Jonathan C. Silverstein
An Open-Source Knowledge Graph Ecosystem for the Life Sciences
Jul 11, 2023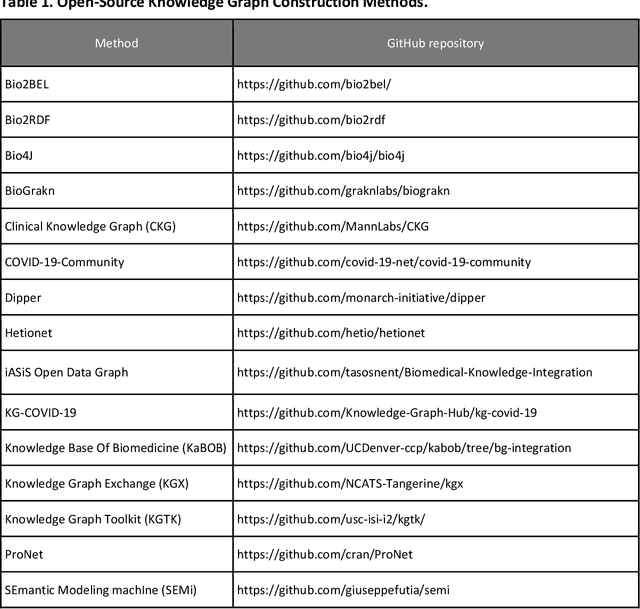
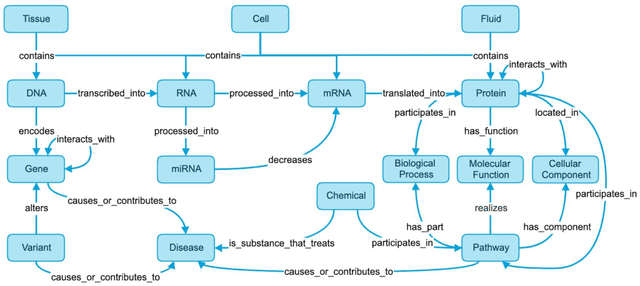
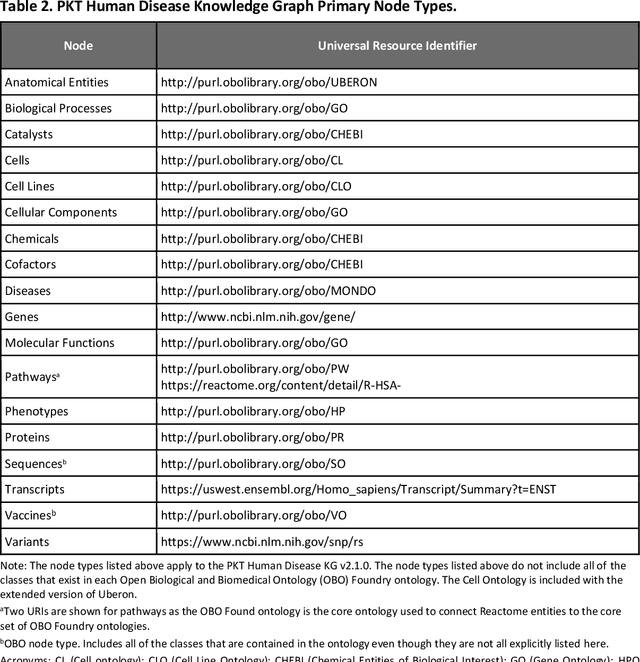
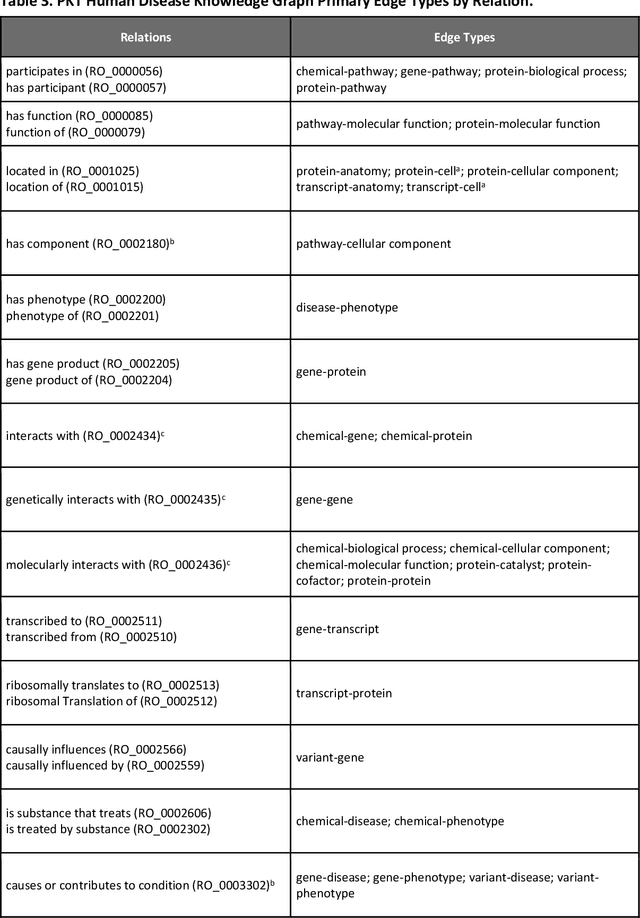
Abstract:Translational research requires data at multiple scales of biological organization. Advancements in sequencing and multi-omics technologies have increased the availability of these data but researchers face significant integration challenges. Knowledge graphs (KGs) are used to model complex phenomena, and methods exist to automatically construct them. However, tackling complex biomedical integration problems requires flexibility in the way knowledge is modeled. Moreover, existing KG construction methods provide robust tooling at the cost of fixed or limited choices among knowledge representation models. PheKnowLator (Phenotype Knowledge Translator) is a semantic ecosystem for automating the FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) construction of ontologically grounded KGs with fully customizable knowledge representation. The ecosystem includes KG construction resources (e.g., data preparation APIs), analysis tools (e.g., SPARQL endpoints and abstraction algorithms), and benchmarks (e.g., prebuilt KGs and embeddings). We evaluate the ecosystem by surveying open-source KG construction methods and analyzing its computational performance when constructing 12 large-scale KGs. With flexible knowledge representation, PheKnowLator enables fully customizable KGs without compromising performance or usability.
ReDWINE: A Clinical Datamart with Text Analytical Capabilities to Facilitate Rehabilitation Research
Apr 12, 2023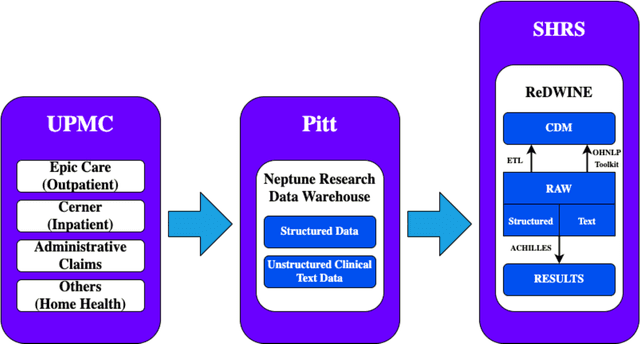
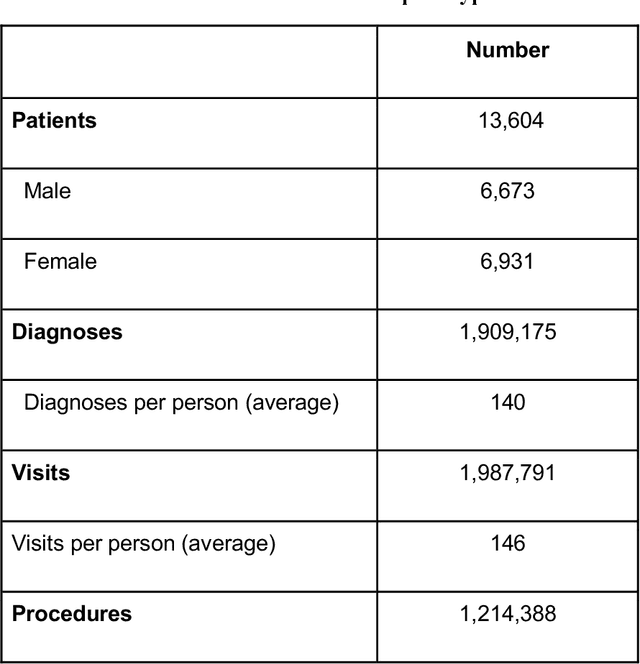
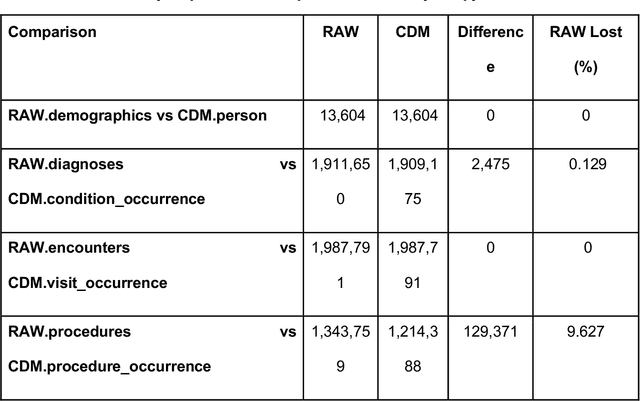
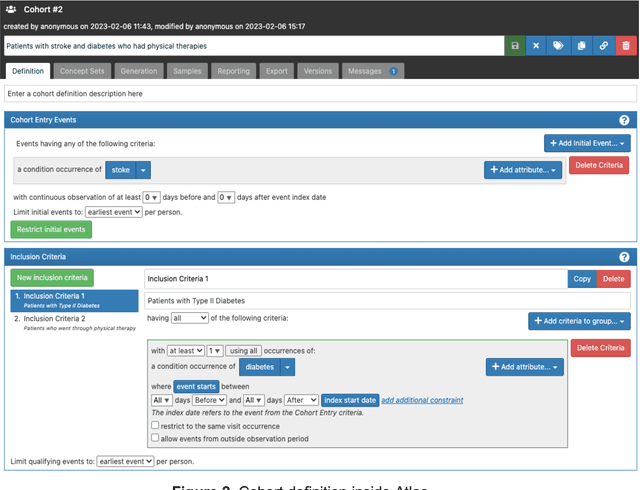
Abstract:Rehabilitation research focuses on determining the components of a treatment intervention, the mechanism of how these components lead to recovery and rehabilitation, and ultimately the optimal intervention strategies to maximize patients' physical, psychologic, and social functioning. Traditional randomized clinical trials that study and establish new interventions face several challenges, such as high cost and time commitment. Observational studies that use existing clinical data to observe the effect of an intervention have shown several advantages over RCTs. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have become an increasingly important resource for conducting observational studies. To support these studies, we developed a clinical research datamart, called ReDWINE (Rehabilitation Datamart With Informatics iNfrastructure for rEsearch), that transforms the rehabilitation-related EHR data collected from the UPMC health care system to the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) Common Data Model (CDM) to facilitate rehabilitation research. The standardized EHR data stored in ReDWINE will further reduce the time and effort required by investigators to pool, harmonize, clean, and analyze data from multiple sources, leading to more robust and comprehensive research findings. ReDWINE also includes deployment of data visualization and data analytics tools to facilitate cohort definition and clinical data analysis. These include among others the Open Health Natural Language Processing (OHNLP) toolkit, a high-throughput NLP pipeline, to provide text analytical capabilities at scale in ReDWINE. Using this comprehensive representation of patient data in ReDWINE for rehabilitation research will facilitate real-world evidence for health interventions and outcomes.
Construction and Usage of a Human Body Common Coordinate Framework Comprising Clinical, Semantic, and Spatial Ontologies
Jul 28, 2020



Abstract:The National Institutes of Health's (NIH) Human Biomolecular Atlas Program (HuBMAP) aims to create a comprehensive high-resolution atlas of all the cells in the healthy human body. Multiple laboratories across the United States are collecting tissue specimens from different organs of donors who vary in sex, age, and body size. Integrating and harmonizing the data derived from these samples and 'mapping' them into a common three-dimensional (3D) space is a major challenge. The key to making this possible is a 'Common Coordinate Framework' (CCF), which provides a semantically annotated, 3D reference system for the entire body. The CCF enables contributors to HuBMAP to 'register' specimens and datasets within a common spatial reference system, and it supports a standardized way to query and 'explore' data in a spatially and semantically explicit manner. [...] This paper describes the construction and usage of a CCF for the human body and its reference implementation in HuBMAP. The CCF consists of (1) a CCF Clinical Ontology, which provides metadata about the specimen and donor (the 'who'); (2) a CCF Semantic Ontology, which describes 'what' part of the body a sample came from and details anatomical structures, cell types, and biomarkers (ASCT+B); and (3) a CCF Spatial Ontology, which indicates 'where' a tissue sample is located in a 3D coordinate system. An initial version of all three CCF ontologies has been implemented for the first HuBMAP Portal release. It was successfully used by Tissue Mapping Centers to semantically annotate and spatially register 48 kidney and spleen tissue blocks. The blocks can be queried and explored in their clinical, semantic, and spatial context via the CCF user interface in the HuBMAP Portal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge