Ruishi Zou
Towards a Design Guideline for RPA Evaluation: A Survey of Large Language Model-Based Role-Playing Agents
Feb 18, 2025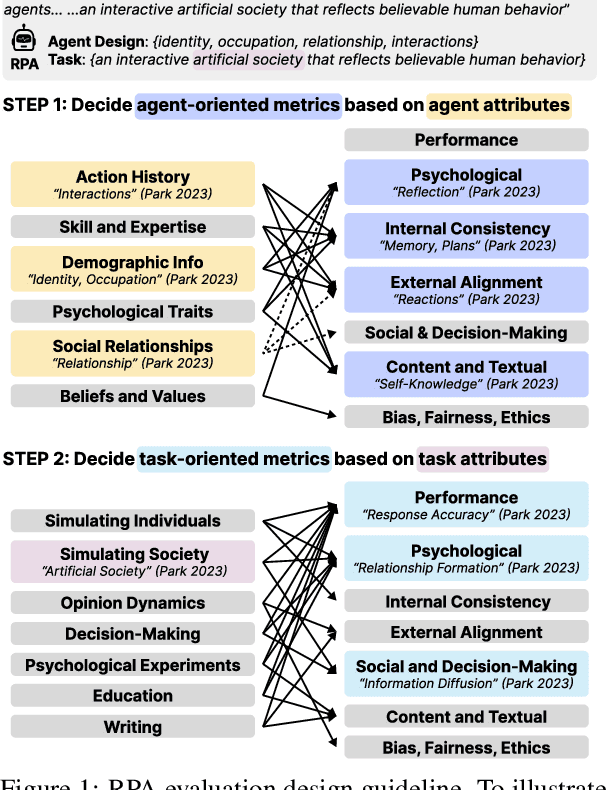
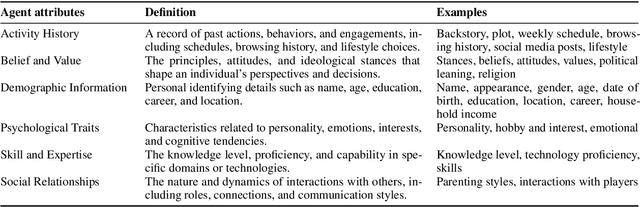
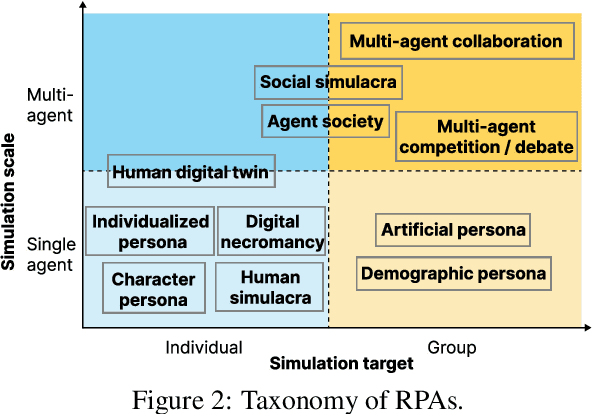

Abstract:Role-Playing Agent (RPA) is an increasingly popular type of LLM Agent that simulates human-like behaviors in a variety of tasks. However, evaluating RPAs is challenging due to diverse task requirements and agent designs. This paper proposes an evidence-based, actionable, and generalizable evaluation design guideline for LLM-based RPA by systematically reviewing 1,676 papers published between Jan. 2021 and Dec. 2024. Our analysis identifies six agent attributes, seven task attributes, and seven evaluation metrics from existing literature. Based on these findings, we present an RPA evaluation design guideline to help researchers develop more systematic and consistent evaluation methods.
More Samples or More Prompt Inputs? Exploring Effective In-Context Sampling for LLM Few-Shot Prompt Engineering
Nov 16, 2023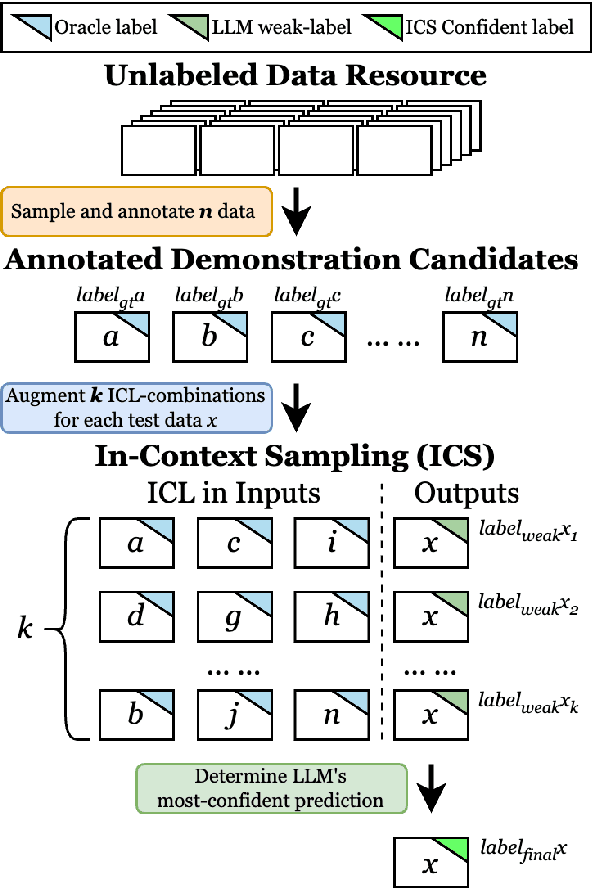
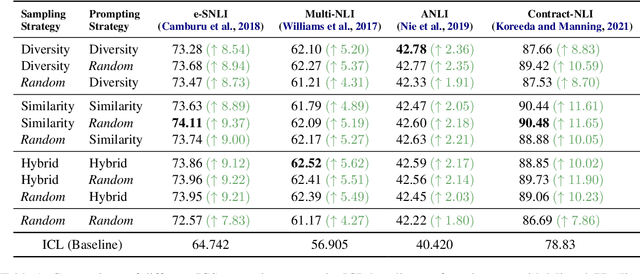
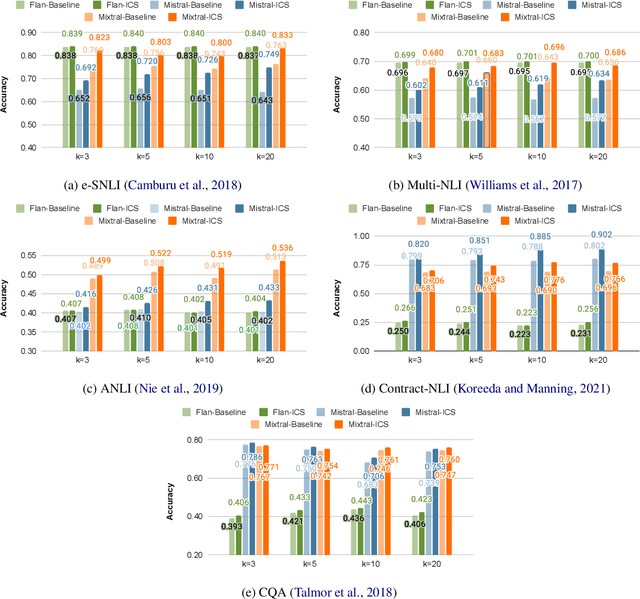
Abstract:While most existing works on LLM prompt-engineering focus only on how to select a better set of data samples inside one single prompt input (In-Context Learning or ICL), why can't we design and leverage multiple prompt inputs together to further improve the LLM performance? In this work, we propose In-Context Sampling (ICS), a low-resource LLM prompt-engineering technique to produce the most confident prediction results by optimizing the construction of multiple ICL prompt inputs. Extensive experiments with two SOTA LLMs (FlanT5-XL and Mistral-7B) on three NLI datasets (e-SNLI, Multi-NLI, and ANLI) illustrate that ICS can consistently enhance LLM's prediction performance and confidence. An ablation study suggests that a diversity-based ICS strategy may further improve LLM's performance, which sheds light on a new yet promising future research direction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge