Samuel E. Otto
Operator learning without the adjoint
Jan 31, 2024



Abstract:There is a mystery at the heart of operator learning: how can one recover a non-self-adjoint operator from data without probing the adjoint? Current practical approaches suggest that one can accurately recover an operator while only using data generated by the forward action of the operator without access to the adjoint. However, naively, it seems essential to sample the action of the adjoint. In this paper, we partially explain this mystery by proving that without querying the adjoint, one can approximate a family of non-self-adjoint infinite-dimensional compact operators via projection onto a Fourier basis. We then apply the result to recovering Green's functions of elliptic partial differential operators and derive an adjoint-free sample complexity bound. While existing theory justifies low sample complexity in operator learning, ours is the first adjoint-free analysis that attempts to close the gap between theory and practice.
A Unified Framework to Enforce, Discover, and Promote Symmetry in Machine Learning
Nov 01, 2023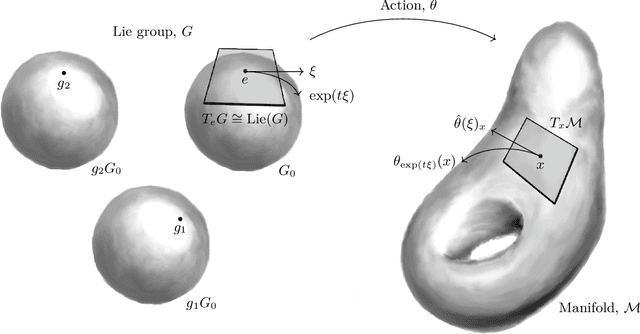
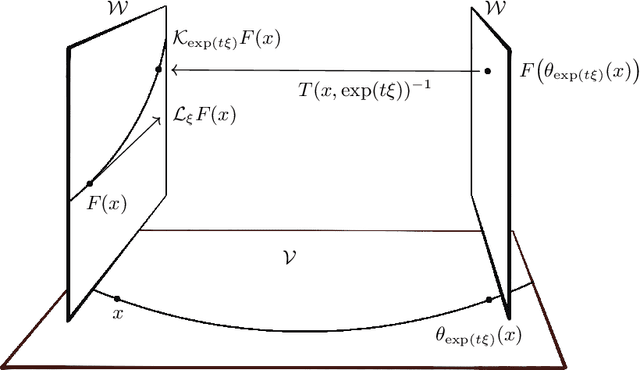
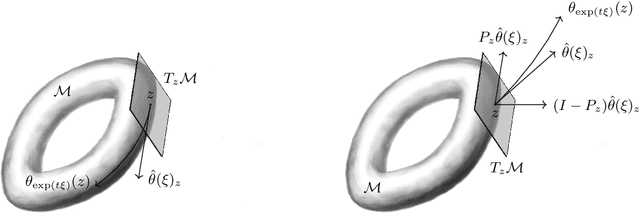
Abstract:Symmetry is present throughout nature and continues to play an increasingly central role in physics and machine learning. Fundamental symmetries, such as Poincar\'{e} invariance, allow physical laws discovered in laboratories on Earth to be extrapolated to the farthest reaches of the universe. Symmetry is essential to achieving this extrapolatory power in machine learning applications. For example, translation invariance in image classification allows models with fewer parameters, such as convolutional neural networks, to be trained on smaller data sets and achieve state-of-the-art performance. In this paper, we provide a unifying theoretical and methodological framework for incorporating symmetry into machine learning models in three ways: 1. enforcing known symmetry when training a model; 2. discovering unknown symmetries of a given model or data set; and 3. promoting symmetry during training by learning a model that breaks symmetries within a user-specified group of candidates when there is sufficient evidence in the data. We show that these tasks can be cast within a common mathematical framework whose central object is the Lie derivative associated with fiber-linear Lie group actions on vector bundles. We extend and unify several existing results by showing that enforcing and discovering symmetry are linear-algebraic tasks that are dual with respect to the bilinear structure of the Lie derivative. We also propose a novel way to promote symmetry by introducing a class of convex regularization functions based on the Lie derivative and nuclear norm relaxation to penalize symmetry breaking during training of machine learning models. We explain how these ideas can be applied to a wide range of machine learning models including basis function regression, dynamical systems discovery, multilayer perceptrons, and neural networks acting on spatial fields such as images.
Learning Nonlinear Projections for Reduced-Order Modeling of Dynamical Systems using Constrained Autoencoders
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:Recently developed reduced-order modeling techniques aim to approximate nonlinear dynamical systems on low-dimensional manifolds learned from data. This is an effective approach for modeling dynamics in a post-transient regime where the effects of initial conditions and other disturbances have decayed. However, modeling transient dynamics near an underlying manifold, as needed for real-time control and forecasting applications, is complicated by the effects of fast dynamics and nonnormal sensitivity mechanisms. To begin to address these issues, we introduce a parametric class of nonlinear projections described by constrained autoencoder neural networks in which both the manifold and the projection fibers are learned from data. Our architecture uses invertible activation functions and biorthogonal weight matrices to ensure that the encoder is a left inverse of the decoder. We also introduce new dynamics-aware cost functions that promote learning of oblique projection fibers that account for fast dynamics and nonnormality. To demonstrate these methods and the specific challenges they address, we provide a detailed case study of a three-state model of vortex shedding in the wake of a bluff body immersed in a fluid, which has a two-dimensional slow manifold that can be computed analytically. In anticipation of future applications to high-dimensional systems, we also propose several techniques for constructing computationally efficient reduced-order models using our proposed nonlinear projection framework. This includes a novel sparsity-promoting penalty for the encoder that avoids detrimental weight matrix shrinkage via computation on the Grassmann manifold.
Learning Bilinear Models of Actuated Koopman Generators from Partially-Observed Trajectories
Sep 20, 2022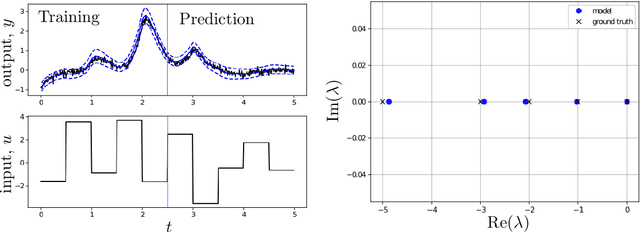
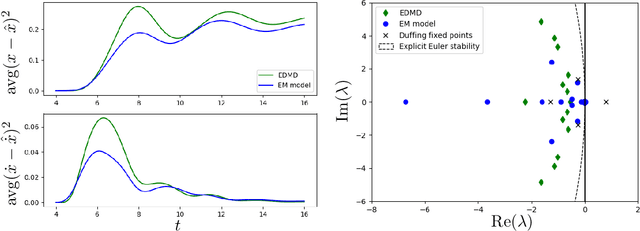
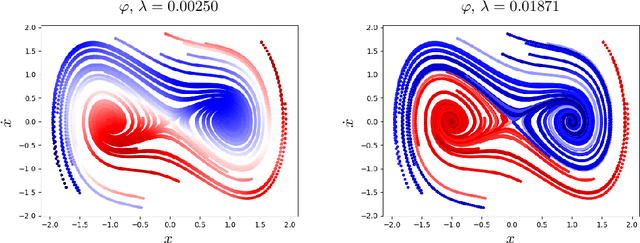
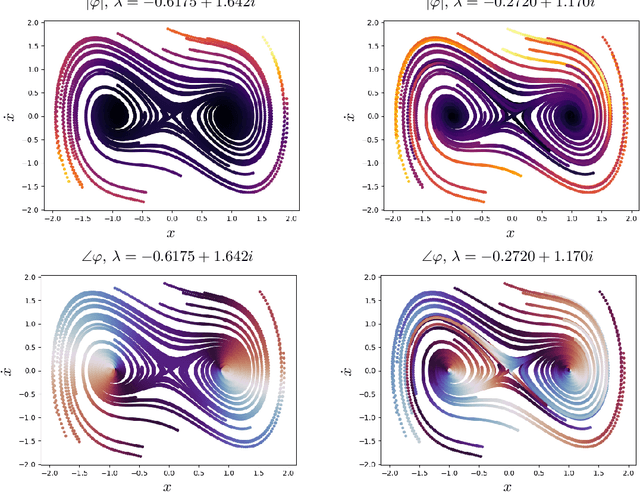
Abstract:Data-driven models for nonlinear dynamical systems based on approximating the underlying Koopman operator or generator have proven to be successful tools for forecasting, feature learning, state estimation, and control. It has become well known that the Koopman generators for control-affine systems also have affine dependence on the input, leading to convenient finite-dimensional bilinear approximations of the dynamics. Yet there are still two main obstacles that limit the scope of current approaches for approximating the Koopman generators of systems with actuation. First, the performance of existing methods depends heavily on the choice of basis functions over which the Koopman generator is to be approximated; and there is currently no universal way to choose them for systems that are not measure preserving. Secondly, if we do not observe the full state, we may not gain access to a sufficiently rich collection of such functions to describe the dynamics. This is because the commonly used method of forming time-delayed observables fails when there is actuation. To remedy these issues, we write the dynamics of observables governed by the Koopman generator as a bilinear hidden Markov model, and determine the model parameters using the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm. The E-step involves a standard Kalman filter and smoother, while the M-step resembles control-affine dynamic mode decomposition for the generator. We demonstrate the performance of this method on three examples, including recovery of a finite-dimensional Koopman-invariant subspace for an actuated system with a slow manifold; estimation of Koopman eigenfunctions for the unforced Duffing equation; and model-predictive control of a fluidic pinball system based only on noisy observations of lift and drag.
Model Reduction for Nonlinear Systems by Balanced Truncation of State and Gradient Covariance
Aug 03, 2022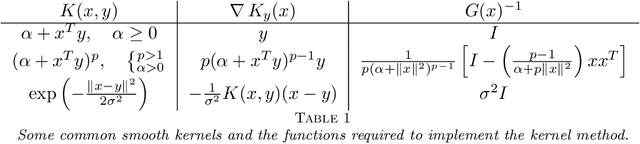
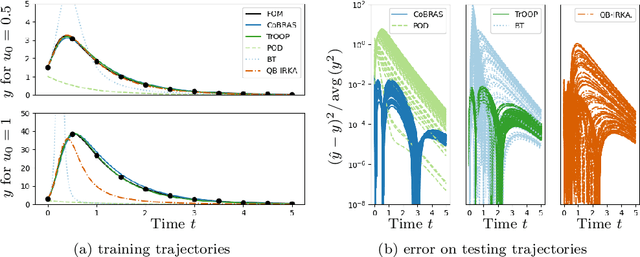
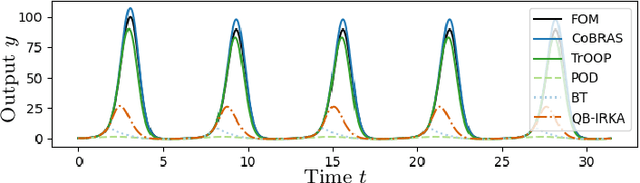
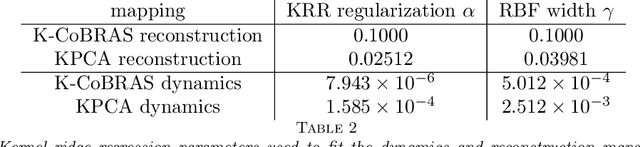
Abstract:Data-driven reduced-order models often fail to make accurate forecasts of high-dimensional nonlinear systems that are sensitive along coordinates with low-variance because such coordinates are often truncated, e.g., by proper orthogonal decomposition, kernel principal component analysis, and autoencoders. Such systems are encountered frequently in shear-dominated fluid flows where non-normality plays a significant role in the growth of disturbances. In order to address these issues, we employ ideas from active subspaces to find low-dimensional systems of coordinates for model reduction that balance adjoint-based information about the system's sensitivity with the variance of states along trajectories. The resulting method, which we refer to as covariance balancing reduction using adjoint snapshots (CoBRAS), is analogous to balanced truncation with state and adjoint-based gradient covariance matrices replacing the system Gramians and obeying the same key transformation laws. Here, the extracted coordinates are associated with an oblique projection that can be used to construct Petrov-Galerkin reduced-order models. We provide an efficient snapshot-based computational method analogous to balanced proper orthogonal decomposition. This also leads to the observation that the reduced coordinates can be computed relying on inner products of state and gradient samples alone, allowing us to find rich nonlinear coordinates by replacing the inner product with a kernel function. In these coordinates, reduced-order models can be learned using regression. We demonstrate these techniques and compare to a variety of other methods on a simple, yet challenging three-dimensional system and an axisymmetric jet flow simulation with $10^5$ state variables.
Inadequacy of Linear Methods for Minimal Sensor Placement and Feature Selection in Nonlinear Systems; a New Approach Using Secants
Jan 27, 2021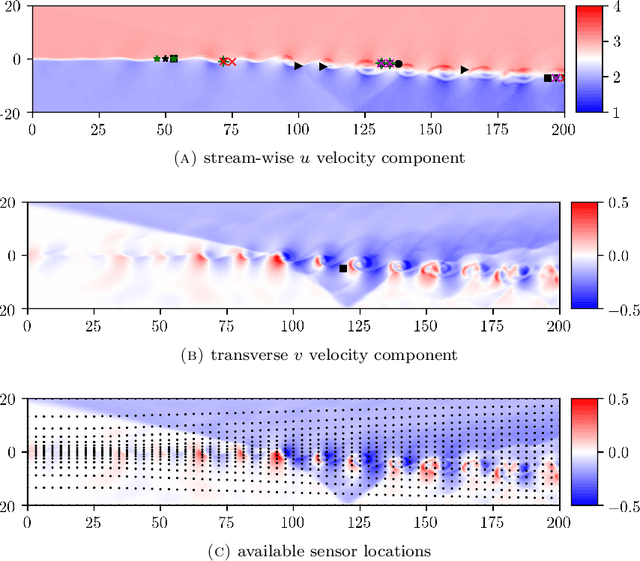
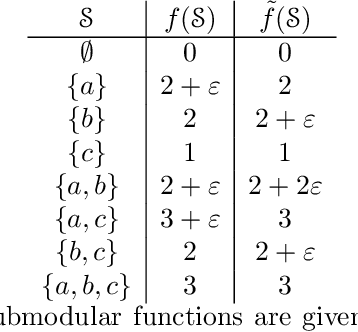
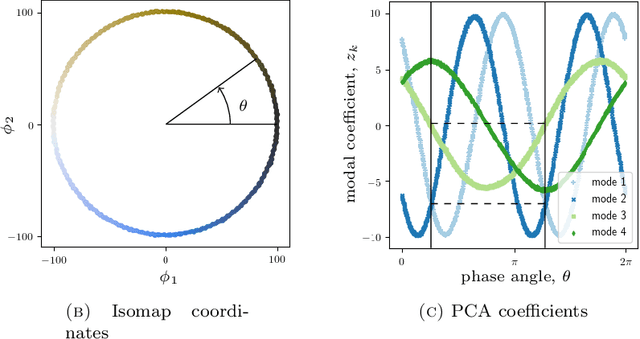
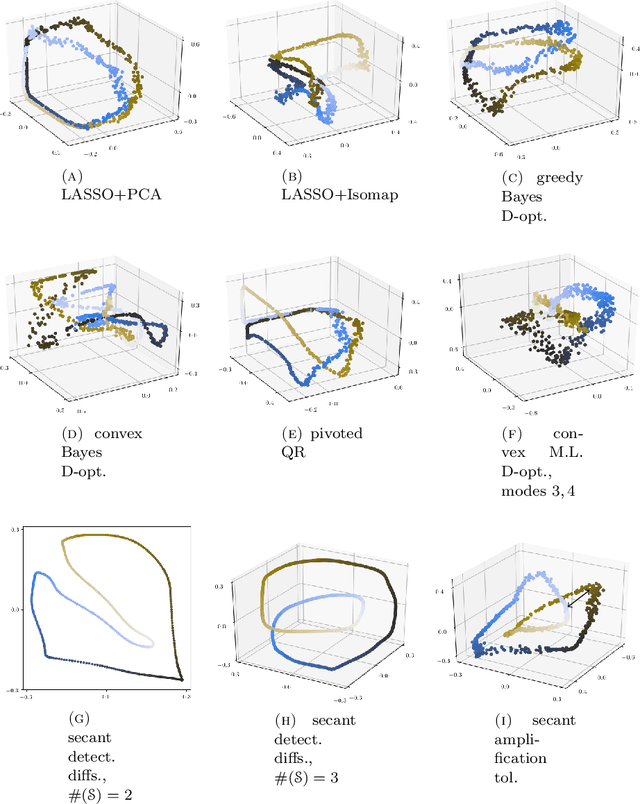
Abstract:Sensor placement and feature selection are critical steps in engineering, modeling, and data science that share a common mathematical theme: the selected measurements should enable solution of an inverse problem. Most real-world systems of interest are nonlinear, yet the majority of available techniques for feature selection and sensor placement rely on assumptions of linearity or simple statistical models. We show that when these assumptions are violated, standard techniques can lead to costly over-sensing without guaranteeing that the desired information can be recovered from the measurements. In order to remedy these problems, we introduce a novel data-driven approach for sensor placement and feature selection for a general type of nonlinear inverse problem based on the information contained in secant vectors between data points. Using the secant-based approach, we develop three efficient greedy algorithms that each provide different types of robust, near-minimal reconstruction guarantees. We demonstrate them on two problems where linear techniques consistently fail: sensor placement to reconstruct a fluid flow formed by a complicated shock-mixing layer interaction and selecting fundamental manifold learning coordinates on a torus.
A Discrete Empirical Interpolation Method for Interpretable Immersion and Embedding of Nonlinear Manifolds
May 21, 2019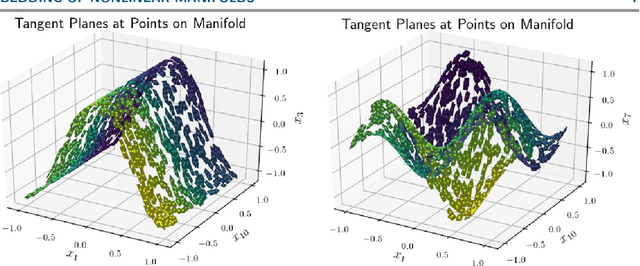
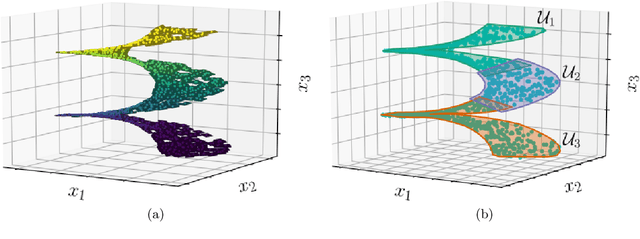
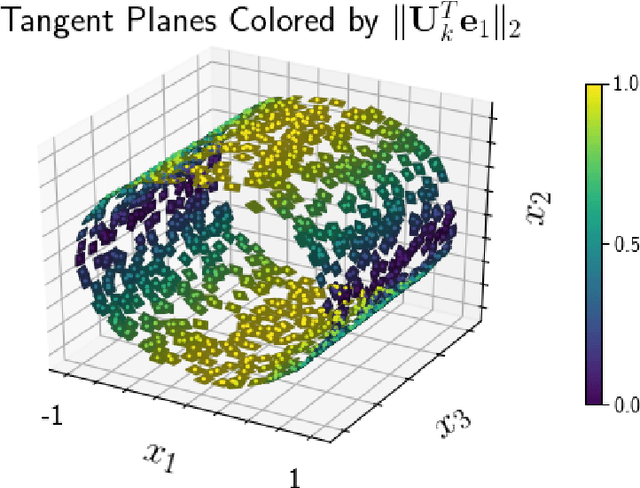
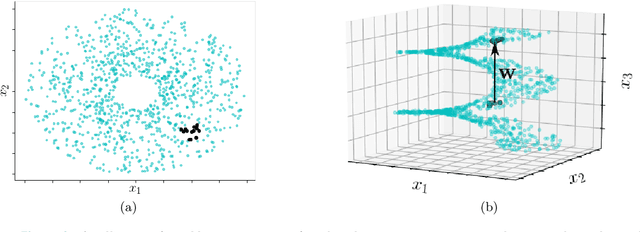
Abstract:Manifold learning techniques seek to discover structure-preserving mappings of high-dimensional data into low-dimensional spaces. While the new sets of coordinates specified by these mappings can closely parameterize the data, they are generally complicated nonlinear functions of the original variables. This makes them difficult to interpret physically. Furthermore, in data-driven model reduction applications the governing equations may have structure that is destroyed by nonlinear mapping into coordinates on an inertial manifold, creating a computational bottleneck for simulations. Instead, we propose to identify a small collection of the original variables which are capable of uniquely determining all others either locally via immersion or globally via embedding of the underlying manifold. When the data lies on a low-dimensional subspace the existing discrete empirical interpolation method (DEIM) accomplishes this with recent variants employing greedy algorithms based on pivoted QR (PQR) factorizations. However, low-dimensional manifolds coming from a variety of applications, particularly from advection-dominated PDEs, do not lie in or near any low-dimensional subspace. Our proposed approach extends DEIM to data lying near nonlinear manifolds by applying a similar pivoted QR procedure simultaneously on collections of patches making up locally linear approximations of the manifold, resulting in a novel simultaneously pivoted QR (SimPQR) algorithm. The immersion provided by SimPQR can be extended to an embedding by applying SimPQR a second time to a modified collection of vectors. The SimPQR method for computing these `nonlinear DEIM' (NLDEIM) coordinates is successfully applied to real-world data lying near an inertial manifold in a cylinder wake flow as well as data coming from a viscous Burgers equation with different initial conditions.
Linearly-Recurrent Autoencoder Networks for Learning Dynamics
Dec 04, 2017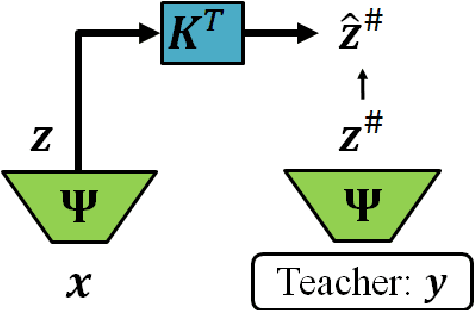
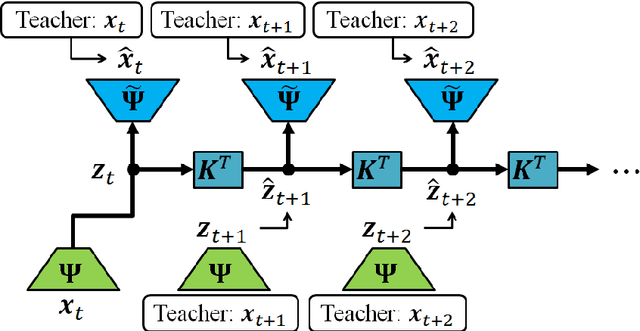
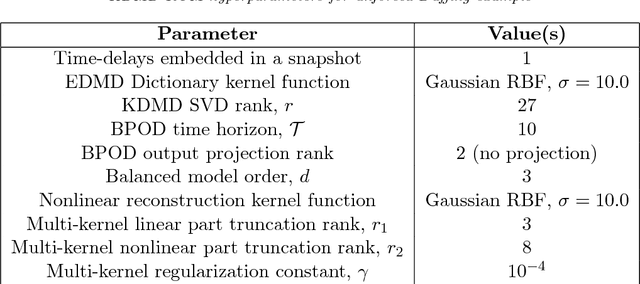
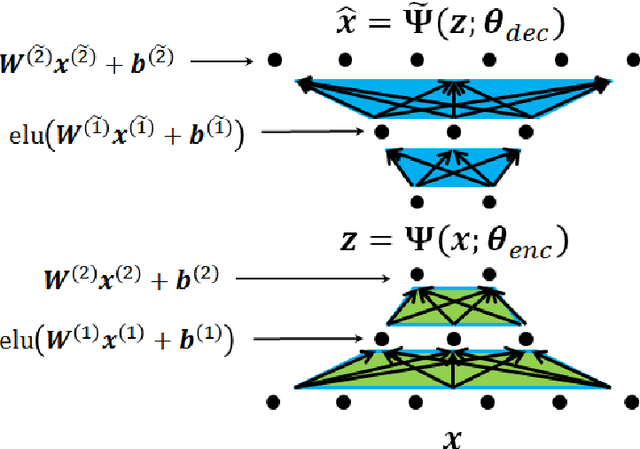
Abstract:This paper describes a method for learning low-dimensional approximations of nonlinear dynamical systems, based on neural-network approximations of the underlying Koopman operator. Extended Dynamic Mode Decomposition (EDMD) provides a useful data-driven approximation of the Koopman operator for analyzing dynamical systems. This paper addresses a fundamental problem associated with EDMD: a trade-off between representational capacity of the dictionary and over-fitting due to insufficient data. A new neural network architecture combining an autoencoder with linear recurrent dynamics in the encoded state is used to learn a low-dimensional and highly informative Koopman-invariant subspace of observables. A method is also presented for balanced model reduction of over-specified EDMD systems in feature space. Nonlinear reconstruction using partially linear multi-kernel regression aims to improve reconstruction accuracy from the low-dimensional state when the data has complex but intrinsically low-dimensional structure. The techniques demonstrate the ability to identify Koopman eigenfunctions of the unforced Duffing equation, create accurate low-dimensional models of an unstable cylinder wake flow, and make short-time predictions of the chaotic Kuramoto-Sivashinsky equation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge