Sanjay Jain
Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri
Hallucination is Inevitable: An Innate Limitation of Large Language Models
Jan 22, 2024Abstract:Hallucination has been widely recognized to be a significant drawback for large language models (LLMs). There have been many works that attempt to reduce the extent of hallucination. These efforts have mostly been empirical so far, which cannot answer the fundamental question whether it can be completely eliminated. In this paper, we formalize the problem and show that it is impossible to eliminate hallucination in LLMs. Specifically, we define a formal world where hallucination is defined as inconsistencies between a computable LLM and a computable ground truth function. By employing results from learning theory, we show that LLMs cannot learn all of the computable functions and will therefore always hallucinate. Since the formal world is a part of the real world which is much more complicated, hallucinations are also inevitable for real world LLMs. Furthermore, for real world LLMs constrained by provable time complexity, we describe the hallucination-prone tasks and empirically validate our claims. Finally, using the formal world framework, we discuss the possible mechanisms and efficacies of existing hallucination mitigators as well as the practical implications on the safe deployment of LLMs.
Construction and Usage of a Human Body Common Coordinate Framework Comprising Clinical, Semantic, and Spatial Ontologies
Jul 28, 2020



Abstract:The National Institutes of Health's (NIH) Human Biomolecular Atlas Program (HuBMAP) aims to create a comprehensive high-resolution atlas of all the cells in the healthy human body. Multiple laboratories across the United States are collecting tissue specimens from different organs of donors who vary in sex, age, and body size. Integrating and harmonizing the data derived from these samples and 'mapping' them into a common three-dimensional (3D) space is a major challenge. The key to making this possible is a 'Common Coordinate Framework' (CCF), which provides a semantically annotated, 3D reference system for the entire body. The CCF enables contributors to HuBMAP to 'register' specimens and datasets within a common spatial reference system, and it supports a standardized way to query and 'explore' data in a spatially and semantically explicit manner. [...] This paper describes the construction and usage of a CCF for the human body and its reference implementation in HuBMAP. The CCF consists of (1) a CCF Clinical Ontology, which provides metadata about the specimen and donor (the 'who'); (2) a CCF Semantic Ontology, which describes 'what' part of the body a sample came from and details anatomical structures, cell types, and biomarkers (ASCT+B); and (3) a CCF Spatial Ontology, which indicates 'where' a tissue sample is located in a 3D coordinate system. An initial version of all three CCF ontologies has been implemented for the first HuBMAP Portal release. It was successfully used by Tissue Mapping Centers to semantically annotate and spatially register 48 kidney and spleen tissue blocks. The blocks can be queried and explored in their clinical, semantic, and spatial context via the CCF user interface in the HuBMAP Portal.
Capsules for Biomedical Image Segmentation
Apr 09, 2020



Abstract:Our work expands the use of capsule networks to the task of object segmentation for the first time in the literature. This is made possible via the introduction of locally-constrained routing and transformation matrix sharing, which reduces the parameter/memory burden and allows for the segmentation of objects at large resolutions. To compensate for the loss of global information in constraining the routing, we propose the concept of "deconvolutional" capsules to create a deep encoder-decoder style network, called SegCaps. We extend the masked reconstruction regularization to the task of segmentation and perform thorough ablation experiments on each component of our method. The proposed convolutional-deconvolutional capsule network, SegCaps, shows state-of-the-art results while using a fraction of the parameters of popular segmentation networks. To validate our proposed method, we perform the largest-scale study in pathological lung segmentation in the literature, where we conduct experiments across five extremely challenging datasets, containing both clinical and pre-clinical subjects, and nearly 2000 computed-tomography scans. Our newly developed segmentation platform outperforms other methods across all datasets while utilizing 95% fewer parameters than the popular U-Net for biomedical image segmentation. We also provide proof-of-concept results on thin, tree-like structures in retinal imagery as well as demonstrate capsules' handling of rotations/reflections on natural images.
Neural Network Segmentation of Interstitial Fibrosis, Tubular Atrophy, and Glomerulosclerosis in Renal Biopsies
Feb 28, 2020



Abstract:Glomerulosclerosis, interstitial fibrosis, and tubular atrophy (IFTA) are histologic indicators of irrecoverable kidney injury. In standard clinical practice, the renal pathologist visually assesses, under the microscope, the percentage of sclerotic glomeruli and the percentage of renal cortical involvement by IFTA. Estimation of IFTA is a subjective process due to a varied spectrum and definition of morphological manifestations. Modern artificial intelligence and computer vision algorithms have the ability to reduce inter-observer variability through rigorous quantitation. In this work, we apply convolutional neural networks for the segmentation of glomerulosclerosis and IFTA in periodic acid-Schiff stained renal biopsies. The convolutional network approach achieves high performance in intra-institutional holdout data, and achieves moderate performance in inter-intuitional holdout data, which the network had never seen in training. The convolutional approach demonstrated interesting properties, such as learning to predict regions better than the provided ground truth as well as developing its own conceptualization of segmental sclerosis. Subsequent estimations of IFTA and glomerulosclerosis percentages showed high correlation with ground truth.
Iterative annotation to ease neural network training: Specialized machine learning in medical image analysis
Dec 18, 2018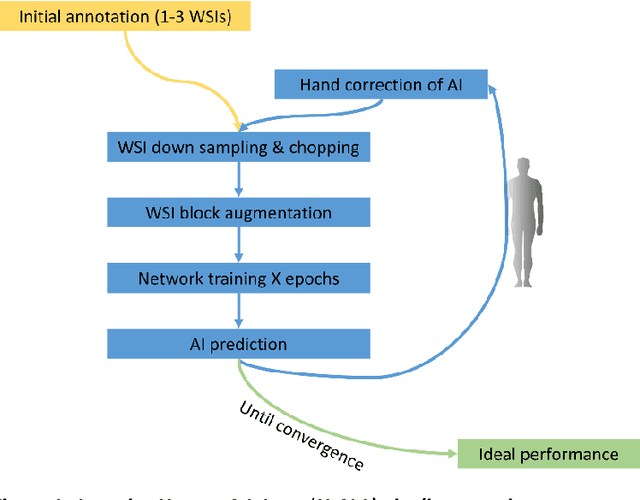
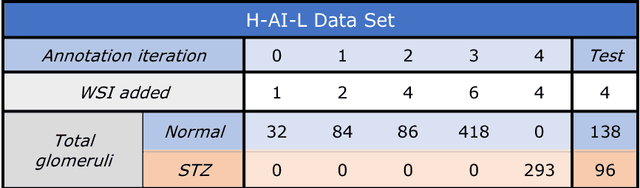
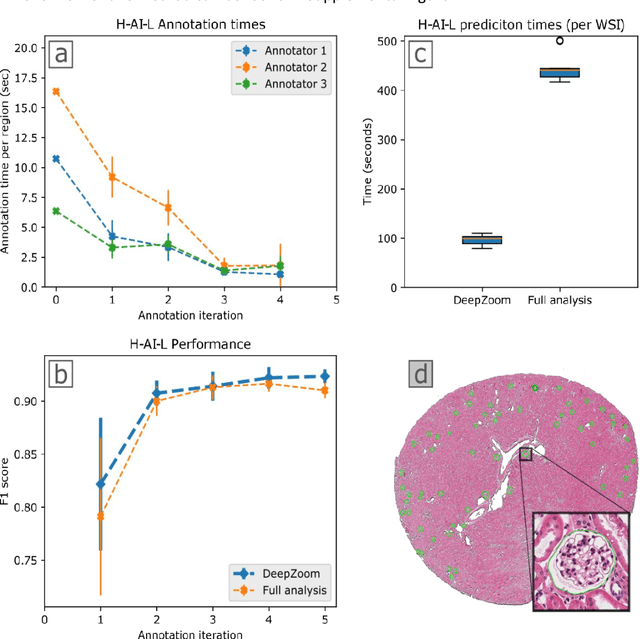
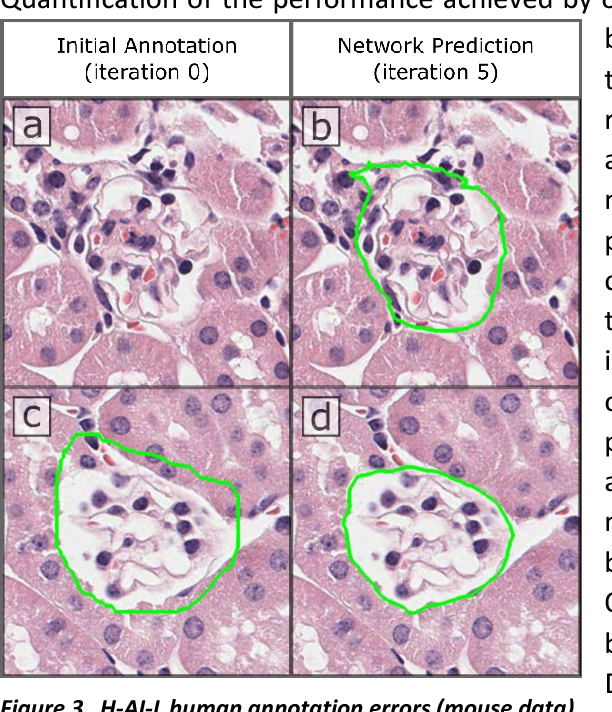
Abstract:Neural networks promise to bring robust, quantitative analysis to medical fields, but adoption is limited by the technicalities of training these networks. To address this translation gap between medical researchers and neural networks in the field of pathology, we have created an intuitive interface which utilizes the commonly used whole slide image (WSI) viewer, Aperio ImageScope (Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc.), for the annotation and display of neural network predictions on WSIs. Leveraging this, we propose the use of a human-in-the-loop strategy to reduce the burden of WSI annotation. We track network performance improvements as a function of iteration and quantify the use of this pipeline for the segmentation of renal histologic findings on WSIs. More specifically, we present network performance when applied to segmentation of renal micro compartments, and demonstrate multi-class segmentation in human and mouse renal tissue slides. Finally, to show the adaptability of this technique to other medical imaging fields, we demonstrate its ability to iteratively segment human prostate glands from radiology imaging data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge