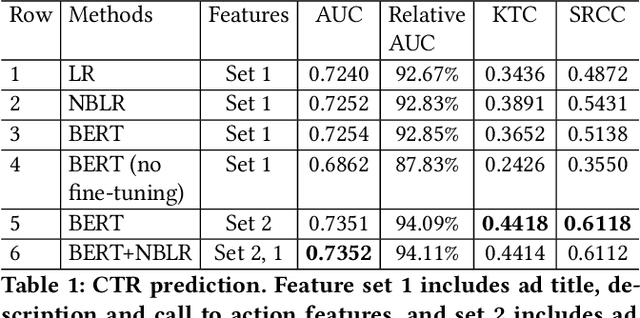
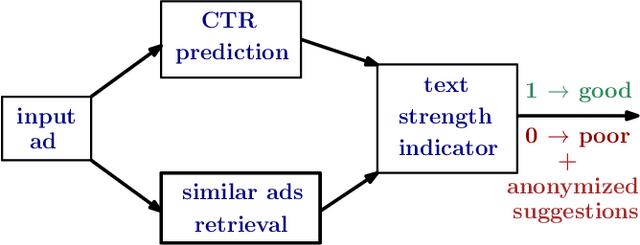

Abstract:Coming up with effective ad text is a time consuming process, and particularly challenging for small businesses with limited advertising experience. When an inexperienced advertiser onboards with a poorly written ad text, the ad platform has the opportunity to detect low performing ad text, and provide improvement suggestions. To realize this opportunity, we propose an ad text strength indicator (TSI) which: (i) predicts the click-through-rate (CTR) for an input ad text, (ii) fetches similar existing ads to create a neighborhood around the input ad, (iii) and compares the predicted CTRs in the neighborhood to declare whether the input ad is strong or weak. In addition, as suggestions for ad text improvement, TSI shows anonymized versions of superior ads (higher predicted CTR) in the neighborhood. For (i), we propose a BERT based text-to-CTR model trained on impressions and clicks associated with an ad text. For (ii), we propose a sentence-BERT based semantic-ad-similarity model trained using weak labels from ad campaign setup data. Offline experiments demonstrate that our BERT based text-to-CTR model achieves a significant lift in CTR prediction AUC for cold start (new) advertisers compared to bag-of-words based baselines. In addition, our semantic-textual-similarity model for similar ads retrieval achieves a precision@1 of 0.93 (for retrieving ads from the same product category); this is significantly higher compared to unsupervised TF-IDF, word2vec, and sentence-BERT baselines. Finally, we share promising online results from advertisers in the Yahoo (Verizon Media) ad platform where a variant of TSI was implemented with sub-second end-to-end latency.
VisualTextRank: Unsupervised Graph-based Content Extraction for Automating Ad Text to Image Search
Aug 05, 2021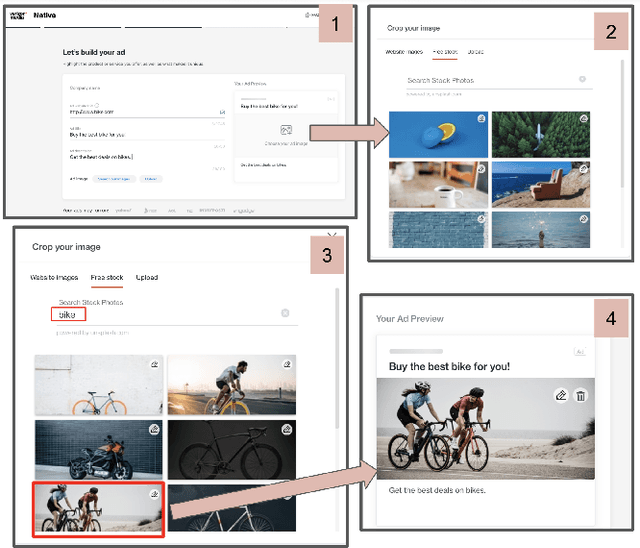
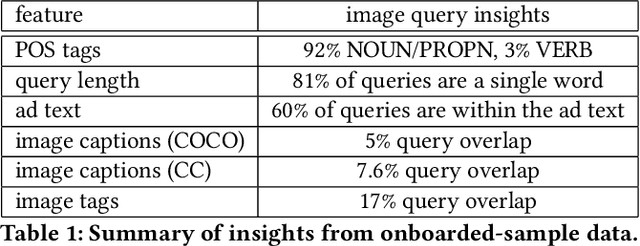
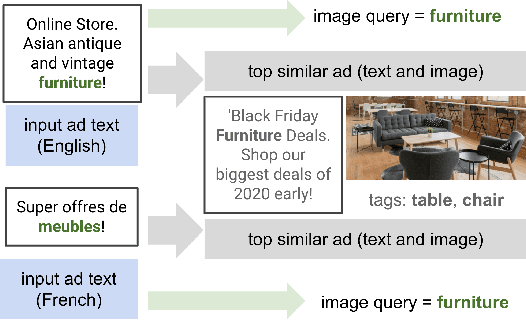
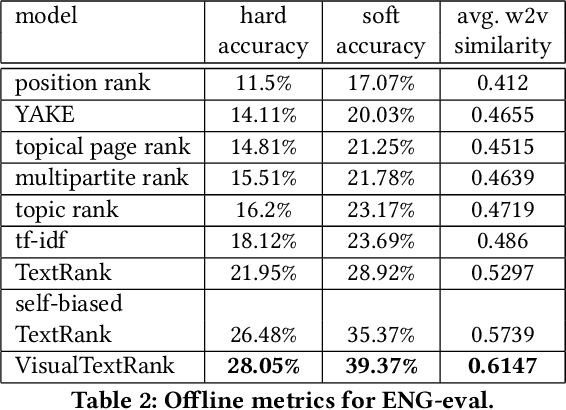
Abstract:Numerous online stock image libraries offer high quality yet copyright free images for use in marketing campaigns. To assist advertisers in navigating such third party libraries, we study the problem of automatically fetching relevant ad images given the ad text (via a short textual query for images). Motivated by our observations in logged data on ad image search queries (given ad text), we formulate a keyword extraction problem, where a keyword extracted from the ad text (or its augmented version) serves as the ad image query. In this context, we propose VisualTextRank: an unsupervised method to (i) augment input ad text using semantically similar ads, and (ii) extract the image query from the augmented ad text. VisualTextRank builds on prior work on graph based context extraction (biased TextRank in particular) by leveraging both the text and image of similar ads for better keyword extraction, and using advertiser category specific biasing with sentence-BERT embeddings. Using data collected from the Verizon Media Native (Yahoo Gemini) ad platform's stock image search feature for onboarding advertisers, we demonstrate the superiority of VisualTextRank compared to competitive keyword extraction baselines (including an $11\%$ accuracy lift over biased TextRank). For the case when the stock image library is restricted to English queries, we show the effectiveness of VisualTextRank on multilingual ads (translated to English) while leveraging semantically similar English ads. Online tests with a simplified version of VisualTextRank led to a 28.7% increase in the usage of stock image search, and a 41.6% increase in the advertiser onboarding rate in the Verizon Media Native ad platform.
Powering COVID-19 community Q&A with Curated Side Information
Jan 27, 2021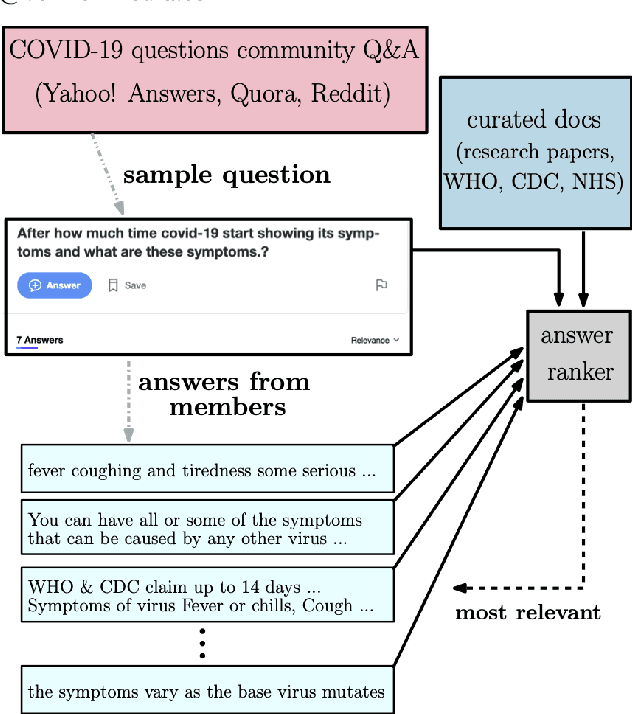

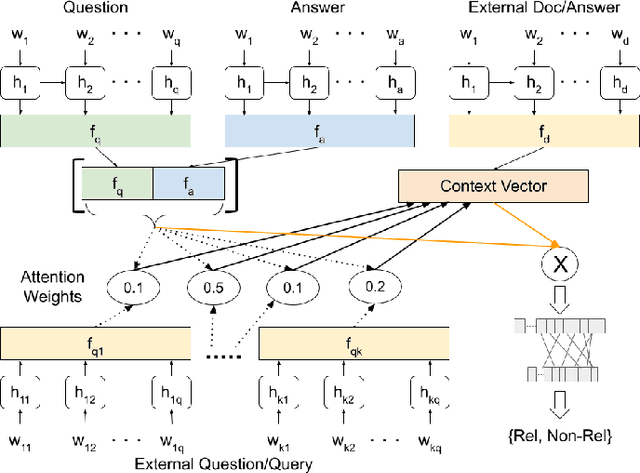
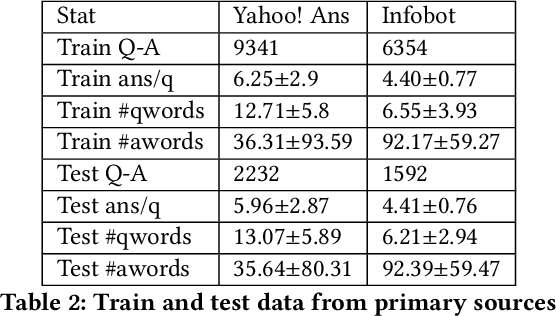
Abstract:Community question answering and discussion platforms such as Reddit, Yahoo! answers or Quora provide users the flexibility of asking open ended questions to a large audience, and replies to such questions maybe useful both to the user and the community on certain topics such as health, sports or finance. Given the recent events around COVID-19, some of these platforms have attracted 2000+ questions from users about several aspects associated with the disease. Given the impact of this disease on general public, in this work we investigate ways to improve the ranking of user generated answers on COVID-19. We specifically explore the utility of external technical sources of side information (such as CDC guidelines or WHO FAQs) in improving answer ranking on such platforms. We found that ranking user answers based on question-answer similarity is not sufficient, and existing models cannot effectively exploit external (side) information. In this work, we demonstrate the effectiveness of different attention based neural models that can directly exploit side information available in technical documents or verified forums (e.g., research publications on COVID-19 or WHO website). Augmented with a temperature mechanism, the attention based neural models can selectively determine the relevance of side information for a given user question, while ranking answers.
Learning to Create Better Ads: Generation and Ranking Approaches for Ad Creative Refinement
Aug 17, 2020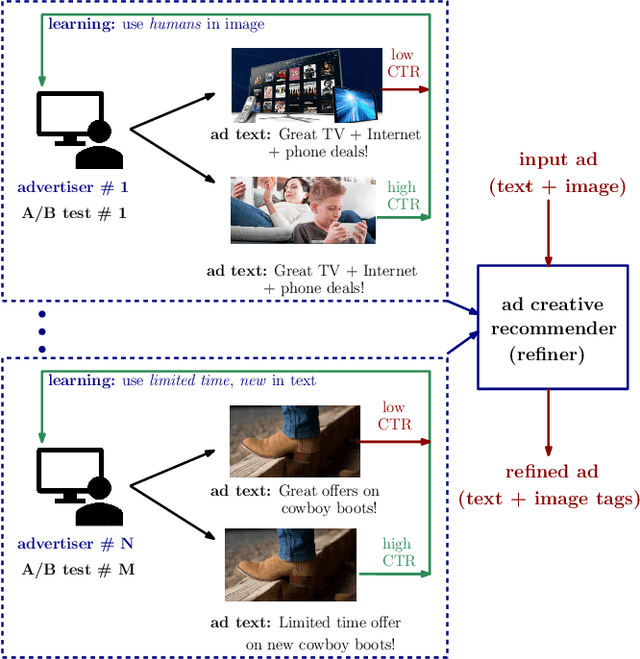
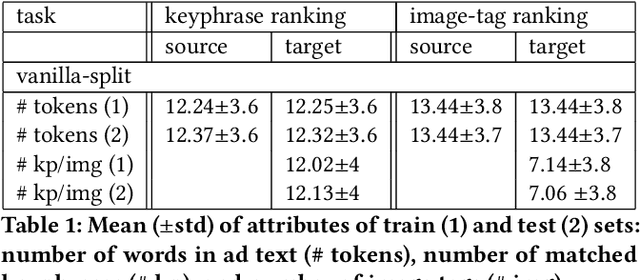
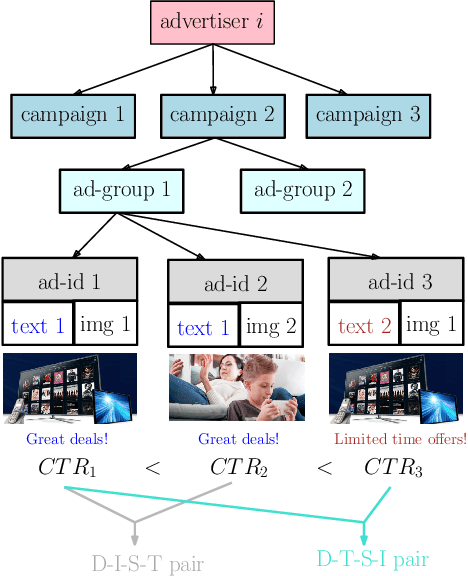
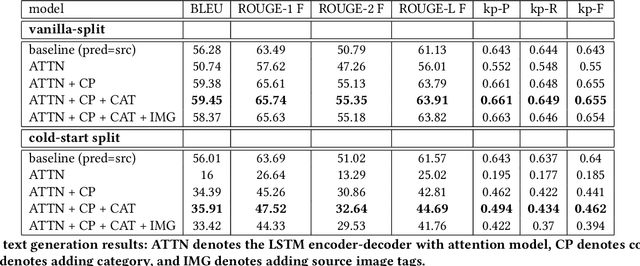
Abstract:In the online advertising industry, the process of designing an ad creative (i.e., ad text and image) requires manual labor. Typically, each advertiser launches multiple creatives via online A/B tests to infer effective creatives for the target audience, that are then refined further in an iterative fashion. Due to the manual nature of this process, it is time-consuming to learn, refine, and deploy the modified creatives. Since major ad platforms typically run A/B tests for multiple advertisers in parallel, we explore the possibility of collaboratively learning ad creative refinement via A/B tests of multiple advertisers. In particular, given an input ad creative, we study approaches to refine the given ad text and image by: (i) generating new ad text, (ii) recommending keyphrases for new ad text, and (iii) recommending image tags (objects in image) to select new ad image. Based on A/B tests conducted by multiple advertisers, we form pairwise examples of inferior and superior ad creatives, and use such pairs to train models for the above tasks. For generating new ad text, we demonstrate the efficacy of an encoder-decoder architecture with copy mechanism, which allows some words from the (inferior) input text to be copied to the output while incorporating new words associated with higher click-through-rate. For the keyphrase and image tag recommendation task, we demonstrate the efficacy of a deep relevance matching model, as well as the relative robustness of ranking approaches compared to ad text generation in cold-start scenarios with unseen advertisers. We also share broadly applicable insights from our experiments using data from the Yahoo Gemini ad platform.
Recommending Themes for Ad Creative Design via Visual-Linguistic Representations
Feb 27, 2020

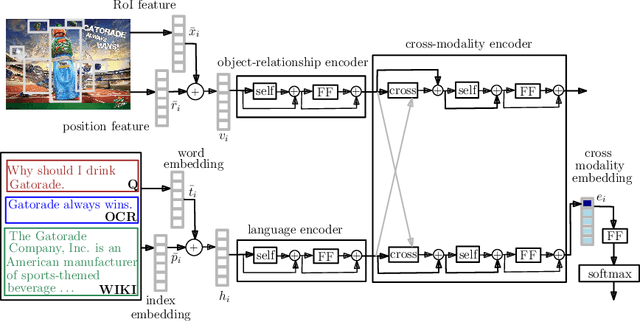

Abstract:There is a perennial need in the online advertising industry to refresh ad creatives, i.e., images and text used for enticing online users towards a brand. Such refreshes are required to reduce the likelihood of ad fatigue among online users, and to incorporate insights from other successful campaigns in related product categories. Given a brand, to come up with themes for a new ad is a painstaking and time consuming process for creative strategists. Strategists typically draw inspiration from the images and text used for past ad campaigns, as well as world knowledge on the brands. To automatically infer ad themes via such multimodal sources of information in past ad campaigns, we propose a theme (keyphrase) recommender system for ad creative strategists. The theme recommender is based on aggregating results from a visual question answering (VQA) task, which ingests the following: (i) ad images, (ii) text associated with the ads as well as Wikipedia pages on the brands in the ads, and (iii) questions around the ad. We leverage transformer based cross-modality encoders to train visual-linguistic representations for our VQA task. We study two formulations for the VQA task along the lines of classification and ranking; via experiments on a public dataset, we show that cross-modal representations lead to significantly better classification accuracy and ranking precision-recall metrics. Cross-modal representations show better performance compared to separate image and text representations. In addition, the use of multimodal information shows a significant lift over using only textual or visual information.
Learning from Multi-User Activity Trails for B2B Ad Targeting
Aug 29, 2019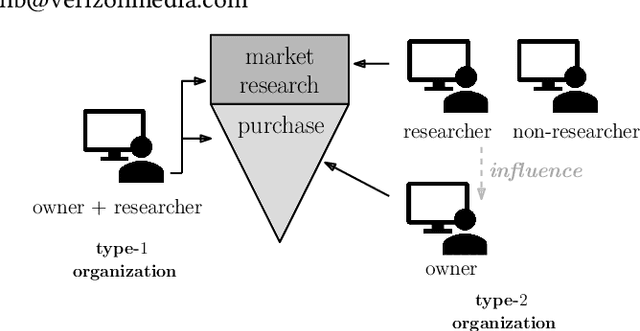
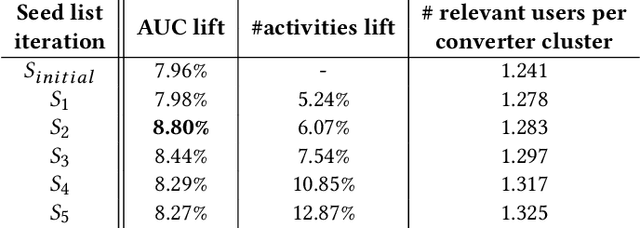
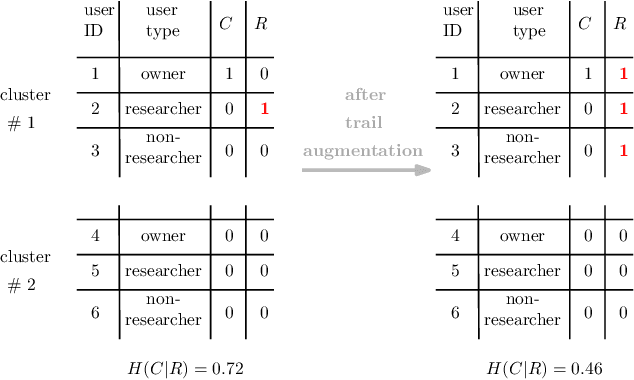
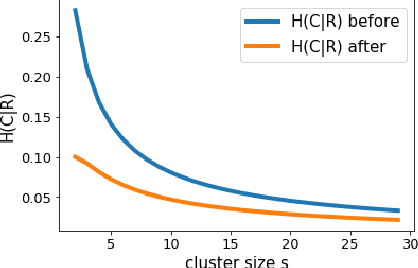
Abstract:Online purchase decisions in organizations can go through a complex journey with multiple agents involved in the decision making process. Depending on the product being purchased, and the organizational structure, the process may involve employees who first conduct market research, and then influence decision makers who place the online purchase order. In such cases, the online activity trail of a single individual in the organization may only provide partial information for predicting purchases (conversions). To refine conversion prediction for business-to-business (B2B) products using online activity trails, we introduce the notion of relevant users in an organization with respect to a given B2B advertiser, and leverage the collective activity trails of such relevant users to predict conversions. In particular, our notion of relevant users is tied to a seed list of relevant activities for a B2B advertiser, and we propose a method using distributed activity representations to build such a seed list. Experiments using data from Yahoo Gemini demonstrate that the proposed methods can improve conversion prediction AUC by 8.8%, and provide an interpretable advertiser specific list of activities useful for B2B ad targeting.
Managing App Install Ad Campaigns in RTB: A Q-Learning Approach
Nov 11, 2018



Abstract:Real time bidding (RTB) enables demand side platforms (bidders) to scale ad campaigns across multiple publishers affiliated to an RTB ad exchange. While driving multiple campaigns for mobile app install ads via RTB, the bidder typically has to: (i) maintain each campaign's efficiency (i.e., meet advertiser's target cost-per-install), (ii) be sensitive to advertiser's budget, and (iii) make profit after payouts to the ad exchange. In this process, there is a sense of delayed rewards for the bidder's actions; the exchange charges the bidder right after the ad is shown, but the bidder gets to know about resultant installs after considerable delay. This makes it challenging for the bidder to decide beforehand the bid (and corresponding cost charged to advertiser) for each ad display opportunity. To jointly handle the objectives mentioned above, we propose a state space based policy which decides the exchange bid and advertiser cost for each opportunity. The state space captures the current efficiency, budget utilization and profit. The policy based on this state space is trained on past decisions and outcomes via a novel Q-learning algorithm which accounts for the delay in install notifications. In our experiments based on data from app install campaigns managed by Yahoo's Gemini advertising platform, the Q-learning based policy led to a significant increase in the profit and number of efficient campaigns.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge