Joao V. B. Soares
SCOT: Self-Supervised Contrastive Pretraining For Zero-Shot Compositional Retrieval
Jan 12, 2025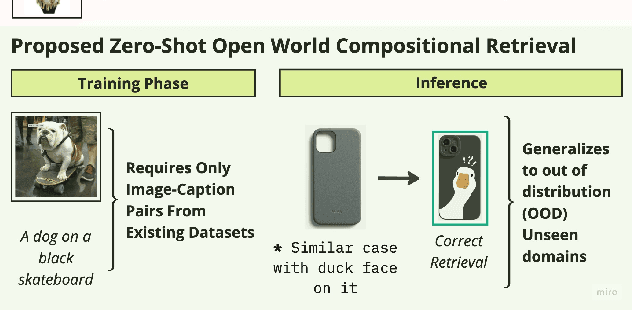
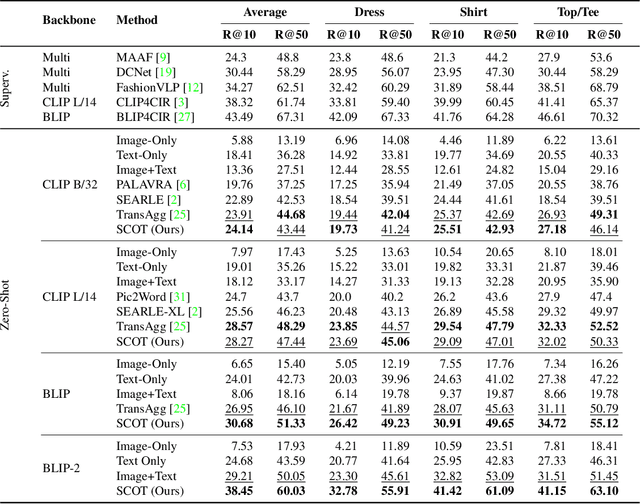
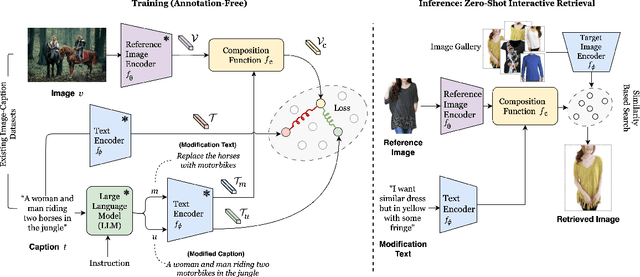
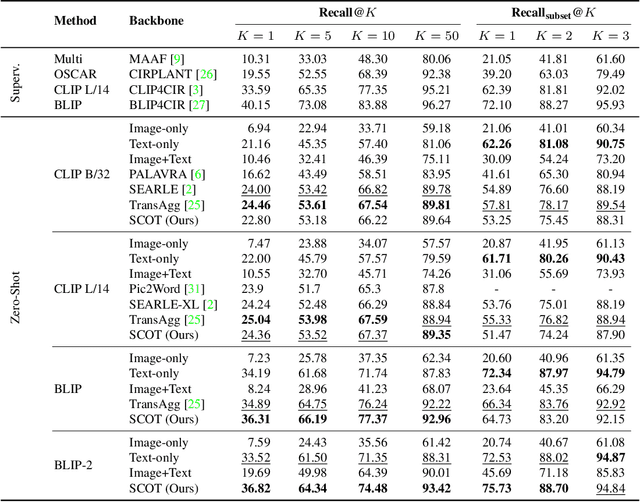
Abstract:Compositional image retrieval (CIR) is a multimodal learning task where a model combines a query image with a user-provided text modification to retrieve a target image. CIR finds applications in a variety of domains including product retrieval (e-commerce) and web search. Existing methods primarily focus on fully-supervised learning, wherein models are trained on datasets of labeled triplets such as FashionIQ and CIRR. This poses two significant challenges: (i) curating such triplet datasets is labor intensive; and (ii) models lack generalization to unseen objects and domains. In this work, we propose SCOT (Self-supervised COmpositional Training), a novel zero-shot compositional pretraining strategy that combines existing large image-text pair datasets with the generative capabilities of large language models to contrastively train an embedding composition network. Specifically, we show that the text embedding from a large-scale contrastively-pretrained vision-language model can be utilized as proxy target supervision during compositional pretraining, replacing the target image embedding. In zero-shot settings, this strategy surpasses SOTA zero-shot compositional retrieval methods as well as many fully-supervised methods on standard benchmarks such as FashionIQ and CIRR.
Salient Object-Aware Background Generation using Text-Guided Diffusion Models
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Generating background scenes for salient objects plays a crucial role across various domains including creative design and e-commerce, as it enhances the presentation and context of subjects by integrating them into tailored environments. Background generation can be framed as a task of text-conditioned outpainting, where the goal is to extend image content beyond a salient object's boundaries on a blank background. Although popular diffusion models for text-guided inpainting can also be used for outpainting by mask inversion, they are trained to fill in missing parts of an image rather than to place an object into a scene. Consequently, when used for background creation, inpainting models frequently extend the salient object's boundaries and thereby change the object's identity, which is a phenomenon we call "object expansion." This paper introduces a model for adapting inpainting diffusion models to the salient object outpainting task using Stable Diffusion and ControlNet architectures. We present a series of qualitative and quantitative results across models and datasets, including a newly proposed metric to measure object expansion that does not require any human labeling. Compared to Stable Diffusion 2.0 Inpainting, our proposed approach reduces object expansion by 3.6x on average with no degradation in standard visual metrics across multiple datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge